Abstract
Skin aging is a multifaceted biological process influenced by internal and external factors, including UV exposure, pollution, and lifestyle choices. The demand for safe, natural anti-aging solutions has driven research toward herbal formulations. This study focuses on formulating and evaluating a novel herbal anti-aging gel-cream using rambutan fruit (Nephelium lappaceum) extracts. Rich in bioactive compounds like alkaloids, flavonoids, and tannins, rambutan demonstrates significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, making it a suitable candidate for skin care. The gel-cream was prepared with rambutan pulp and seed extracts, combined with ingredients such as beeswax, olive oil, almond oil, and aloe vera for hydration and stabilization. Six formulations (F1-F6) were developed, evaluated for physical, pharmaceutical, and stability parameters. Key tests included pH determination, viscosity, spreadability, and skin irritation, alongside phytochemical analysis for active components. Results indicated that formulations F2 and F6 showed optimal stability, homogeneity, spreadability, and non-greasy properties. No signs of irritation were observed during dermatological testing. The study concludes that the rambutan-based herbal gel-cream is a safe, effective anti-aging product with potential for cosmetic development.
Keywords
Herbal cosmetics, Rambutan extract, Gel cream formulation, Anti-oxidant property, Herbal anti-aging.
Introduction
Skin aging is a component of the "aging mosaic" that occurs naturally in humans and takes distinct paths over time in various organs, tissues, and cells. The skin offers the earliest visible indications of time passing, while the surrounding "eyes" conceal the aging symptoms of interior organs. A complicated biological process, skin aging is impacted by both exogenous (external) and endogenous (internal) causes. Numerous anti-aging techniques have been created in recent years due to the fact that skin health and beauty are seen to be among the primary variables representing general "well-being" and the perception of "health" in humans.[1] Regardless of age, sex, education, or occupation, everyone in the modern world has a strong desire to seem young and attractive, which is driving up demand for cosmetics. The anti-aging business is a quickly expanding subset of the cosmetics sector, which eventually raises demand for goods and services that address the obvious signs of aging. The demand for natural and organic cosmetics is rising as consumers become more aware of the ingredients in products. Natural ingredients, which come from plants, minerals, and other natural sources, are thought to be healthier and kinder to the skin than synthetic ones. This is where our research and creation of a herbal anti-aging cream come in. [2]
Skin:
Skin, also known as the integumetary system, is the largest organ in our body, covering the entire external surface; measuring up to 2m2 and weighing approximately 4.5?5kg in an average adult (or about 12?15% of total adult body weight). Skin is the first physical barrier protecting us from the external environment. [3] Additionally, the skin contributes to immunologic monitoring, sensory perception, the regulation of insensible fluid loss, and overall homeostasis. Additionally, the skin is quite adaptive, having varying thicknesses and specialized roles in various bodily parts.
The skin is primarily made up of three layers.
- The epidermis, the outermost layer of skin, provides a waterproof barrier and contributes to skin tone.
- The dermis, found beneath the epidermis, contains connective tissue, hair follicles, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and sweat glands.
- The deeper subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis) is made of fat and connective tissue. [4]
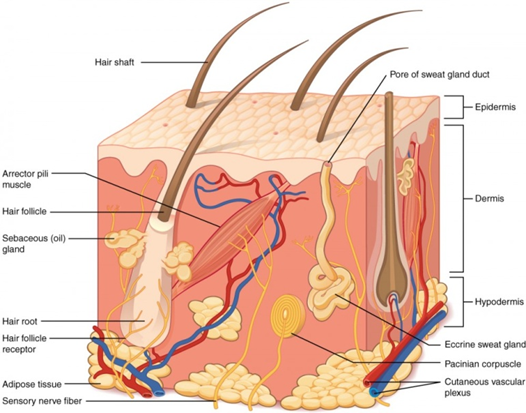
(Figure 1: Anatomy of Skin)
Functions of skin:[5]
Skin performs the following functions:
- Protection:
- Langerhans cells in the skin are the part of adaptive immune system.
- An anatomical barrier from pathogens and damage between the intrernal and external environment in bodily defence.
- Sensation:
It contains a variety of nerve endings that react to heat and cold, touch, pressure, vibration and tissue injury.
- Heat regulation:
Dilated blood vessels increase perfusion and heat loss while constricted vessels greatly reduce cutaneous blood flow and conserve heat.
- Control of evaporation:
It act as a semi-impermeable barrier to fluid loss.
- Aesthetics and communication:
Skin can assess our mood,physical state and attractiveness.
- Storage and synthesis:
Act as a storage centre for lipids and water as well as a means of synthesis of vitamin D by action of UV on certain parts of the skin.
- Water resistance:
Act as a water resistant barrier so essential nutrients aren’t washed out of the body.
Creams:
Creams find primary application in topical skin products and in products used on mucous membranes, such as rectally and vaginally. Many patients and physicians prefer creams to ointments because they are easier to spread and remove. Pharmaceutical manufacturers frequently manufacture topical preparations of a drug in both cream and ointment bases to satisfy the preference of the patient and physician. [6] The localized effect of these topical formulations allows the medicine to be delivered into the mucous membrane or the skin's underlying layer. These treatments are intended to be applied topically to improve the drug's site-specific distribution into the skin for skin conditions. [7]
Types of Skin Creams:
They are divided into two types:
- oil-in-water (O/W) creams which are composed of small droplets of oil dispersed in a continuous phase.
- water-in-oil (W/O) creams which are composed of small droplets of water dispersed in a continuous oily phase.
Oil-in-water creams are more comfortable and cosmetically acceptable as they are less greasy and more easily washed off using water. Water-in-oil creams are more difficult to handle but many drugs which are incorporated into creams are hydrophobic and will be released more readily from a water-in-oil cream than an oil-in-water cream.[8]
Herbal Creams:
Herbal cosmetics, here in after referred as products, are formulated, using various permissible cosmetic ingredients to form the base in which one or more herbal ingredients are used to provide defined cosmetic benefits only, shall be called as “Herbal Cosmetics” Herbs include crude plant material, such as leaves, flowers, fruit, seeds, stems, wood, bark, roots, rhizomes or other plant parts, which may be entire, fragmented or powdered. [9] The natural content in the herbs does not have any reactions on the human body; rather enhance the body with supplements and other helpful minerals. The natural content in the herbs does not have any reactions on the human body; rather enhance the body with supplements and other helpful minerals. The natural content in the herbs does not have any reactions on the human body; rather enhance the body with supplements and other helpful minerals. The natural content in the herbs does not have any reactions on the human body; rather enhance the body with supplements and other helpful minerals. The natural content in the herbs does not have any reactions on the human body; rather enhance the body with supplements and other helpful minerals. Herbs' natural ingredients don't react with the human body; instead, they aid it by supplying it with minerals and other beneficial substances. Another name for herbal cosmetics is "natural cosmetics." Because herbal treatments have no negative side effects, their demand is rising quickly. [10]
Gel Cream:
A gel-cream consists of oily and aqueous phases together with a stabilizing, thickening and/or emulsifying agent. Gel-cream has a smooth texture, good spreadability, feel and provides good nourishment with moisturization. It has rapid drug permeation and is also thermodynamically stable. The present work aims to formulate and evaluate a herbal anti-ageing gel-cream which is safe, highly stable and less toxic as compared to synthetic formulations. [2]
External Factors:
1. UV radiation : Prolonged sun exposure can cause photoaging, wrinkles, and age spots.
2. Smoking : Smoking damages skin elasticity, reduces blood flow, and leads to premature aging.
3. Pollution : Exposure to environmental pollutants can generate free radicals, damaging skin cells.
4. Diet : A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can lead to inflammation and skin aging.
5. Stress : Chronic stress can increase inflammation, leading to skin issues like acne, rosacea, and premature aging.
6. Lack of sleep : Poor sleep quality and duration can affect skin regeneration, leading to puffy, dull skin.
7. Harsh skincare products : Using products that are too harsh or contain irritating ingredients can strip skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and aging. These factors can contribute to various signs of aging, including wrinkles, fine lines, age spots, and loss of skin elasticity. [11]
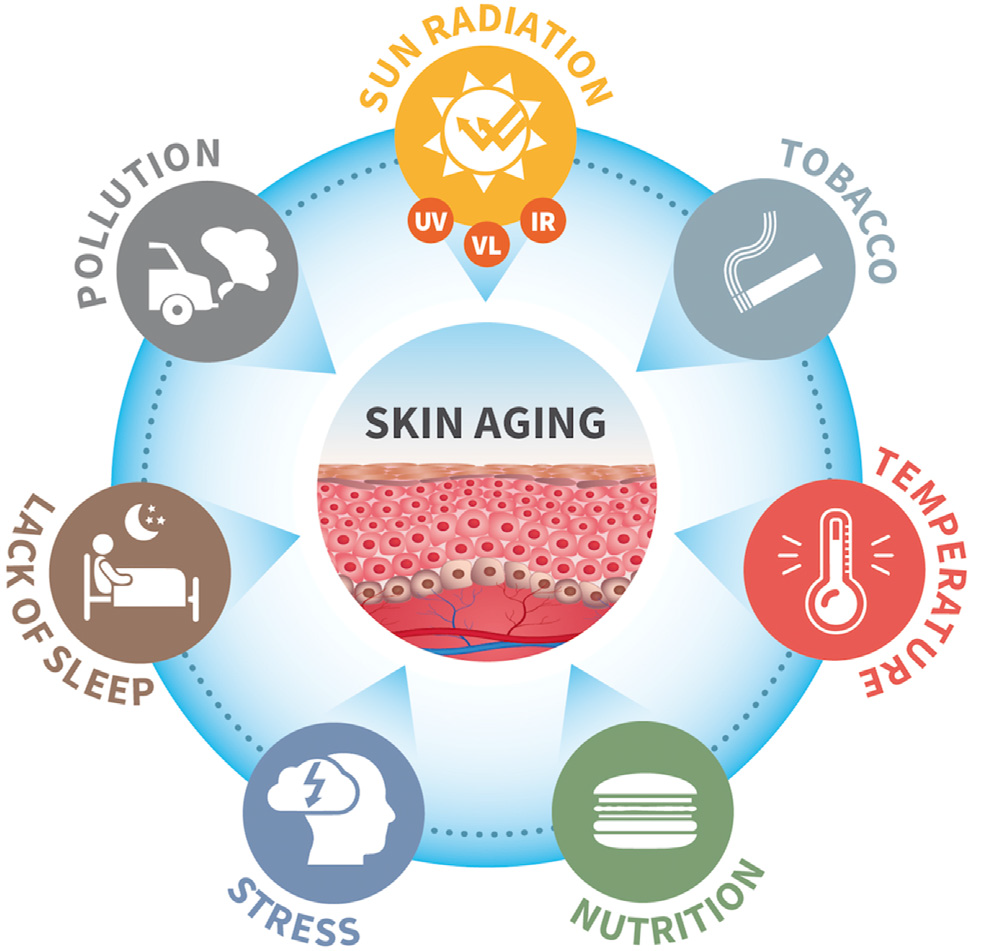
Fig 2 : Factors Influencing Aging
Ideal Characterstics:
Ideal Characteristic of Creams:
- Good penetrating property so that the drug present in cream penetrates into skin and shows the desired effect.
- It should be non-toxic so that it does not have any adverse effects on skin such as itching, rashes or redness.
- When applied on skin it should spread easily on skin.
- It should melt or liquify at body temperature when applied on skin.
- It should be non-irritant and should not cause any inflammation on skin. [12]
ADVANTAGES:
-
- Ease of application.
- Easy to utilize.
- Steering clear of danger.
- There is no special risk or technician needed for application.
- Avoid drug level fluctuations in the event of intra- and inter-patient variance.
- Very good patient adherence.
The benefit of employing cream formulations is their practicality; they can be applied directly to the skin without leaving any traces behind, and they are simple to wash and clean. [13]
Aim:
To formulate and evaluate the novel herbal antiaging gel-cream from the rambutan fruit extract.
Objectives:
- To prepare herbal antiaging gel-cream from the ethanol/water(80:20) mixture extract of Rambutan fruit.
- To perform the evaluation test for the suitable formulation:
- Physical parameter:
- Pharmaceutical parameter:
- Irritancy study
- Phytochemical assay:
- Stability study
- To prevent aging of skin,reduce the rate of premature ageing,nourish and beautify the skin.
- They are believed to be safer with fewer side effect than synthetic products.
Plan Of Work:
- Preparation of herbal extract.
- Rambutan fruit extract.
- Rambutan seed extract.
- Preparation of herbal anti-aging gel-cream.
- Preparation of oil phase
- Preparation of water phase
- Preparation of gel-cream phase
- Preparation of gel-cream formulation
- Evaluation of herbal anti-aging gel-cream
- Colour
- Odour
- Constistency
- Greasiness
- Water washability
- Grittiness
- % Moisture content
- pH observation
- Spreadability
- Viscosity
- Irritancy study.
- Phytochemical studies.
- Stability studies.
Plant Profile: [14]
Botanical Name: Nephelium Iappaceum
Common Name: Rambutan, Hairy lychee
Kingdom: Plantae
Subkingdom: Tracheobionta
Super Division: Spermatophyta
Division: Magnoliophyta
Class: Magnoliopsida
Subclass: Rosidae
Order: Sapindales
Family: Sapindaceae
Genus: Nephelium
Species: Nepheliumlappaceum

Fig. 3: Rambutan
History Of Fruit: [15]
The Rambutan is a medium –sized tropical tree that produces the edible fruit of the name.It’s native to the Malay –Indonesian region and other topical southeast Aian counties like Indonesia, Philippines, Vietnam , Srilanka ,Cambodia and Thailand. The name Rambutan comes from the Malay word for “Hair” which describe the fruit’s reddish or yellow, fleshy, pliable spine-like protuberances. The fruit is a transulant , whitish aril, and the seed is brown. The various parts of rambutan fruit extract reported that it has antioxidant and antiaging properties.This chapter focuses to present an updated informing about the antioxidant and antiaging potency of rambutanfruits;the constituent that are responsible for its antiaging effect hsve also been discussed. Rambutan peel extract have been mainly involved in antioxidant and antiaging effect due to the presence of huge amount of polyphenolic compound. Therambutan peel phenolic against oxidative stress in H2O2-induced HepG2 Cells in dose –response manner. Moreover the antiaging cream was prepared using rambutan peel extract and tested for its antiaging effect.The result indicated that the rambutan peel extract can be used for the development of cosmetic product.It is also used as an essential antioxidant strategy in reducing oxidative stress caused by skin exposure to UV radiation in thr prevention and treatment of skin aging. Based on the result demonstrated by many researchs,the formulation containing rambutan peels extract can be usable for the skin, and it has good potential for cosmetic product development.
Chemical composition of Rambutan : [16]
Carbohydrates, Vitamin C, Phenolic compounds, minerals like potassium calcium magnesium phosphorus iron, flavonoids, tannins, ellagic acid, gallic acid, lipids, oleic acid, arachidic acid, stearic acid, saponins, alkaloids.
Uses of Rambutan : [17]
- Antimicrobial
- Antioxidant
- Antidiabetic
- Anticancer
- Antiobesity
- Wound healing
- Antihypercholesterolemia
Excipients Profile
Bees Wax:
Structure:
Molecular Formula: C15H31COOC30H61
Molecular weight: 677.2215 g.
Melting Point: Between 14H-1HT°F (62-64°).
Appearance: White, Light yellow, Medium Yellow, Dark Brown and also most Black.
Solubility: Insoluble in water but soluble in many Organic solvents, Including ether,acetone, xyol, Benzene, chloroform tetra chloromethane, esters and Ketones.
Stability: Stable and chemical Resistant.
Hydrophobicity: Imparted by esters of long chain Fatty alcohols, acids & long chain alkanes Present with is.
PH: 7.0
Specific Gravity: About 0.95
Cetylstearyl Alcohol: -
Structure: -
Molecular Formula: CH3(CH2)nOH.
Molecular weight: 512.95 g/mol.
Melting point : 50°c (122°F).
Appearance: White (or) Cream colored waxy substance that appears as flakes pellets, granules (or) unctuous masses.
Solubility: Insoluble in water, Soluble in ethanol (96%) and in light petroleum.
Stability: Depends on the ratio of cetyl and stearyl alcohol and the phase Volume to emulsifer HLB ratio.
Hydrophobicity: cetylstearyl alcohol is a combination of cetyl alcohol and stearyl alcohol that founds a crystaline bilayer with a hydrophilic portion that faces the Interlamellar spaces.
PH:-5.5-7.5.
Specific gravity: 0.80-0.85 (at 20°c/68°F).
Liquid Paraffin: -
Structure: -
Molecular Formula: Cn H2n+2.
Molecular weight: 200-500g/mol.
Melting point : 10°C to 20°c (50°F to 68°F).
Appearance: It is a colourless (or) pale yellow.
Solubility: It is soluble in Non-polar solvent, Aromatic, chlorinated solvent. Soluble in polar, water Alkaline solution, partially Soluble in Ether, Glycerin.
Stability: It stables the chemical, oxidative, Thermal and storage condition.
Hydrophobicity: High Hydrophobicity makes it Insoluble in water Solvents and polar solvents.
PH: 6.5-8.5
Specific Gravity: 0.835 - 0.905 g/cm3.
Olive Oil: -
Structure: -
Molecular Formula: C88H164O10
Molecular weight : 875-900 g/mol.
Melting point : 10°c -15°c 50°~59°F).
Appearance : Greenish yellow to Golden yellow depending on olive Variety. Variety.
Solubility: It is Insoluble in water, ethanol, Methanol and acetone and soluble in Hexane, Heptane, petroleum ether Benzene, Toluene, chloroform and Carbon Tetra chloride.
Stability: It stables at storage, composition and Oxidative Stability.
Hydrophobicity : It Repels water and has very little solubility.
PH: PH is not measured because olive oil is not Soluble in water.
Specific gravity: 0.80 - 0.92 at 20°c.
Almond Oil:
Structure:
Molecular Formula : C18H32O2.
Molecular weight : 850-1920 g/mol.
Melting point : -10°/-18°c (19°F to 28°F).
Appearance : Pale yellow liquid with a slight Odor and a Nutty taste.
Solubility: Insoluble in water, ethanol, Methanol and acetone and soluble in hexane, heptane,Ether, Benzene, Xylene, chloroform and carbon Tetrachloride.
Stability: It stable physical and chemical Reactions.
Hydrophobicity: It is due to chemical structure, which consists of non-polar hydrophobic fatty acid chains.
PH: 5.5-7.0
Specific Gravity: It ranges from 0.91 to 0.93.
Aloe Vera Mucilage:
Structure: -
Molecular Formula: C16 H13NO3.
Molecular weight: 928-277-105,003 Da.
Melting Point : 15 to 250°C.
Appearance: It a Transparent, Jelly like substance that is viscous.
Solubility: It is soluble in water but not in oil. Acetone, ethanol, Methanol (or) benzene.
Stability: It stable the Temperature, PH and storage condition.
Hydrophobicity: It can be used to Create hydrophobic coating and Films.
PH : 5.5-6.5.
Specific Gravity: 1.02 -1.05 It is slightly denser than water.
Carbopol 940 :
Structure:-
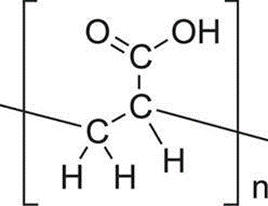
Molecular Formula: (C3H402)n..
Molecular weight : 72.06 g/mol.
Melting point: 12.5? to 95°c.
Appearance: white, odourless Fluffy powder.
Solubility: Soluble in water when Neutralize with alkali hydroxide (or) amine. It is also soluble in alcohol and glycerin.
Stability : It is stable in Temperature (100’C).
Hydrophobicity : It is dispersible but not soluble water (or) alcohol
PH: 2.5 to 7.5.
Specific Gravity: 1.41.
Triethanolamine:
Structure:
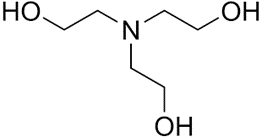
Molecular Formula : C6H15 NO3.
Molecular weight: 149 - 188 g/mol.
Melting point: 21-25°C (69.8-77°F).
Appearance: Clear, colourless to pale yellow, viscous.
Solubility: Miscible with water and acetone, ethanol, methanol, chloroform. Benzene, diethyl ether, n-heptane are soluble in nature.
Stability: It stable chemical, storage, Incompatible materials.
Hydrophobicity : Hydrophobic glycol ether that is partly water soluble and miscible with most Organic solvent.
PH: 10-11.
Specific Gravity: 1.120-1.130. It is slightly denser than water.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Plant Collection:
- Rambutan (Nepheliumlappaceum) fruits was purchased from the local market and identified.
- The flesh, peels and seeds of Rambutan fruits were separated, dried in hot air oven at 35-40°C and grinded to coarse powder using blender.
- They were employed to create the formulation after being extracted using the necessary solvents.
Excipient Profile:
|
S. No
|
Ingredients
|
Properties
|
|
1.
|
Rambutan seed extract
|
Antioxidant
|
|
2.
|
Rambutan pulp extract
|
Anti-inflammatory
|
|
3.
|
Beeswax
|
Emulsifyin gagent, stablizer
|
|
4.
|
Stearic acid
|
Cooling sensation, Texture enhancer
|
|
5.
|
Cetyl alcohol
|
Thickening agent and stabilizer
|
|
6.
|
Liquid paraffin
|
Lubricating agent
|
|
7.
|
Olive oil
|
Moisturizing agent
|
|
8.
|
Almond oil
|
Moisturization agent
|
|
9.
|
Alovera mucilage extract
|
Antimicrobial
|
|
10.
|
Carbopol 940
|
Thickening, Binding
|
|
11.
|
Triethonolamine
|
pH adjuster, Surfactant
|
|
12.
|
Methyl paraben
|
Preservative
|
|
13.
|
Water (Q.S.)
|
Vehicle
|
METHODOLOGY [18]:
1. Preparation of herbs extract
A. Rambutan pulp extract:
Materials Needed
- Fresh or frozen Rambutan pulp.
- Solvent (e.g., ethanol, methanol, or water).
- Grinder or blender
- Filter paper or cheesecloth
- Rotary evaporator (optional)
- Drying oven (optional)
Preparation Methods
Method 1: Solvent Extraction
1. Grind the pulp: Grind the Rambutan pulp into a fine paste using a grinder or blender.
2. Mix with solvent: Mix the ground pulp with a solvent (e.g., ethanol, methanol, or water) in a ratio of 1:1 to 1:5 (pulp: solvent).
3. Stir and steep: Stir the mixture well and let it steep for 2-24 hours, depending on the desired extraction efficiency.
4. Filter: Filter the mixture using filter paper or cheesecloth to separate the liquid extract from the solids.
5. Concentrate: Concentrate the liquid extract using a rotary evaporator or by reducing the volume through evaporation.
Drying and Storage:
1. Dry the extract: Dry the concentrated extract using a drying oven or by freeze-drying.
2. Store the extract: Store the dried extract in an airtight container, protected from light and moisture.
B. Rambutan seed extract:
Materials Needed
- Dried Rambutan seeds.
- Solvent (e.g., ethanol, methanol, or water).
- Grinder or mortar and pestle.
- Filter paper or cheesecloth.
- Rotary evaporator (optional).
- Drying oven (optional).
Preparation Methods
Method 1: Solvent Extraction
1. Grind the seeds: Grind the dried Rambutan seeds into a fine powder using a grinder or mortar and pestle.
2. Mix with solvent: Mix the ground seeds with a solvent (e.g., ethanol, methanol, or water) in a ratio of 1:1 to 1:5 (seed:solvent).
3. Stir and steep: Stir the mixture well and let it steep for 2-24 hours, depending on the desired extraction efficiency.
4. Filter: Filter the mixture using filter paper or cheesecloth to separate the liquid extract from the solids.
5. Concentrate: Concentrate the liquid extract using a rotary evaporator or by reducing the volume through evaporation.
Drying and Storage:
1. Dry the extract: Dry the concentrated extract using a drying oven or by -drying.
2. Store the extract: Store the dried extract in an airtight container, protected from light and moisture.
2.Preparation Of Herbal Anti-Ageing Gel-Cream
A. Preparation of oil phase:
The oil phase ingredients were weighed mixed with continuous stirring using mechanical stirrer to form uniform liquid.
B. Preparation of water phase:
The water phase ingredients were weighed mixed with continuous stirring using mechanical stirrer to form uniform liquid.
C. Preparation of Gel-cream base:
The oil phase was incorporated in the water phase with continuous stirring using mechanical stirrer. Methyl paraben was added as preservative.
D. Preparation of Gel-cream formulation:
Different concentrations of rambutan water and alcohol added with continuous stirring using mechanical stirrer to gel-cream bases till the uniform dispersion of the ingredients was achieved. All these batches were allowed to equilibrate for 24 hours at room temperature. The prepared gel-cream was filled and stored in a wide mouth polypropylene container. The formulation was further evaluated.
Formulation
Formulation For Rambutan Pulp Extract:
|
Ingredients
|
F1 (20g)
|
F2
(20g)
|
F3 (20g)
|
|
Rambutan Pulp Extract
|
0.4 g
|
0.5 g
|
0.6 g
|
|
Beeswax
|
0.4 g
|
0.3 g
|
0.5 g
|
|
Stearic acid
|
0.6 g
|
0.6 g
|
0.6 g
|
|
Cetyl Stearyl alcohol
|
1 ml
|
1 ml
|
1 ml
|
|
Liquid paraffin
|
2 ml
|
2 ml
|
2 ml
|
|
Olive oil
|
0.4 ml
|
0.4 ml
|
0.4 ml
|
|
Almond oil
|
0.4 ml
|
0.4 ml
|
0.4 ml
|
|
Aloe vera mucilage Extract.
|
1.6 ml
|
1.6 ml
|
1.6 ml
|
|
Carbopol 940
|
0.1 ml
|
0.1 ml
|
0.1 ml
|
|
Triethanolamine
|
0.1 ml
|
0.1 ml
|
0.1 ml
|
|
Methyl paraben
|
0.1 ml
|
0.1 ml
|
0.1 ml
|
|
Water
|
Q. S
|
Q. S
|
Q. S
|
Formulation Procedure for Rambutan Pulp Extract:
Preparation of Rumbutan pulp Extract.
?
Heat the Beeswax, cetyl stearyl alcohol,
liquid paraffin, olive oil, almond oil in Beaker. (oil phase)
?
Take another beaker and add aloe vera mucilage Extract, Carbopol 940, Triethanolamine. (Aqueous phase)
?
Slowly add the aqueous phase to oil phase.
?
Then add measured amount of Rambutan pulp Extract and stir continuously un it forms a gel cream.
?
Emulsification (Oil in Water Phase).
?
Check and adjust the PH.
?
Packaging
Formulation For Rambutan Seed Extract:
|
Ingredients
|
F4
(20g)
|
F5
(20g)
|
F6
(20g)
|
|
Rambutan Seed Extract
|
0.3 g
|
0.4 g
|
0.5 g
|
|
Beeswax
|
0.4 g
|
0.3 g
|
0.2 g
|
|
Stearic acid
|
0.6 ml
|
0.6 ml
|
0.6 ml
|
|
CetylStearyl alcohol
|
1 ml
|
1 ml
|
1 ml
|
|
Liquid paraffin
|
2 ml
|
2 ml
|
2 ml
|
|
Olive oil
|
0.4 ml
|
0.4 ml
|
0.4 ml
|
|
Almond oil
|
0.4 ml
|
0.4 ml
|
0.4 ml
|
|
Aloe vera mucilage Extract.
|
1.6 ml
|
1.6 ml
|
1.6 ml
|
|
Carbopol 940
|
0.1 ml
|
0.1 ml
|
0.1 ml
|
|
Triethanolamine
|
0.1 ml
|
0.1 ml
|
0.1 ml
|
|
Methyl paraben
|
0.1 ml
|
0.1 ml
|
0.1 ml
|
|
Water
|
Q. S
|
Q. S
|
Q. S
|
Formulation Procedure for Rambutan Seed Extract:
Preparation of Rumbutan pulp Extract.
?
Heat the Beeswax, cetyl stearyl alcohol,
liquid paraffin, olive oil, almond oil in Beaker. (oil phase)
?
Take another beaker and add aloe vera mucilage Extract, Carbopol 940, Triethanolamine. (Aqueous phase)
?
Slowly add the aqueous phase to oil phase.
?
Then add measured amount of Rambutan pulp Extract and stir continuously un it forms a gel cream.
?
Emulsification (Oil in Water Phase).
?
Check and adjust the PH.
?
Packaging
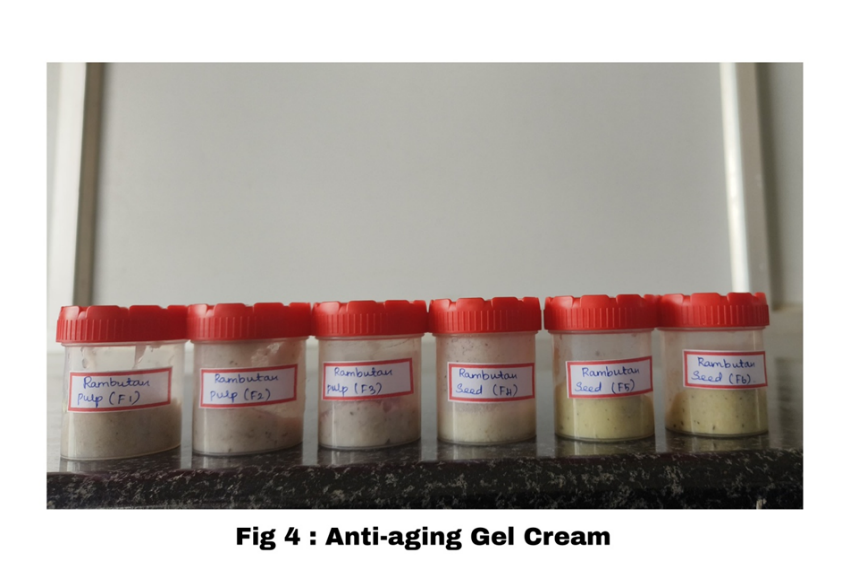

3. Evaluation Of Herbal Anti-Ageing Gel-Cream:
I) Physical Parameter: [19,20]
a) Colour:
All the formulated gel-creams were tested for color by visual inspection. They werechecked against white background.
b) Odor:
The odors of all formulated gel-creams were checked by mixing the gel-cream in water.
c) Consistency:
The consistency was checked by applying on skin.
d) Greasiness:
The greasiness was assessed by the application on the skin.
e) Grittiness:
All the formulations were evaluated for the particulate matters under light microscope.
F) Water washability:
All the formulations were applied on the skin the ease and extent of washing with water were checked manually.
g) Percentage Moisture Content:
Percentage moisture loss for the different batches was determined. The accurately weighed quantity 2gm of formulation was kept in a desiccators containing 50gm anhydrous calcium chloride. After three days, the formulation was weighed and the percentage moisture loss was calculated using the formula.
Percentage moisture loss = calculated using the formula
Percentage moisture loss =
Initial weight - Final weight x 100
Final weight
ii) Pharmaceutical Parameter: [21]
a) pH determination:
The pH of the prepared gel-cream was determined using digital pH meter. 1% solution of the formulation was prepared using distilled water. The pH of each formulation was done in triplicate and average values were calculated.
b) Rheological Study/ Viscosity:
The viscosity of formulations was studied using viscometer (Brookfield digital viscometer RVT). The spindle (62) was rotated at 0.5 rpm. Samples of the gel-cream were allowed to settle over 30 min at the temperature (25 ±/1°C) .
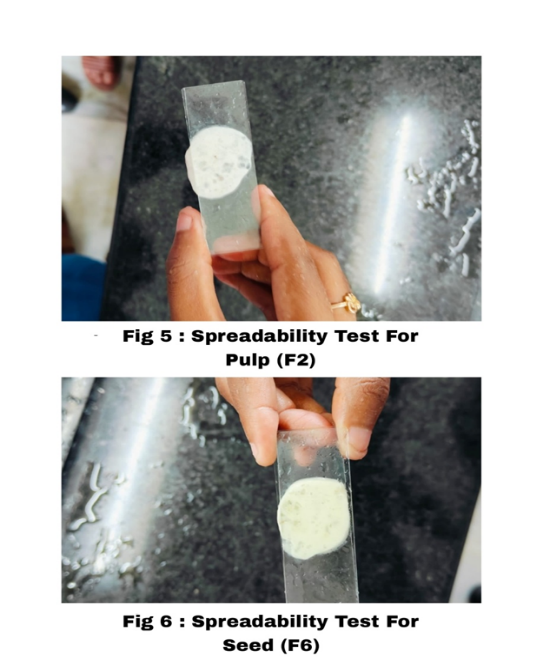
c) Spreadability:
Spreading coefficient was determined by apparatus suggested by Mutimer et al (1956). It consists of wooden block, which is attached to a pulley at one end. Spreading coefficient was measured on the basis of 'Slip' and 'Drag' characteristics of gel. A ground glass slide was fixed on the wooden block. An excess of gel-cream (about 2 gm) under study was placed on this ground slide. Gel-cream preparation was then sandwiched between two slides of which the second glass slide has same dimension as that of the fixed ground slide. The second slide is provided with the hook, the pan is attached to the pulley with the help of hook. Weight of 1 g was placed on the top of the two slides for 5 min to expel air and to provide a uniform film of gel-cream between the two slides. Known weight was placed in the pan attached to the pulley with the help of hook. The time (in sec) required by the top slide to separate from ground slide was noted. A shorter interval indicates better spreading coefficient. It is calculated by using the formula.
S=M.L/T
Where S is spreadability in g.cm/sec, M is the mass in grams, L is length and T is time in sec.
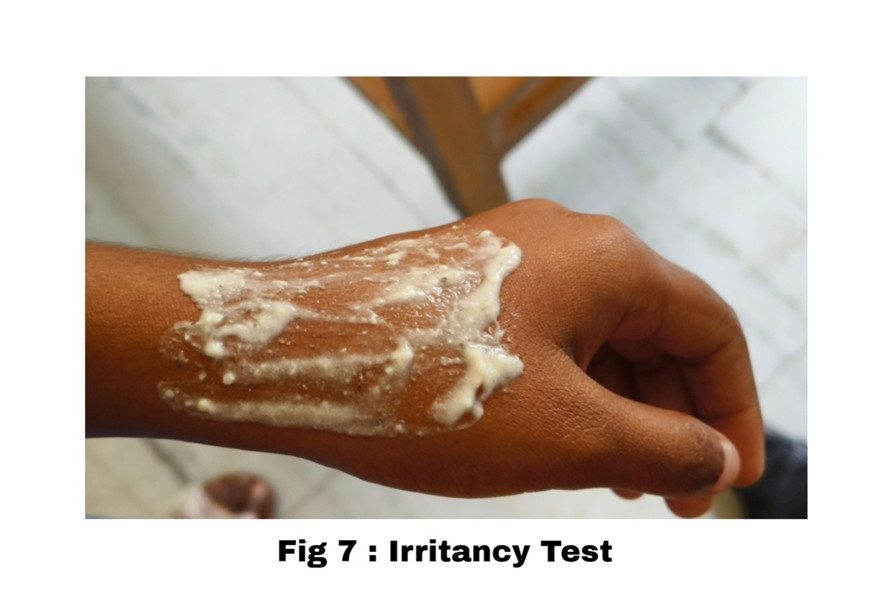
4). Irritancy Test: [22]
Mark an area (1sq.cm) on the left hand dorsal surface. The cream was applied to the specified area and time was noted. Irritancy,erythematic, edema, was checked if any for regular intervals up to 24 hrs.' and reported.
5) Phytochemical Assay of Optimized Gelll-Cream: - [33]
Test For Alkaloids: -
|
S. No
|
Experiment
|
Observation
|
Inference
|
|
1.
|
Mayer's Test:
A Small amount of Extract was treatedy with Mayer's reagent.
|
Gives Cream colour precipitate.
|
presence of Alkaloids.
|
|
2.
|
Dragendra's Test: -
A small amount of Extract was treated with drageudroff's reagent
|
Gives Reddish Brown precipitate
|
presence of Alkaloids.
|
Test For Carbohydrates: -
|
S. No
|
Experiment
|
Observation
|
Inference
|
|
1.
|
Molisch's Test-
The Extract was treated with 2-3 drops of 10% alcoholic &Napthol and 2ml of conc. H2SO4 was added along with the side of the test tube.
|
A purple ring is formed on the upper Layer
|
presence of Carbohydrates.
|
|
2.
|
Fehling's Test: -
The Foctract was treated with Fehling's Soln A & B then heated on a boiling water bath for hay an hr.
|
Red precipitate was obtained.
|
presence of carbohydrates
|
|
S. No
|
Experiment
|
Observation
|
Inference
|
|
1.
|
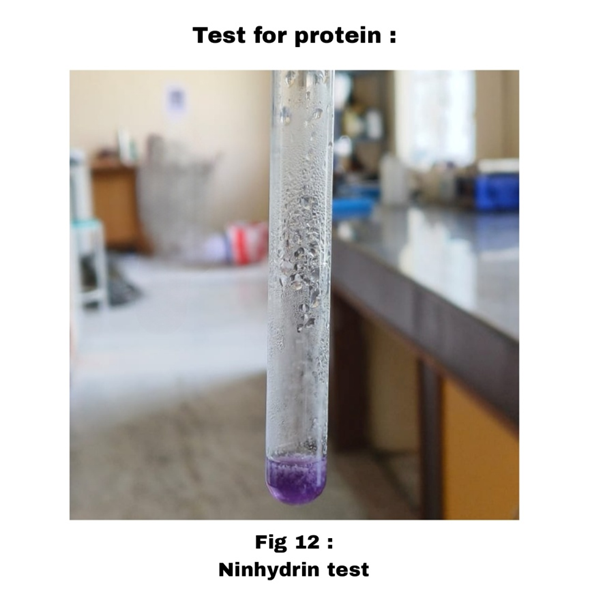
Ninhydrin Test:-
To take small amount of sample and add Ninhydrin Solution and Boil.
|
Violet colour was obtained
|
presence of Protein.
|
|
S. No
|
Experiment
|
Observation
|
Inference
|
|
1.
|
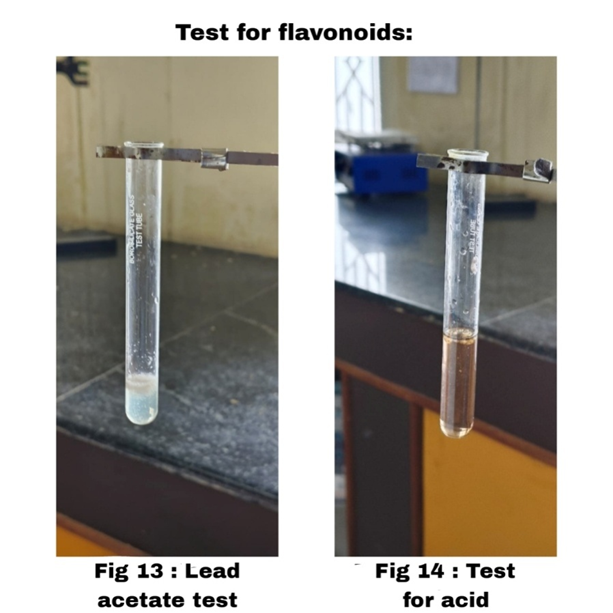
Lead acetate Test: -
Take small amount of sample and add a Lead acetate solution.
|
Gives white precipitate.
|
Presence of Flavonoids
|
|
2.
|
Test for Acid: -
Take small amount of sample and add few drops of conc H? SOH.
|
Yellow Orange colour was a obtained.
|
Presence of Flavonoids
|
Test For Tannins: -
|
S. No
|
Experiment
|
Observation
|
Inference
|
|
1.
|
Ferric chloride Test: -
Take sample extract with H?O then add few drops of Ferric chloride.
|
Bluish Black colour was obtained.
|
presence of Tannins.
|
6). Stability Study:
The optimized herbal gel-cream formulation was tested for stabilityunder two conditions for a period of three months. The gel-cream waskept in polypropylene air tight wide mouth containers and stored in stability chamber maintained at 40°C/75% RH and room temperature. Formulation was evaluated for their physical characteristics, in vitro drug release, content of active ingredient and anti-oxidant activity at the end of 30 days, 60 days and 90 days of storage period.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION: -
Physical Parameter: -
|
Physical
|
Pulp
|
Seed
|
|
Parameters
|
F1
|
F2
|
F3
|
F4
|
F5
|
F6
|
|
Colour
|
Light Pink
|
Light Pink
|
Light Pink
|
Greenish yellow
|
Greenish yellow
|
Greenish yellow
|
|
Odor
|
pleasant
|
pleasant
|
pleasant
|
pleasant
|
Pleasant
|
pleasant
|
|
Consistency
|
Satisfactory
|
Excellent
|
Good
|
Satisfactory
|
Good
|
Excellen
|
|
Homogeneity
|
Homogenous
|
Homogenous
|
Homogenous
|
Homogenous
|
Homogenous
|
Homogenous
|
|
Greasiness
|
Non Greasy
|
Non Greasy
|
Non Greasy
|
Non Greasy
|
Non Greasy
|
Non Greasy
|
|
Grittiness
|
No Grittiness
|
No Grittiness
|
No Grittiness
|
No Grittiness
|
No Grittiness
|
No Grittiness
|
|
Percentage Moisture content.
|
71.2
|
79.5
|
80.5
|
31.0
|
33.4
|
34.4
|
|
water wash ability
|
washable
|
washable
|
washable
|
washable
|
Washable
|
washable
|
All the developed formulations were found to be homogenous non-greasy, non-gritty, light pink & greenish yellow with characteristics odour. The studies showed that F2 and F6 formulation complies with required of Physical parameters and found to be the best among all the batches.
Physical Parameter of Herbal Gel-Cream.
Pharmaceutical parameter Of Herbal Gel-cream-(F1-F6)
All the developed formulations were found to be within the Limits of pharmaceutical Parameter. The F2 & F6 formulation was found to be highest.
|
S. No
|
Formulation code
|
PH
|
viscosity
|
Spreadability
|
|
1.
|
F1
|
5.2
|
2567cp
|
15 sec
|
|
2.
|
F2
|
5.8
|
3010cp
|
10 sec
|
|
3.
|
F3
|
5.6
|
2210cp
|
18 sec
|
|
4,
|
F4
|
5.7
|
271.58cp
|
10 sec
|
|
5.
|
F5
|
5.9
|
271.61cp
|
15 sec
|
|
6.
|
F6
|
6.3
|
270.83cp
|
8 sec
|
Skin Irritation Test:
All these formulation (F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, F6) Shows does not have any sign of Symptoms like redness, itchiness, Swelling, edema, Irritation Occurs at the site of application.
Phytochemical Assay of Gel-Cream:



|
Extract
|
Colour
|
yield
|
Alkaloids
|
Carbohydrates
|
protein
|
Flavonoids
|
Tannins
|
|
Rambutan Pulp Extract
|
Pale pink
|
29.90
|
P
|
P
|
P
|
P
|
P
|
|
Rambutan Seed Extract.
|
Greenish Yellow
|
4.50
|
P
|
P
|
P
|
P
|
P
|
P ? Present A ? Absent
Stability Studies: -
physical parameters of herbal Gel-Cream F2 & F6.
The physical parameters after 0,30th, 60th, day were as mentioned in the table. All the physicalparameters were in the acceptable limits which showed that optimized formulation was stable over the Period of 60 days.
|
Physical Parameter
|
Condition
|
0 Day
|
30th Day
|
60th Day
|
|
Appearance
|
Room Temperature
|
No change
|
No change
|
No change
|
|
PH
|
Room Temperature
|
5.8
|
5.6
|
5.2
|
|
Viscosity
|
Room Temperature
|
3010cp
|
2210cp
|
2567cp
|
The result of the physical parameter stability studies indicated that herbal-gel reasonable stability.
CONCLUSION: -
?Now days aging phenomenon has become one of the main obstacles among people.
?Rambutan pulp Extract (F1, F2, F3) and Rambutan seed extract (F4, F5, F6) was used as main ingredient of antiaging cream.
?Rambutan fruit Includes Alkaloids, Carbohydrates, flavonoids, protein & Tannins that are bioactive compounds which contribute the antiaging activity Beeswax , cetylstearyl alcohol, Liquid paraffin, olive oil, Almond oil, Aloe vera mucilage extract, carbopol 940, Triethanolamine etc,.. constitute the rest part of the cream.
?By changing the concentration of ingredients 6 different formulation were developed. ? From all the results & considerationF2 & F6 is more stable and safe because of its physical parameter, PH, spreadability, viscosity, skin Irritation test & stability study shows excellent results & overcome among the four formulations (F1, F3, F4, F5)
REFERENCES
- Ruta Ganceviciene,Aikaterini i. Liakou, Athanasios Theodoridis, evgenia Makrantonaki and Christos C. Zouboulis, Skin anti-aging strategies July–December 2012
- Anjali Varghese, Ann Maria Devassy, Aswathy V., Bhagyasree S., Anupriya Mahesh FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF ANTI AGEING CREAM FROM HERBAL EXTRACT 26 July 2024
- Zahra Lotfollahi The anatomy, physiology and function of all skin layers and the impact of ageing on the skin 7 March 2024
- Wilfredo Lopez Ojeda; Amarendra Pandey Mandy Alhajj Amanda M. Oakley. Anatomy, skin October 17, 2022
- Golara Honari and Howard Maibach - Skin Structure and Function 2014
- Loyd V. Allen, Jr. Howard C. Ansel – Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms and Drug Delivery Systems TenTh ediTion
- Siddhant Hagavane, Sneha Sonawane, Akshay Katkale, Vishvam Kunde - Review on cream as topical drug delivery system - 21-02-2022
- Mohiuddin AK, Department of Pharmacy, World University of Bangladesh, 151/8, Green Road Dhanmondi, Dhaka – 1205, Bangladesh - Skin Care Creams: Formulation and Use May 20, 2019
- Rohit Kumar Bijauliya, Shashi Alok, Mayank Kumar, Dilip Kumar Chanchal and Shrishti Yadav - A COMPREHENSIVE REVIEW ON HERBAL COSMETICS 28 July, 2017
- Davinder Kumar, Gajendra Rajora, Om Parkash, Himanshu, Mamta Antil, Virender Kumar - Herbal cosmetics: An overview - 4; July 2016
- Jean Krutmann, M.D.a,, Anne Bouloc, M.D., Ph.D.b, Gabrielle Sore, Ph.D.c, Bruno A. Bernard, Ph.D.d, Thierry Passeron, M.D., Ph.D. - The skin aging exposome - 19 September 2016
- M.Swetha1, VT.Iswariya2, K.Maryswarnalatha3, Dr.T.Rama Rao4 - Review article on preparation and evaluation of herbal face cream 2022
- Jayita Roy1, Arna Pal1, Sudipta Chakraborty1, Ayon Haldar1, Malay Biswas1 - Herbal Creams: An Overview - 7; July 2024
- Bianca R. Albuquerque, Jos´ e Pinelaa, Maria Inˆ es Diasa,b, Carla Pereiraa,b, Jovana Petrovi´cd, Marina Sokovi´ cd, Ricardo C. Calhelhaa,b, M. Beatriz P.P. Oliveirac, Isabel C.F.R. Ferreiraa, Lillian Barrosa - Food Research International 2023
- Prakash Chandra Tripathi - Rambutan (Nephelium lappaceum var. lappaceum)
- Bianca R. Albuquerquea,b,c, Jos´ e Pinelaa,b,Maria Inˆ es Diasa,b, Carla Pereiraa,b, Jovana Petrovi´cd, Marina Sokovi´ cd, Ricardo C. Calhelhaa,b, M. Beatriz P.P. Oliveirac, Isabel C.F.R. Ferreiraa, Lillian Barros- Food Research International 2023
- Gursimran Kaur, Muskaan, Nitish Chaudhary and Zorempuii - A review paper on rambutan – 2022
- Dr. Rashmi Shukla Srivastava1 and Khushbu Pravin Shah - Formulation And Evaluation Of Novel Herbal Anti-Ageing Formulation (Gel-Cream) 06 July 2015
- Pounikar J, Jain P, Khurana N, Omray K.L., Patil S, Gajbhiye A. Formulation and characterization of Aloe Vera cosmetic herbal hydrogel. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Science 2012; 4(4): 85-86.
- Vats A, Sharma P. Comparative study and analysis of release kinetics of coriander formulations. Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2013; 3(1): 1334-1348.
- Patel KK, Mehta JN, Dhandhalia CM, Bhanupriy KA, Shastri HD, Shelat KP, Shah BG. Development and evaluation of herbal anti-acne formulation. Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences, 2012; 3(3): 334-339.

 S. Nivetha*
S. Nivetha*


















 10.5281/zenodo.14854758
10.5281/zenodo.14854758