Abstract
To design and develop propranolol hydrochloride sustained-release capsules using HPMC, ethylcellulose and MCC and their in vitro evaluations. The study investigated impact of intra-granular Microcrystalline cellulose, SR beads coat with Ethyl cellulose ECN50 and Hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose level on drug product. The impact of solvent uptake (Methanol and DCM) was evaluated on the drug product.
Materials and Methods:
Propranolol hydrochloride, microcrystalline cellulose (PH-101), HPMC, Isopropyl alcohol, were used in the different formulations. granulation , extrusion and spheronization and FBP were used for the preparation of pellets.
Results:
All formulations were evaluated for in vitro drug release by a predictive dissolution method which was developed during development program (USP apparatus I Basket pH 1.2 pH buffer followed by 6.8 pH Phosphate buffer, 100 Rpm 900 mL for 24 Hours) by performing an extensive evaluation of dissolution conditions. The dissolution profile of Innovator and prepared Propranolol sustained release capsules were determined. The batches were loaded for stability study as per ICH guidelines at 3 different conditions (25°C/60% RH, 30°C/75% RH, 40°C/75% RH for 3 months) and evaluated in comparison to the innovator product which shows no change in physical appearance, assay and drug release which indicate the stability of the product. From the results, batch (F08) which was repro batch of batch 07 was found to be optimized due to results comparable to the innovator product.
Keywords
Multi-particulates, Drug delivery, Pellets, Pelletization technique, Sustained release.
Introduction
The foremost objective of treatment is to attain steady state concentration all through the treatment stage. Since disadvantages of conventional systems, modified systems, have overcome them. The United States Pharmacopoeia (USP) defines the modified-release (MR) dosage form as “the one for which the drug release characteristics of time course and/or location are chosen to accomplish therapeutic or convenience objectives not offered by conventional dosage forms.”. One class of MR dosage form is an extended-release (ER) dosage form and is defined as the one that allows at least a 2-fold reduction in dosing frequency or significant increase in patient compliance or therapeutic performance when compared with that presented as a conventional dosage form (a solution or a prompt drug-releasing dosage form). The terms “controlled release (CR)”,“prolonged release”, “sustained or slow release (SR)” and “long-acting (LA)” have been used synonymously with “extended release
Advantages:
sustained blood levels, attenuation of adverse effects, Improved patient compliance.
Sustained blood levels
The size and frequency of dosing is determined by the pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties of the drug. The slower the rate of absorption, the less the blood concentrations fluctuate within a dosing interval. This enables higher doses to be given less frequently. For drugs with relatively short half-lives, the use of sustained-release products may maintain therapeutic concentrations over prolonged periods.
Attenuation of adverse effects
With conventional dosage forms, high peak blood concentrations may be reached soon after administration with possible adverse effects related to the transiently high concentration.
Improved patient compliance
Drugs with short half-lives often need to be given at frequent intervals to maintain blood concentrations within the therapeutic range. There is an inverse correlation between the frequency of dosing and patient compliance. A reduction in the number of daily doses offered by sustained-release products has the potential to improve compliance. However, this advantage probably only occurs when conventional formulations need to be given 3 or more times a day.

Fig.No.1. Plasma Drug Concentration Profiles for Conventional Tablet or Capsule Formulation, Sustained-Release Formulation and a Zero-Order Controlled Release Formulation.
Advantages of sustained release dosage forms
- The frequency of drug administration is reduced.
- Patient compliance can be improved.
- Drug administration can be made more convenient as well.
- The blood level oscillation characteristic of multiple dosing of conventional dosage forms is reduced.
- Better control of drug absorption can be attained, since the high blood level peaks that may be observed after administration of a dose of a high availability drug can be reduced.
- The characteristic blood level variations due to multiple dosing of conventional dosage forms can be reduced.
Mechanism of Drug Release from Pellets
The mechanism of drug release from pellets can occur in three ways:
Erosion:
Some coatings are designed to erode gradually with time, thereby releasing the drug contained within the pellet in a controlled manner. Examples of these types of coating are usually those that consist of natural materials such as shellac (the solubility of which in water increases with increasing pH) or waxes and fats that become soft enough to facilitate erosion as the coated multiparticulates are subjected to intense agitation as they pass through the gastrointestinal tract.
Osmosis: Once water has passed through the film coating, dissolution of soluble components (excipients and drug) within the core can allow an osmotic pressure to be generated inside the coated particle that will influence the rate at which the drug will be pushed out through pores or a preformed aperture in the membrane.
Diffusion:
Diffusion is primarily a process whereby a drug will partition into the film coat membrane and permeate it. The rate at which the drug is released by this mechanism is primarily influenced by the drug concentration gradient across the membrane, the thickness of the membrane, the solubility of the drug in the membrane and the permeability coefficient governing passage of the drug through the membrane.
- Diffusion of solution through the continuous plasticized polymer phase: The polymer forms a phase in which the plasticizer and other additives are homogeneously dispersed. The diffusion of a solute molecule through polymer phase involves the movements of the drug and the polymer chain segments around it. The frequency with which a diffusion step occurs depends on the size and shape of the drug, tightness of bonds between adjacent polymer chains and the stiffness of the polymer chain.
- Solution/diffusion through plasticizer channels: Occurs when the plasticizer is not uniformly distributed in the coating polymer and its content is high. The plasticizer takes the form of a continuous phase in the form of patched channels. Diffusivity in the plasticizer will generally be lower than in water since plasticizers tend to be relatively viscous
- through Diffusion aqueous pores: Intervenes when a continuous but inhomogeneous coating layer is punctuated with pores. These pores fill with solution thus facilitating the diffusion of the drug. During the coating and curing processes, the pseudo latex particles often do not fuse completely, thereby creating a porous coating. The pores may be of 1?m size and the release mechanism is illustrated below.
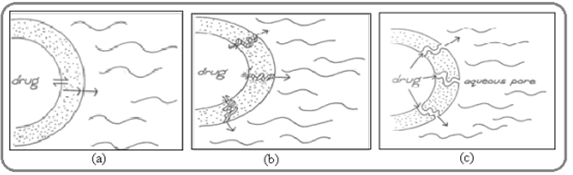
Fig.No.2. Drug release from coated pellets via (a) solution/diffusion through the polymer film (b) solution/diffusion through plasticizer channels (c) diffusion through aqueous channels
Preparation of Extended-release pellets of Propranolol Hydrochloride:
Materials :
Propranolol Hydrochloride (PPNL HCl), Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) - Avicel PH101, Microcrystalline Cellulose spheres (CP 708: 750-810 µm), Aqueous Ethyl cellulose (25% dispersion),Ethyl cellulose (EC)- 4 cps and 7 cps, Hypromellose (HPMC) - 5 cps, Isopropyl Alcohol (IPA), Purified water.
Table.No.1: Process parameters of pellet formation
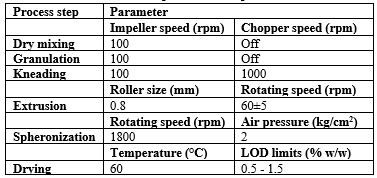
Table.No.2: FBP Parameters
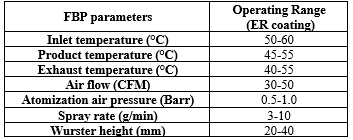
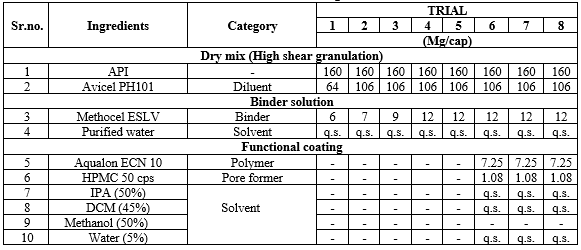
Table.No.3: Manufacturing Formula
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Standard curve of propranolol:
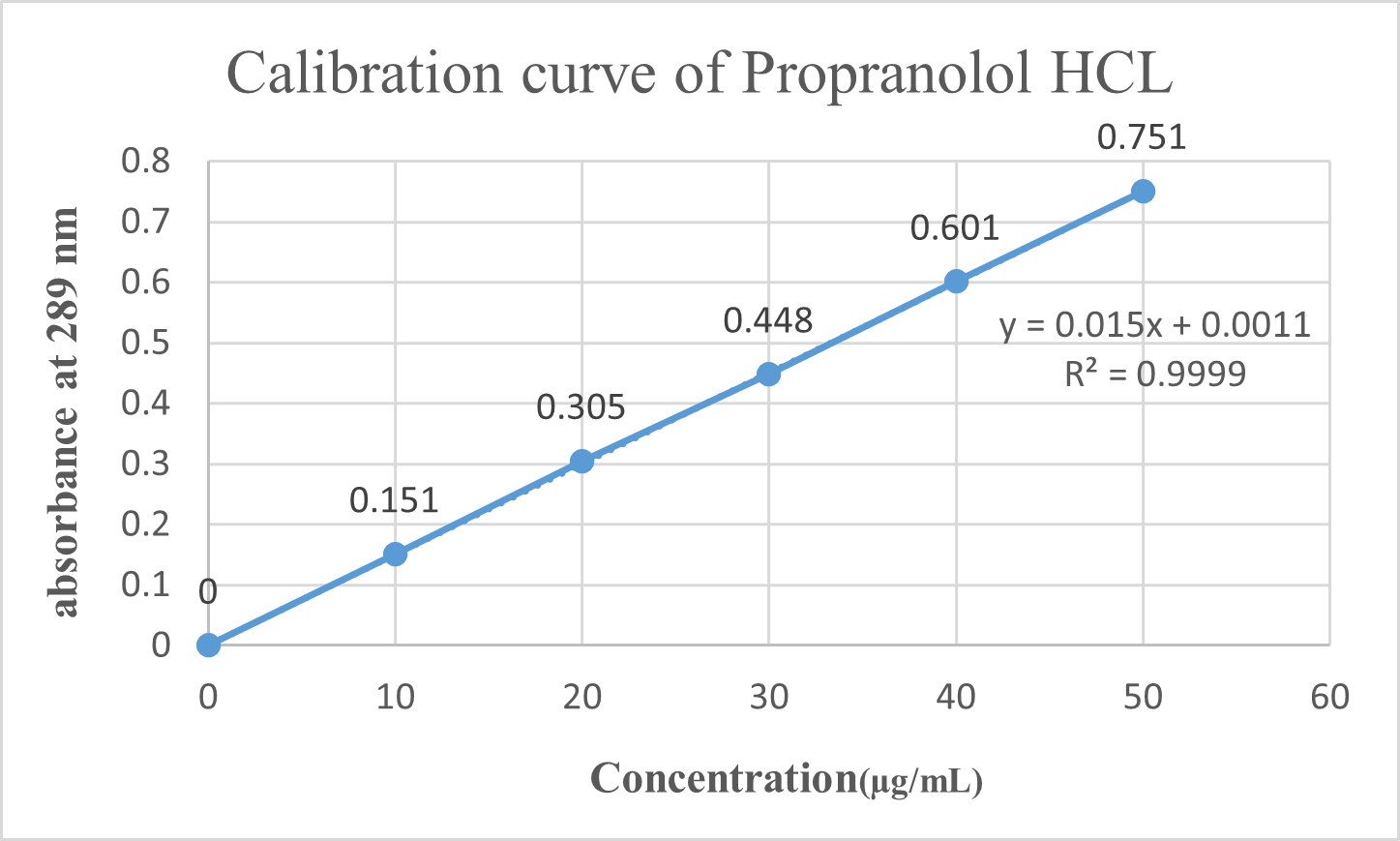
The standard calibration curve of drug in water is depicted as Fig.No.3. The data of absorbance was shown in Table No.4. The data has correlation coefficient of 0.9999 and the equation of regressed line depicted as Equation below.
Y = 0.015X + 0.0011
Table.No.4 : Calibration curve values of Propranolol Hydrochloride at 289 nm
Fig. No.3 : standard plot of Propranolol HCL
Pre-formulation Study
The goal of Pre-formulation studies is to choose the correct form of drug substance, evaluate its physical properties and generate a thorough understanding of the materials stability under various condition leading to optimal drug delivery. To confirm the identity, purity and suitability of the drug for formulation and to establish a drug profile, Pre-formulation were undertaken which lead to the following conclusions.
Organoleptic properties
Drugs was tested for organoleptic properties such as nature, colour, odour, taste, etc.
Solubility Analysis
Based on the solubility data one can set the specification for the dissolution studies as well as can predict its fate inside the body. The solubility of drug was determined by dissolving the drug in different solvents viz water, 0.1N HCl, methanol, DMSO, Chloroform, PBS pH6.8 and diethyl ether and the results were observed. The highest solubility was recorded in chloroform where as in water the lowest solubility was obtained and very soluble in methanol and ethanol. Propranolol is lipophilic substance with very low solubility in water within the physiological PH range.
Melting Point Determination
The melting point was found to be 430Cdetermined by the capillary method using digital melting point apparatus.
Loss On Drying
LOD value of orlistat that accounts for moisture content in the level by drying at 105 °C and optimized drying time to achieve LOD in particular limit was found to be not more 0.2% w/w within a limit.
EVALUATION PARAMETER OF PELLETS
Pellet is evaluated for pre-capsulation parameters such as bulk density, tapped density, Carr’s index, Hausner’s ratio and angle of repose and results obtained are shown in Table No.5
Table.No.5 : Flowability parameters of Propranolol pellets
Bulk density and Tapped density
Both bulk density and tapped density results are shown in Table No.8.5. The loose bulk density for all the batches varied in range of 0.6080±0.21 gm/mL to 0.6505±0.14gm/mL and tapped density for all the batches varied in range of 0.6805±0.017 gm/mL to 0.7215±0.41gm/mL respectively. These results may further the influence properties such as compressibility and capsule dissolution.
Angle of repose
Table 8.5 shows the results obtained for angle of repose of all the batches. As a general guide angle of repose greater than 500 have unsatisfactory flow properties were as minimum angle close to 250 correspond to very good property. The values were found to be in the range of 20.4±1.7 to 26.1±2.6 indicating excellent flow property and this was further supported by lower compressibility index values.
Carr’s Index
Percent compressibility of powder mix was determined by Carr’s compressibility index is shown in Table No.8.5.The percent Carr’s index for all batches lies within the range of 9.84±0.032 to 10.72±1.004. Powders showing Carr’s index up to 21 are considered for acceptable flow property.
Hausner’s ratio
Hausner’s ratio was found to be in range of 1.09±0.075to 1.12±1.023.
LOD (loss on drying) of the pellets
The results of moisture determination using moisture analyzer should be compared to those obtained using the drying oven which is the official standard. If such a value is not available for comparison the experiment should rerun using exactly the same material under the same condition several time to make sure that the results can be reproduced without losing the rapidity of determination. The sample in such cases requires proper preparation because it requires to be homogeneous fine enough the maximum surface area to drying and capable of being uniformly spread over the pan.
Friability Test
The friability tests have been carried out in abrasive drum and the value ranges from 0.198- 0.894. The values depict friability is within and passes USP limit which is not greater than 1% w/w, indicating enough mechanical integrity and strength for prepared pellets.
Sieve Analysis
Arrange the set of sieves in descending order. Weigh accurately the given sample (20 gm) and pour on the top sieves. Place the lid to keep away from loss during shaking. Function the sieve shaking machine for 5 min. Collect fraction of sample retained on each sieve and on receiver at the bottom of set. Weigh the sample retained on each sieve. Calculate percent frequency of every size of particle. Determine geometric mean weight diameter and geometrical standard deviation. Sieve analysis revealed that almost 80% of pellets were distributed between 30# sieves. So pellets size distribution was found uniform.
Table.No.6 : Sieve Analysis

Evaluation Parameter Of Capsule
Description
It is white opaque hard gelatin (Size 1) capsule contains white to off white uniform, spherical size orlistat beads. In size 1 hard gelatin capsule the 286 mg of beads are filled. The 286 mg of beads content 160 mg of propranolol
Weight Variation
A capsule was designed to contains a specific amount of drug. When the average mass of the capsule was 366 mg the pharmacopeial limit for ?viation is 7.5%. The ?viation of average capsule weight for all capsules were found to be within the specified limit. In F01 and F04 the bead formed are of uneven shape. Hence the weight variation was observed. In F05 and F08 batch, spherical and uniform size of beads are observed and weight variation of capsules were found in specified limit shown in Table No.7.
Table.No.7 : Weight Variation of Propranolol Capsule

Content Uniformity
Drug content of formulation was once found to be satisfactory. The results indicate all the formulation containing drugs have been within the limit (90- 110%) as per USP and the results had been given in Table No.8.
Table.No.8 : Content Uniformity Of Propranolol Capsule

Lock Length of capsules
It was measured by vernier calipers. In F01 and F02 batch the beads are uneven and dumbbell shape ,after filling in capsule the capsule not lock properly. F03 to F06 result found satisfactory had been given in Table No.9
Table.No.9 : Lock Length of Propranolol Capsule

Disintegration Test
The capsules are placed in the basket rack assembly with disc, 900 ml water. which is repeatedly immersed 30 times per minute in to a thermostatically controlled fluid at 37ºc and observed over the time described in the individual monograph. The result had been given in Table No.10.
Table.No.10 : Disintegration Test Of Propranolol Capsule

Assay
Propranolol capsule contain an amount of orlistat equivalent to NLT 90% and NMT 110% of the labelled amount of Propranolol.
Table No.11 : Assay Of Propranolol Capsules

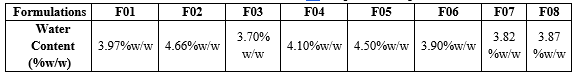
Water Content
Table No.12 : Water Content Of Propranolol Capsules
Related Substances
The total impurity observed was within acceptance criteria. Acceptance criteria will be any individual specified impurity NMT 3.6 %. Any individual unspecified impurity NMT 0.2% and total impurities NMT 3.0 %. The results had been given in Table No.8.13
Table.No.13 : Related substance Of Propranolol Capsules
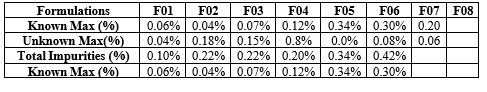
Table.No.14 : Comparative dissolution of RLD and test product
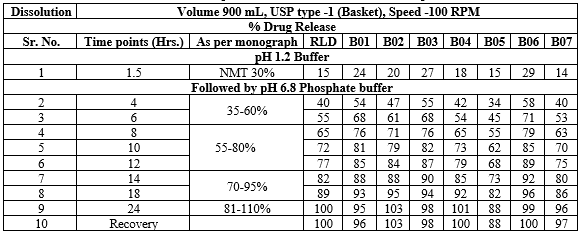
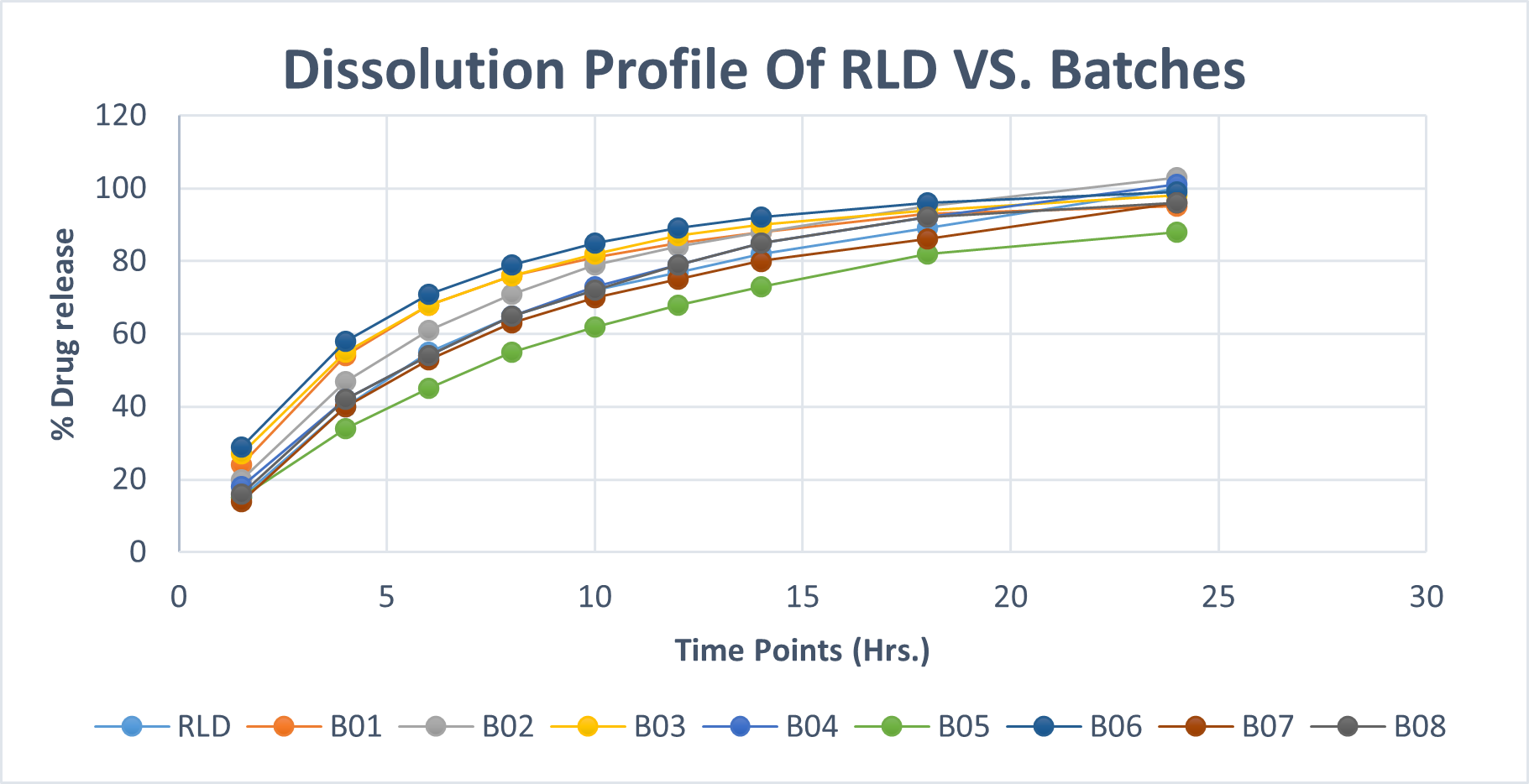
Fig.No.4 : Comparative dissolution of RLD and test products
Comparative In-vitro Drug Release Studies With Marketed Drug:
The test formulations were made keeping the market formulation in mind. Various trials were conducted and finally the optimized trial was then comparatively studied with the marketed drug. The following dissolution data was obtained as mentioned below
Instrument:
Dissolution test Apparatus, USP type -1 (Basket), Electro lab
Medium :
buffer PH 1.2 followed by buffer PH 6.8, 900 ml volume, type II paddle with coil wire sinker.
Apparatus :
Type I, 100 rpm
Temperature :
37°C
Time Point :
1.5,4,6,8,10,12,14,18,24 hrs & Recovery.
A comparative study of dissolution profile was performed for both marketed as well as optimized batch and it was observed that the optimized test formulation showed similar dissolution profile as that of the marketed drug. It was observed that the test formulation for drug delivery. Also lag time was maintained similar to that of the marked drug. The cumulative % drug release was achieved to almost 99% as that of the marked drug Fig.No.8.3.
Table No.15. Comparison Of Dissolution Profile Of Optimized Batch With Marketed Drug
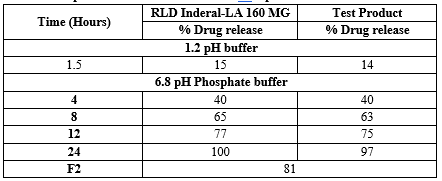
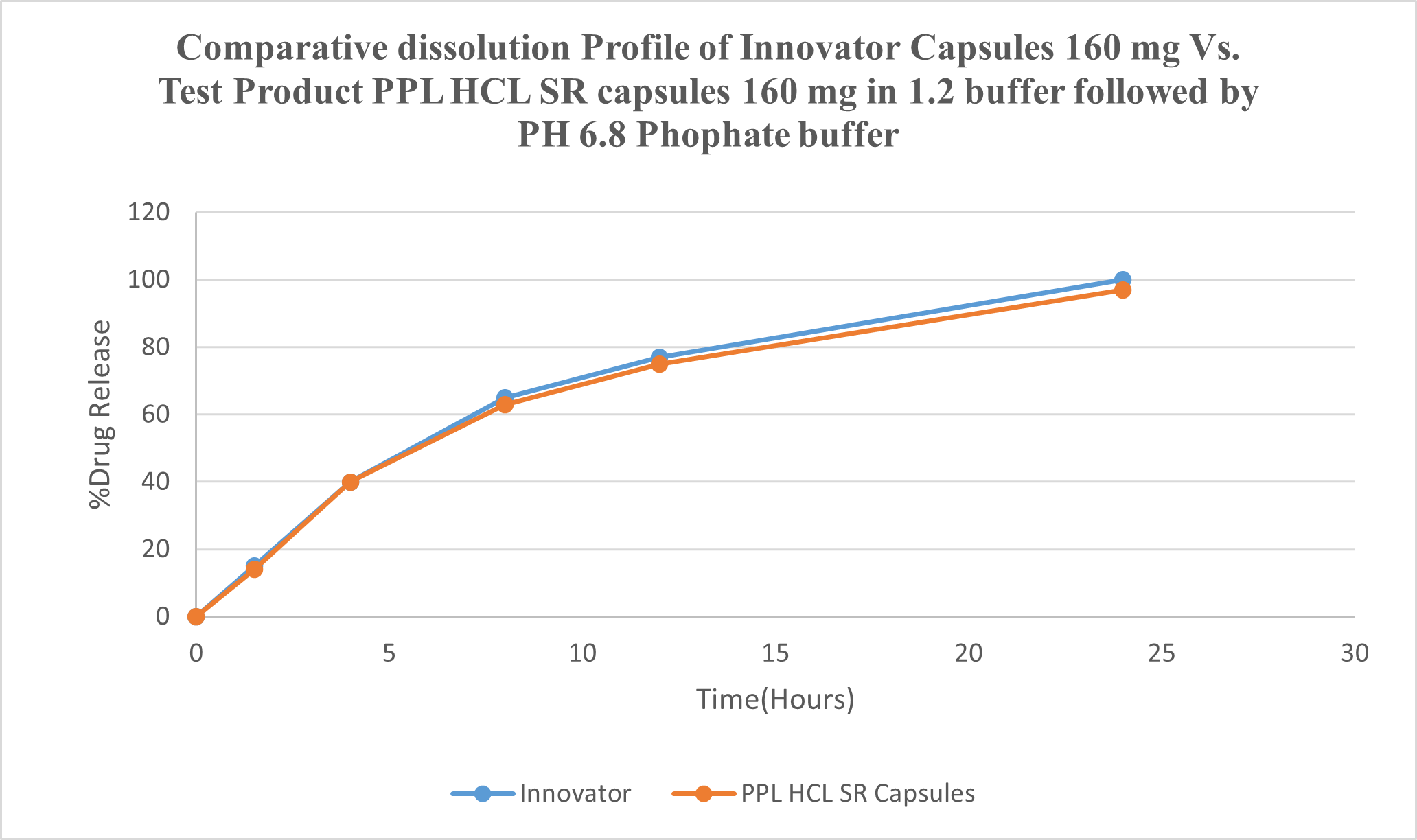
Fig.No.5 : Comparative dissolution Profile of Inderal-LA® Capsules 160 mg Vs. Test Product
OBSERVATION:
Dissolution of Test Product B No.: PROC-160-2211-044 was comparable with RLD Inderal-LA® T30481 (Propranolol Hydrochloride) Capsules 160 mg in OGD Media and F2 found to be 81.
Table No.16 : Comparative Multimedia dissolution of RLD and Batch 08
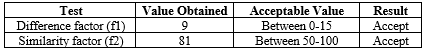
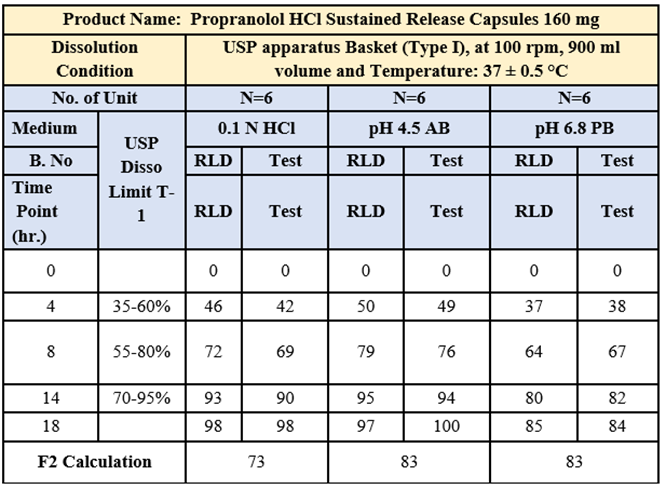
Fig.No.6 : Comparative Multimedia dissolution of Innovator Inderal-LA 160 mg SR capsule & Test product Propranolol HCL 160 mg SR Capsule in 0.1 N HCl, 900ml, 100 rpm using USP Type I (Basket)
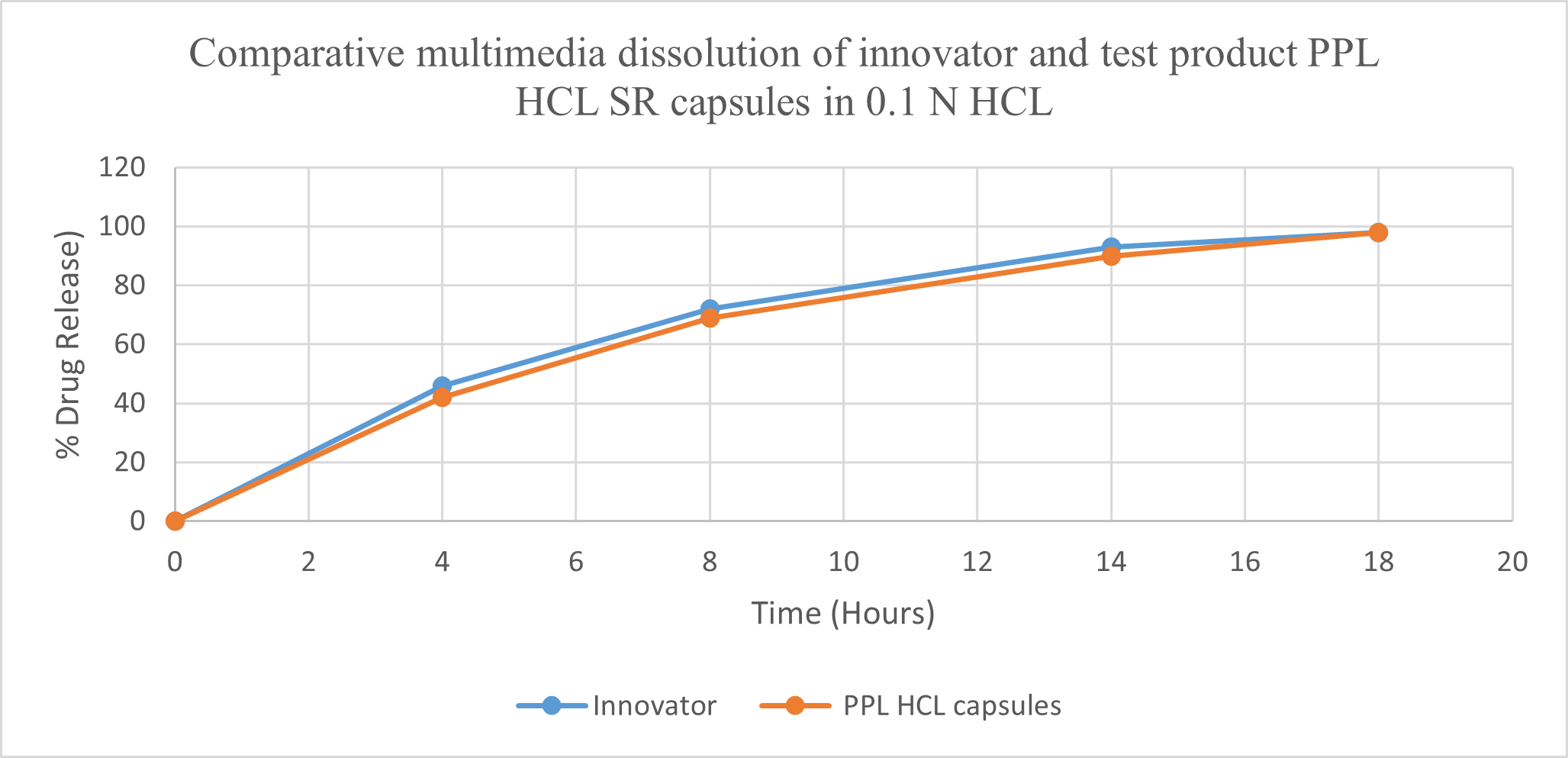
Fig.No.7 : Comparative Multimedia dissolution of Innovator Inderal-LA 160 mg SR capsule & Test product Propranolol HCL 160 mg SR Capsule in pH 4.5 acetate buffer, 900ml, 100 rpm using USP Type I (Basket).
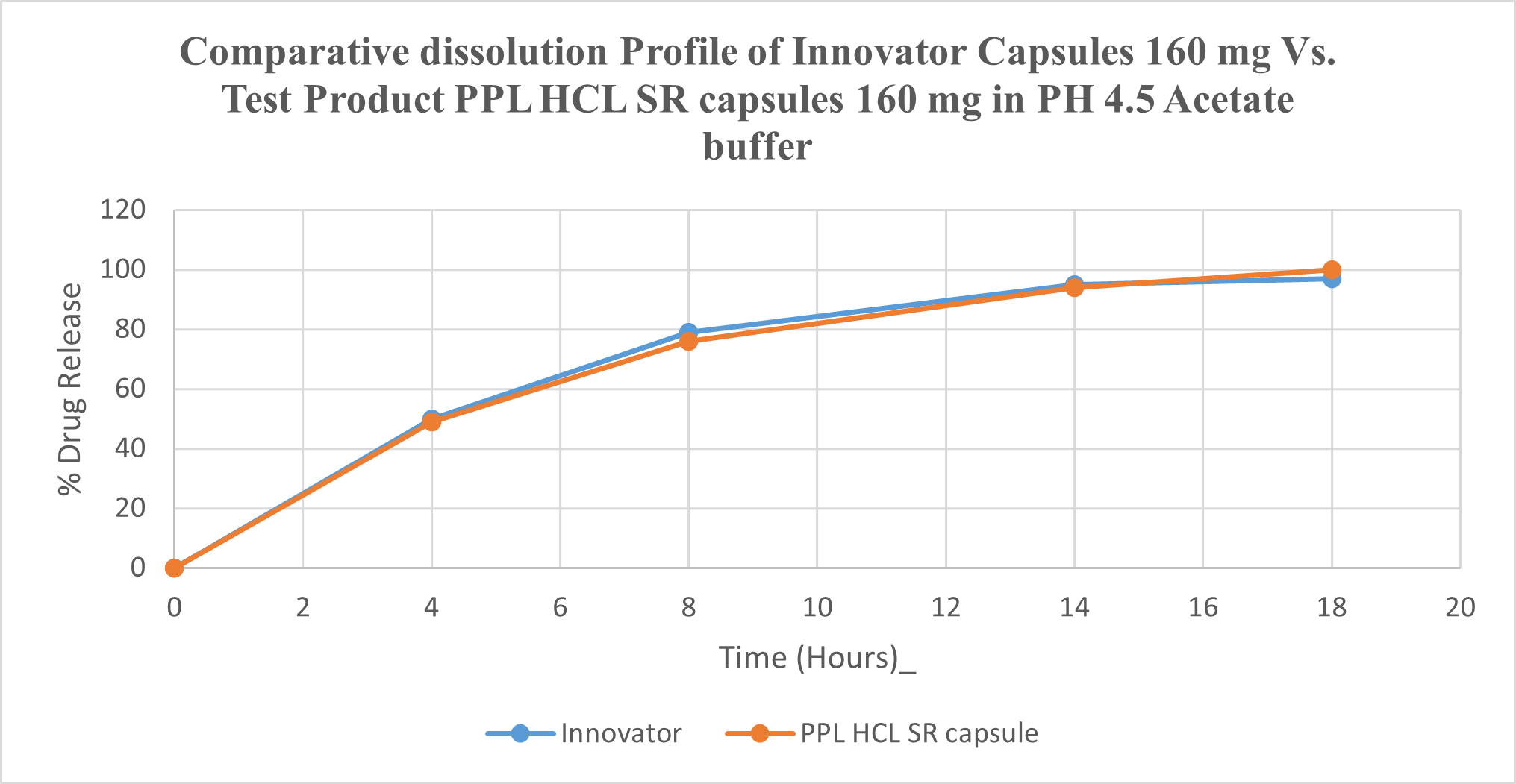
Fig.No.8: Comparative Multimedia dissolution of Innovator Inderal-LA 160 mg SR capsule & Test product Propranolol HCL 160 mg SR Capsule in pH 6.8 Phosphate buffer, 900ml, 100 rpm using USP Type I (Basket).
Observation: -
Multimedia dissolution of Test propranolol hydrochloride 160 mg SR capsule of batch no PROC-160-2211-044 was found Comparable with Innovator Lot No. T30481 Inderal-LA SR Capsule 160 mg.
Dissolution Profile Comparison by F1& F2
The results of dissolution profile comparison by f1 and f2 shows the acceptable range in Table No.8.17. In-vitro release profile of formulation(F06) is compared to marketed product. The results of dissolution profile comparison by f1 (between 0-15) and f2 (between50-100) shows that both the values of f1 (5.26) and f2 (65.44) were in acceptable range. Hence it can be concluded that the in vitro release profile of orlistat capsule 120mg was similar to the marketed product to an appreciable extent and also the developed formulation was found to be stable in desired pack.
Table No.17 : Results of f1 and f2 analysis
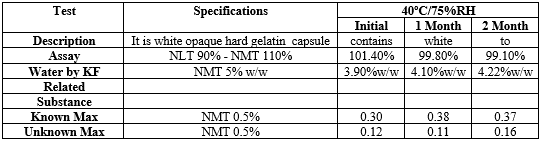
Stability Study Results
The stability studies of final trial were done for 1, 2 ,3& 6 months by packing in PVC/PVDC Blister Containing 21 capsules in humidity chamber (40°C/75% RH, 30°C/75% RH, 25°C/60% RH) Table No.7.5. The stability observations showed that all parameters of formulation including physical parameters, impurity profile, content uniformity or dissolution profile were within specification limit. So it indicates optimized formulation found to be stable at stress conditions of temperature and humidity.
Table No.18 Stability Observations (40ºC/75%RH) of Optimized Trial [F08]

Stability Dissolution result at 40ºC/75%RH
Stability study was done on the optimized formulation (F06) for a period of 2 months. The formulation was exposed to accelerated conditions i.e. 40ºC/75%RH. Later the study proceeded to evaluate the capsules for dissolution to know if there is any change observed whether the formulation remains stable.
Table No.19 Stability Dissolution result at 40ºC / 75%RH


Fig.No.9: Plot In-vitro Drug Released Data Of Stability Batch
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
The goal in designing sustained release system is to reduce the frequency of dosing or to increase effectiveness of the drug by localizing at the site of action. research work was aimed with formulation, development and evaluation of Propranolol Hydrochloride Sustained Release Capsule 160 mg a generic version of the reference listed drug (RLD), Brand Inderal-LA?. The drug powders were subjected to preformulation studies. The preformulation characteristics are within the pharmacopoeia specification. The preformulation studies were carried out and the results found to be satisfactory. The drug and excipients compatibility were carried out by HPLC method and physical observation showed there was no interactions between them. The drug assay and impurity were carried out by HPLC method and the results found to be satisfactory. The objective was to develop the stable, robust, cost-effective formulation of Propranolol Hydrochloride Sustained Release Capsule that is therapeutically equivalent to the Inderal-LA? Propranolol Hydrochloride Sustained Release Capsules 160 mg . The study investigated impact of intra-granular Microcrystalline cellulose, SR beads coat with Ethyl cellulose ECN50 and Hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose level on drug product. The impact of solvent uptake (Methanol and DCM) was evaluated on the drug product. The formulation composition was finalized based on the knowledge gained from these studies The research development study focuses on four key steps for ER beads and final Capsules process development: 1) extrusion spheronization by wet granulation method, 2) SR polymer coating, 3) Capsule Filling. bottom spray of fluid bed processor was selected for polymer coating of the ER beads. The pellets have been analysed for the parameters such as bulk density, tap density, compressibility index and Hausner 's ratio. Drug release rate was same when compared with the innovator sample. The Propranolol sustained release pellets were capsulation into capsules. All formulations were evaluated for in vitro drug release by a predictive dissolution method which was developed during development program (USP apparatus I Basket pH 1.2 pH buffer followed by 6.8 pH Phosphate buffer,100 Rpm 900 Ml for 24 Hours) by performing an extensive evaluation of dissolution conditions. The dissolution profile of Innovator and prepared Propranolol sustained release capsules were determined. The batches were loaded for stability study as per ICH guidelines at 3 different conditions (25°C/60% RH, 30°C/75% RH, 40°C/75% RH for 3 months) and evaluated in comparison to the innovator product which shows no change in physical appearance, assay and drug release which indicate the stability of the product. From the results, batch (F8) was found to be optimized due to results comparable to the innovator product.
REFERENCE
- Singh, L., Sharma, V. (2021). Implementation of Quality by Design principles for the evolution of optimized sustained release drug delivery system. Drug Delivery Letters; 11(3): 233-247.
- Bailey, MM., Berkland, CJ., (2010) Modified Release Delivery Systems. In: Morishita M., Park M., (Eds) Biodrug Delivery Systems. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida; pp 250–63.
- Yvonne Perrie, Thomas Rades. Pharmaceutics: Drug Delivery and Targeting,2012, p. 7-13
- United States Pharmacopeia 23/National Formulary 18, USPC, Inc., Rockville, MD, 1995
- Tarun Parashar, Soniya, Vishal Singh, Gaurav Singh, Satyanand Tyagi, Chirag Patel, and Anil Gupta. International Journal of Research and Development in Pharmacy and Life Sciences. Novel Oral Sustained Release Technology: A Concise Review 30, 2016
- Siegel, RA., Rathbone, MJ (2012). Overview of Controlled Release Mechanisms. Fundamentals and Applications of Controlled Release Drug Delivery. Springer US 27;19–43
- Fassihi, R. (2017) Modified-Release Delivery Systems (2017). In: Augsburger, BL., Hoag, SW., (Eds) Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida; pp 317–44.
- Collett J, Moreton C. Modified-release peroral dosage forms. Pharmaceutics–the Science of Dosage Form Design. 2002:289-305.
- Majumder, J., Taratula, O., Minko, T. (2019). Nanocarrier-based systems for targeted and site-specific therapeutic delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews;144:57–77
- Jain KK. Drug delivery systems. 1st edition. Switzerland: Humana Press; 2008. P. 1-51.
- Lachman L, Herbert AL, Joseph LK. The theory and practice of industrial pharmacy. 3rd edition. Bombay: Varghese publishing house; 1986. P. 430-455.
- Joseph RR, Vincent HLL. Controlled drug delivery fundamentals and applications. 2nd edition revised and expanded. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc; 1987. P. 3-56.
- Venkatesan K, Krishnaraju K, Vs S, Pichaivel M, et al. World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences rats. 2021;9(8):69–72.
- Nashed, N., Lam, M. and Nokhodchi, Ali.,(2021). A comprehensive overview of extended-release oral dosage forms manufactured through hot melt extrusion and its combination with 3D printing. International Journal of Pharmaceutics: 596, 120237.
- Pallab Roy, Aliasgar Shahiwala, Multiparticulate formulation approach to pulsatile drug delivery: Current perspectives, Journal of Controlled Release, Volume 134, Issue 2, 2009,Pages 74-80
- Ghebre-Selassie I. Pellets: a general overview. In: Ghebre- Selassie I, editor. Pharmaceutical palletisation technology. New York: Marcel Dekker; 1989. p. 1–15.
- Vervaet C, Baert L, Remon JP. Extrusion–spheronisation a literature review. Int J Pharm 1995;116:131–146.
- Multiple Unit Dosage Form Pellets and Pelletisation Techniques: An Overview .Kumar Vikash et al/IJRAP 2011, 2 (1)121-125.
- Lavanya K. Pelletization technology: a quick review. Int J Pharm Sci Res 2011;2:1337–1355.
- Kader A and jalil R In vitro release theophylline poly sustained release pellets prepared by direct compression.1998
- Sagar Muley, Tanaji Nandgude, Sushilkumar Poddar,Extrusion–spheronization a promising pelletization technique: In-depth review,Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Volume 11, Issue 6,2016,Pages 684-699.
- Hicks DC, Freese HL. Extrusion and spheronizing equipment. InPharmaceutical pelletization technology 1989 (pp. 71-100).
- Rowe RC. Spheronization-a novel pill-making process. Pharmacy International. 1985 Jan 1;6(5):119-23.
- kandhukuri JM .Allenkiv ,keshetty V,Jannu K,Pelletization techniques for oral drug delivery.2009;63-70
- Kumar V,mishrask.design of multiple unit dosage form of pellets and pelletization techniques.2011;121-125.
- V.A. Loyd, G.P. Nicholas, C.A. Howard, Pharmaceutical dosage forms and drug delivery systems, 8 (1998) 260-268
- Porter S.C. Coating of Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms. Remington; Madison, NC, USA: Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2021. pp. 551–564.
- Wang Z, Yu X, Wu L, Ye Y, Zhou M, Yu LX. Profiling the process development of Wurster coating for modified release capsule products in approved drug product applications. Int J Pharm. 2022 Sep 25;625:122053.
- Mohanty, Rozy and Anisur Rashid Khan. “CHALLENGES DURING SCALE-UP IN WURSTER COATING.” (2020).
- Mehta AM. Scale-up considerations in the fluid-bed process for controlled release products. Pharm Technol 1988;12:46-52


 Akash R. Shahu*
Akash R. Shahu*
 Amol S. Warokar
Amol S. Warokar
 Sagar S. Yadav
Sagar S. Yadav
 Akash M. Bhakare
Akash M. Bhakare
























 10.5281/zenodo.12657315
10.5281/zenodo.12657315