Abstract
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a condition characterized by an autoimmune response. This disorder primarily affects multiple joints in the body and has a global impact, affecting numerous individuals worldwide. RA is a progressive, chronic illness that manifests in various stages. As the disease advances, joint deterioration worsens, ultimately leading to the loss of joint function. Additionally, RA can also impact other organs within the body. The development of RA is influenced by several factors, including environmental elements, age, weight, genetics, and lifestyle choices. Etiological factors such as autoantibodies, inflammatory mediators, and genes contribute to the onset of RA. Symptoms of this disease encompass swelling, pain, decreased appetite, joint inflammation, fatigue, and pericarditis. The primary objective of RA treatment is to alleviate pain and inflammation while preventing joint dysfunction and deformity. To achieve this, a variety of medications are utilized, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, steroids, and disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. However, the use of synthetic drugs is associated with potentially life-threatening side effects. Consequently, individuals seek alternative medicines for RA treatment. The focus of this study is to emphasize the utilization of herbal medicines for the benefit of RA patients. Herbal medicines and isolated phytoconstituents derived from herbal and synthetic drugs offer advantages such as affordability, accessibility, high patient acceptance, and minimal side effects. These medications also enhance the patient's overall condition and reduce stress. Numerous researchers have demonstrated the efficacy of herbal drugs and phytoconstituents in treating RA patients. Therefore, this study aims to raise awareness regarding the importance of increasing the utilization of herbal drugs for RA treatment.
Keywords
Rheumatoid Arthritis, Pathophysiology, Herbal Treatment of RA, Synthetic Treatment of RA.
Introduction
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune condition characterized by inflammation in the joints and other areas of the body. It is a chronic inflammatory disorder that is often caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, such as smoking. The condition primarily affects the synovial joints, starting in the smaller peripheral joints and progressing to the larger joints if left untreated. [1] Over time, the inflammation in the joints leads to the destruction of cartilage and bone erosion. RA can be classified as early RA if the symptoms have been present for less than six months, and established RA if the symptoms have been present for more than six months. If left untreated, RA can lead to increased morbidity and mortality. [2] [3] [4] Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis in the early stages can be challenging as there is no definitive laboratory test for the condition. A comprehensive clinical approach is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis and prevent further joint damage. The treatment of RA involves a combination of medication and non-pharmacological therapies. Early treatment with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs is considered the standard of care. However, despite treatment, many patients still experience disability and significant morbidity over time. [5] Therefore, a comprehensive approach that includes both medication and non-medication interventions, such as physical therapy, counseling, and patient education, is necessary to improve clinical outcomes. [4]

Fig No.1 Rheumatoid Arthritis
Pathophysiology
The pathophysiology of OA and RA is distinct although the primary manifestations of both involve the joints. OA is characterized by progressive cartilage loss. Increased thickness of the subchondral plate, osteophytes and subchondral bone cysts are the characteristic features. Vascular invasion and further calcification of nearby articular cartilage may occur as the disease progresses, leading to decreased thickness of articular cartilage. Bone remodeling and enhanced cartilage deterioration takes place over time. The inflammation is generally milder in severity than that observed in rheumatoid arthritis and typically involves the periarticular tissues. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, autoimmune syndrome. Autoimmune inflammation is a result of a response to self-antigens. Thus, a dysregulated immune system results in autoimmune diseases. Synovial inflammation leading to cartilage and bone damage is characteristic of the disease. Persistent inflammation leads to progressive destruction of articular and periarticular structures which in turn, lead to deformity. Morning stiffness is a common problem for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Characteristic features of RA pathophysiology are increased angiogenesis, cellular hyperplasia, influx of inflammatory cells, changes in the expression of cell surface adhesion molecules and presence of many cytokines. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-1 are in abundance in the joints. They are the stimulators of proliferation, metalloproteinase expression, adhesion molecule expression, and further secretion of other cytokines. CD4 T cells, mononuclear phagocytes, fibroblasts, osteoclasts, and neutrophils play major role in pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Presence of anti-cyclic citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) and rheumatoid factor (RF) is highly specific for RA [2].
Features of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Symmetrical pattern of affected joints
- Fatigue, occasional fevers, loss of energy.
- Joint inflammation often affecting the wrist and finger joints
- Joint inflammation sometimes affecting the joints in the neck, shoulders, elbows,
- Warm, swollen joints
- Hips, knees, ankles and feet
Causes
- There is no definite cause of arthritis. Causes of arthritis depend upon the particular form of arthritis. Probable of arthritis cause are:
Genetic susceptibility
- An immunological reaction: possible involving a foreign antigen , preferentially focused on synovial tissue
- An inflammatory reaction in joints and tendons sheaths
- The appearance of rheumatoid factor in the blood and synovial
- Articular cartilage destruction

Figure No: 2. show comparison of normal joint and joint affected by rheumatoid arthritis.
Symptoms
- Swelling: Arthritis causes an abnormal enlargement of a part of the body. This is due to the accumulation of fluid.
- Pain: The feeling of constant pain in the many parts of the body.
- Stiffness: Stiffness in the muscle upon waking up, or sitting at one place for long or after sitting at a desk. One may feel stiffness in the fingers, wrist, elbow, knees, ankles, shoulders or in any other joints.
- Fever, chills, fatigues, loss of appetite and headache are some other common symptoms of arthritis [5].
Diagnosis
- Blood culture: Diagnosis of RA depends on the symptoms and some blood tests can also help to confirm RA. Telltale signs include: Anemia (a low red blood cell count);rheumatoid factor (an antibody, or blood protein, found in about 80% of patients with RA in time, but in as few as 30% at the start of arthritis); antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides (pieces of proteins), or anti -CCP for short (found in 60-70% of patients with RA); Elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (a blood test that, in most patients with RA, confirms the amount of inflammation in the joints).
- X-Ray: X-rays can help in detecting RA, but may not show anything abnormal in early arthritis. Even so, these first X-rays may be useful later to show if the disease is progressing.
- Often, MRI and ultrasound scanning are done to help judge the severity of RA.
- There is no single test that confirms an RA diagnosis for most patients with this disease

Figure No: 3. show comparison of normal joint and joint affected by rheumatoid arthritis
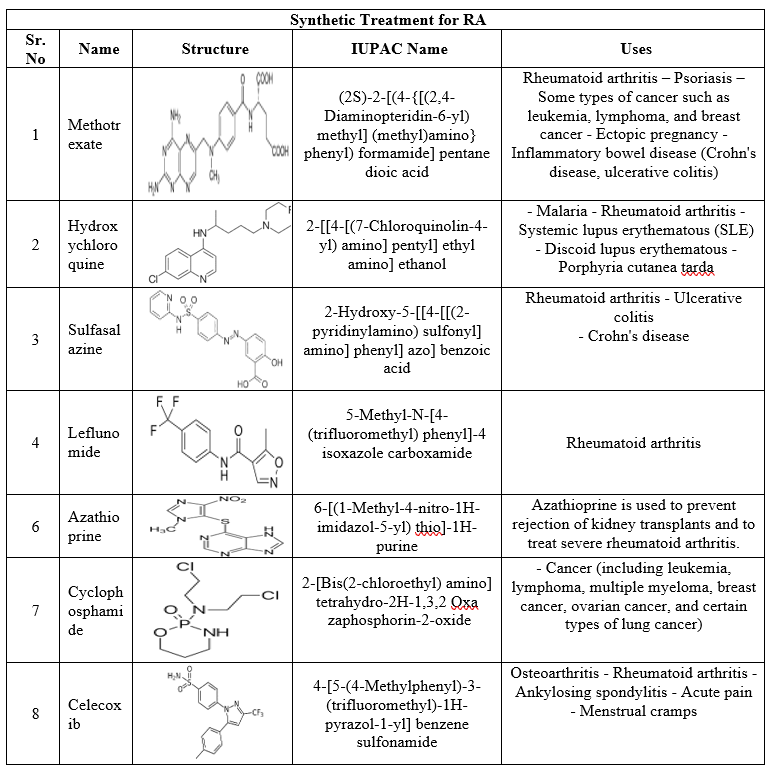
Table No.1: - Herbal Treatment for RA

Table No.2: Synthetic Treatment for RA
Home Remedies for Arthritis
Exercise Regularly: Gentle exercise can help to strengthen muscles around joints and also helps to fight fatigue.
Relax: Techniques such as hypnosis, guided imagery, deep breathing and muscle relaxation can be done to control.
Yoga: Yoga can help to improve strength and flexibility. The exercises should be performed with caution by people with rheumatoid arthritis who have spinal problems [6].
Surgery and other Treatments
In some cases, surgery may be done if other treatments have not worked. This may include:
- Arthroplasty to rebuild the joint
- Joint replacement, such as a total knee joint replacement
CONCLUSION
The review article was reported and compared both type of herbal and synthetic drugs. The potential herbal drug was found to be effective as that of synthetic and thus proves more potency of herbs in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis disorders. Given the fact that the pathophysiology of RA is still clear, the development of a curative compounds is markedly limited. This limitation is even more compounded by the unavailability of appropriately validated animal models are important in the efficient and rational development of other treated compounds for RA.
REFERENCE
- Klareskog L, Rönnelid J, Saevarsdottir S, Padyukov L, Alfredsson L. The importance of differences; On environment and its interactions with genes and immunity in the causation of rheumatoid arthritis. J Intern Med. 2020 May;287(5):514-533. [PubMed]
- Smolen JS, Aletaha D, McInnes IB. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2016 Oct 22;388(10055):2023-2038. [PubMed]
- Bullock J, Rizvi SAA, Saleh AM, Ahmed SS, Do DP, Ansari RA, Ahmed J. Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Brief Overview of the Treatment. Med Princ Pract. 2018;27(6):501-507. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sparks JA. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Intern Med. 2019 Jan 01;170(1):ITC1-ITC16. [PubMed]
- Pincus T, O'Dell JR, Kremer JM. Combination therapy with multiple disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis: a preventive strategy. Ann Intern Med. 1999 Nov 16;131(10):768-74. [PubMed]
- Scott D.L., Wolfe F., Huizinga T.W. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2010;376:1094–1108. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60826-4. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- McInnes I.B., Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011;365:2205–2219. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1004965. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Petsch C., Araujo E.G., Englbrecht M., Bayat S., Cavallaro A., Hueber A.J., Lell M., Schett G., Manger B., Rech J. Prevalence of monosodium urate deposits in a population of rheumatoid arthritis patients with hyperuricemia. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2016;45:663–668. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.11.014. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Kany S., Vollrath J.T., Relja B. Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:6008. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236008. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S.H., Cantrell D.A. Signaling and Function of Interleukin-2 in T Lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018;36:411–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-042617-053352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Shamriz O., Nussinovitch U., Rose N.R. Chapter 1—Pathophysiology of Autoimmunity and Immune-Mediated Mechanisms in Cardiovascular Diseases. In: Nussinovitch U., editor. The Heart in Rheumatic, Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2017. pp. 3–23. [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Summers K.M., Kockler D.R. Rituximab treatment of refractory rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Pharmacother. 2005;39:2091–2095. doi: 10.1345/aph.1G311. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Lau C.S., Chia F., Dans L., Harrison A., Hsieh T.Y., Jain R., Jung S.M., Kishimoto M., Kumar A., Leong K.P., et al. 2018 update of the APLAR recommendations for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019;22:357–375. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13513. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro F., Elefante E., Luciano N., Talarico R., Todoerti M. One year in review 2017: Novelties in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017;35:721–734. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu T., Liu S., Zhao J., Feng G., Pi Z., Song F., Liu Z. A study on the effective substance of the Wu-tou formula based on the metabonomic method using UPLC-Q-TOF-HDMS. Mol. Biosyst. 2015;11:3081–3091. doi: 10.1039/C5MB00454C. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang C., Fan L., Fan S., Wang J., Luo T., Tang Y., Chen Z., Yu L. Cinnamomum cassia Presl: A Review of Its Traditional Uses, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology and Toxicology. Molecules. 2019;24:3473. doi: 10.3390/molecules24193473. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y.L., Luo B., Zhang H., Zheng W.J., Wu M.L., Li S.Y., Gao H.Y., Li Q., Ge Y.W., Yang Q. Advances in quality research of Cinnamomum cassia. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020;45:2792–2799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L., Zong S.B., Li J.C., Lv Y.Z., Liu L.N., Wang Z.Z., Zhou J., Cao L., Kou J.P., Xiao W. The essential oil from the twigs of Cinnamomum cassia Presl alleviates pain and inflammation in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016;194:904–912. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.10.064. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P., Wang J., Wen W., Pan T., Chen H., Fu Y., Wang F., Huang J.H., Xu S. Cinnamaldehyde suppresses NLRP3 derived IL-1? via activating succinate/HIF-1 in rheumatoid arthritis rats. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020;84:106570. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106570. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]
- Braddock M., Quinn A., Canvin J. Therapeutic potential of targeting IL-1 and IL-18 in inflammation. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2004;4:847–860. doi: 10.1517/14712598.4.6.847. [PubMed] [CrossRef] [Google Scholar]

 Abhijit Daf*
Abhijit Daf*





 10.5281/zenodo.12750540
10.5281/zenodo.12750540