Abstract
A Transdermal patch loaded with drug Enalapril Maleate was developed in order to treat Antihypertension. TDP was formulated by using combination of hydrophilic and hydrophobic polymer by employing Solvent casting Method using TDP/ODF machine. For Optimum formulation patches were generated using Box-Bhenken Design & evaluated for various evaluation parameters such as Thickness, Weight variation , Folding endurance, moisture content, moisture uptake, Drug content & In-Vitro Drug permeation Study (Diffusion) . The data obtained from in vitro diffusion study of TDP-7 is fitted to various mathematical models like zero order, first order, Higuchi and Koresmeyer-peppas model. The results of mathematical model fitting data indicated that, the best fit model for batch TDP-7 was Korsmeyer-Peppas model with highest r' value of (r' = 0.9972).TDP7 was found as optimized batch which shows 85% Drug release for 24 hr. Patch of Enalapril Maleate was passed all evaluation test and shows good % DR within their time.
Keywords
Enalapril maleate, Franz Diffusion cell, TDP/ODF Machine, permeation enhancer
Introduction
Controlled drug delivery system is one which delivers the drug at a predetermined rate, for locally or systemically, for a specified period of time. TDDS are system that utilize skin as a site for continuous drug administration into the systemic circulation. Transdermal patch is a medicated adhesive patch that is placed on the skin to deliver a specific dose ofmedication through the skin and into the bloodstream. The drug initially penetrate through the stratum corneum and then passes through the deeper epidermis and dermis without drug accumulation in the deeper layer. It is a painless method of delivering drugs systematically by applying a drug formulation onto intact and healthy skin. Drug Enalapril maleate act as an Antihypertensive drug which belongs to BCS Class-III. An advantage of a transdermal drug delivery route over other types of medication delivery is that the patch provides a controlled release of medication into patient.
Enalapril maleate, act as antihypertensive drug, in which with the help of ACE inhibitor the Angiotensin I get converted into angiotensin II (peptide hormone that causes the vasoconstriction and increase the blood pressure) where the narrowing of the blood vessels can occure , which result in slowed or blocked the blood flow which causes hypertension. Drug Enalapril maleate causes the ACE inhibition which prevent an enzyme in the body from making angiotensin II and reduce the hypertension.
Materials and Method:
Enalapril Maleate was purchased from Yarrow chem Pvt. Ltd, Mumbai. HPMCK4M, Propylene glycol, Span80 and Methyl Paraben were purchased from Jinendra scientific.
Preparation of Transdermal Patch:
Patch was prepared by using the solvent casting method using TDP/ODF machine. All the ingredient were weighed properly. HPMCK4M was dissolved in water stir using magnetic stirrer for 15-20 min, Span80 as penetration enhancer and propylene glycol as plasticizer are added to the above solution , methyl paraben was heated and add into the HPMCK4M solution .This solution was kept aside for 3-4 hr to remove all the bubbles. Release liner was fix on glass topper of TDP machine ,solution was pour on release liner with the help of dragger and leave for drying after semi drying of solution put the backing membrane after drying , the patch was removed from machine and into 2×2 cm and use for further evaluation.

Fig: 2.1. TDP/ODF Machine used for preparation of patches
Evaluation of Formulated Transdermal Patches of Enalapril Maleate
1. Physical Appearance
All the transdermal patches were visually inspected for colour, clarity, flexibility and smoothness.
2. Thickness
The thickness of the film was measured at three different points using digital thickness gauge and the average thickness was calculated. The experiment was performed in triplicate (n=3)
3. Weight Uniformity
For each formulation, three randomly selected patches were used. For weight variation test, 3 films from each batch were weighed individually and the average weight was calculated.
4. Folding Endurance
Folding endurance of the film was determined by repeatedly folding a small strip of film (2cm x 2cm) at the same place till it broke. The number of times, the film could be folded at the same place without breaking, gave the value of folding endurance.
5. Percentage Moisture Content
The prepared films were weighed individually and kept in a desiccator containing fused calcium chloride at room temperature for 24 hrs. After 24 hrs the films were reweighed and the percentage moisture content was determined by using the given formula.
6. Percentage Moisture Uptake
The weighed films were kept in a desiccator at room temperature for 24 hrs containing saturated solution of potassium chloride in order to maintain 84% RH. After 24 hrs the films were reweighed and the percentage moisture uptake was determined by using the given formula.
7. Drug Content Uniformity
The uniformity of drug content of the transdermal film was determined, based on dry weight of drug and polymer used, by means of a UV/VIS spectrophotometer method. A specified area (2cm?2;) of patch was cut and dissolved in 10 ml of phosphate buffer pH 7.4. Then the solution was transferred in a volumetric flask and the volume made up to 10 ml. Appropriate dilutions were made using phosphate buffer pH 7.4, filtered and analysed for drug content at 290 nm by using UV spectrophotometer and determine the % drug content.
8. In-vitro Drug Permeation Study of Optimized Batches of Transdermal Patches of Enalapril maleate:
In-vitro permeation studies were performed by using a modified Franz diffusion cell with a receptor compartment capacity of 25ml. The treated synthetic cellophane membrane was mounted between the donor and receptor compartment of the diffusion cell. The formulated patches were cut into the size of 4cm?2; and placed over the cellophane membrane and the receptor compartment of the diffusion cell was filled with pH 7.4 phosphate buffer. The whole assembly was placed on a magnetic stirrer with continuously stirred at 50 rpm, the temperature was maintained at 32 ±20C. The samples of 2 ml were withdrawn at a time interval of 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and 24 h, analyzed for drug release by using UV spectrophotometer. The receptor phase was replenished with an equal volume of phosphate buffer at each time of sample withdrawal. Finally, by doing the proper dilutions samples were analysed by using UV-visible spectrophotometer at 226nm. The data treatment for optimized batches was done in the same way as for the preliminary batches.
9. Stability Study
Stability studies were carried out for 30 days at 400c and 75 % RH. The patch were observed for physical ? changes, folding endurance, percentage drug content, percentage drug release and other parameters. TDP of Enalapril maleate were found to be physically and chemically stable and showed no significant change in terms of physical characteristics, formulation TDP7 was stable and retained their original properties with minor differences in drug content, %DR and other parameter which are in acceptable limits.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION:
Preformulation Studies:
Table: 3.1. Organoleptic properties –

Table 3.2. Melting point -By using digital melting point apparatus & DSC
Determination of ?max:
The ultraviolet spectrum was recorded in the range 200 nm to 400 nm, the standard solution (100 µg/ml) of pure drug was prepared in phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) . From the standard solution 2 to 30µ g/ml dilutions were prepared and 10 µg/ml solution was scanned in the range of 200 nm to 400 nm. The solution showed maximum absorbance at 226 nm. At the ?max of 226 nm enalapril maleate was estimated using phosphate buffer (pH 7.4).

Calibration curve of Enalapril maleate:
Result obtained are present in table no.3.3 & fig no 3.2
Table 3.3. Absorbance of different dilution at 226 nm

Fig: 3.2 Calibration curve of Enalapril maleate
Compatibility Study by FTIR :
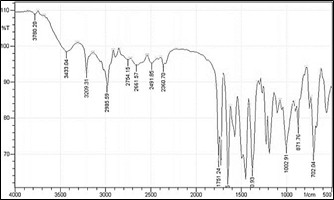
Fig: 3.3.FTIR spectra of Enalapril Maleate

Fig: 3.4. FTIR Spectra of Drug + Excipient
From FTIR studies it was clear that the drug has not undergone any type of structural change or any chemical reaction with the polymers and other excipients used. Therefore it was concluded that in the present investigation there was no interaction of the drug with the polymers or the excipients used.
DSC Thermogram:
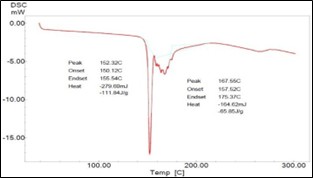
Fig 3.5.DSC Thermogram of Enalapril Maleate
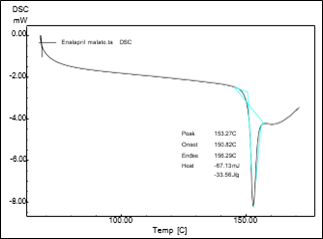
Fig 3.6.DSC Thermogram of Drug +Excipient
Evaluation of Optimized Batches of Transdermal patch: *± SD(n=3)
Result of evaluation parameters are given in table no 3.4
Table No.3.5: % Drug Released of Batches generated by BBD:

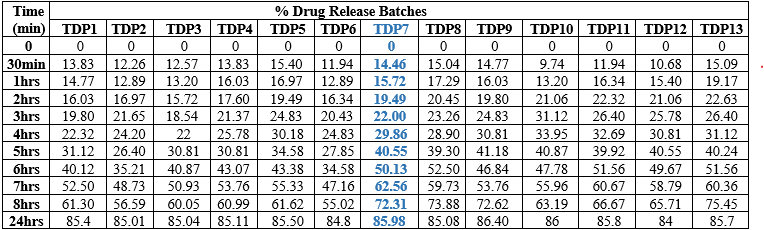
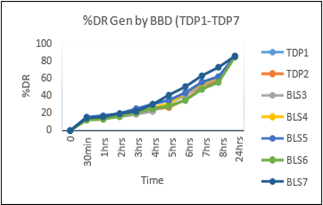
Fig.3.7: In-Vitro Drug Released Study of Optimized Batches of Enalapril maleate Generated by BBD (TDP1-TDP7)
|
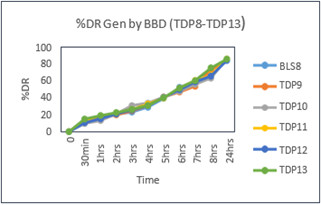
Fig.3.8: In-Vitro Drug Released Study of Optimized Batches of Enalapril maleate Generated by BBD (TDP8-TDP13)
|
Optimization and Data Analysis : (Box-Bhenken Design)
Table No.3.6 : Result of Analysis of Variance for Batches by BBD of Enalapril Maleate TDP
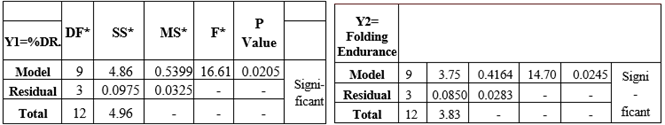
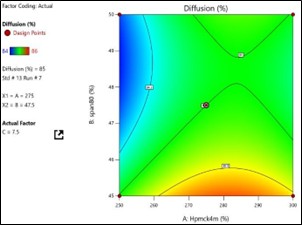
Fig No. 3.9: Response Surface Contour Graph Showing the Influence of HPMC (X1) and PEG Span80 On % Drug Release (Y)
|
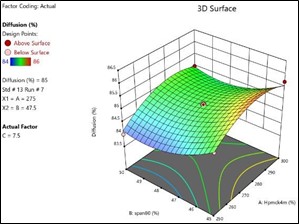
Figure No. 3.10: 3D Response Surface Graph Showing the Influence of HPMC (X1) and Span80 on% Drug Release(Y)
|
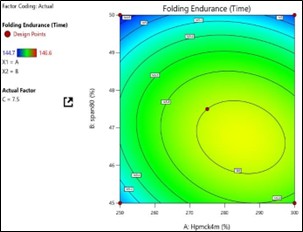
Fig No.3.11: Response Surface Contour Graph Showing the Influence of HPMC (X1) and Span80 on Folding Endurance (Y)
|
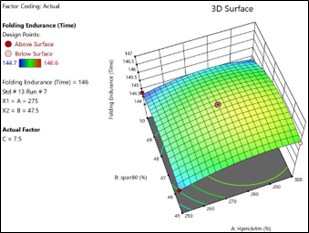
Fig No.3.12: 3D Response Surface Contour Graph Showing the Influence of HPMC (X1) and Span80 On Folding Endurance (Y)
|
The general Box-Behnken design was applied to optimize the TDP of Enalapril Maleate. The response surface methodology analysed data clearly indicate that the % DR, Folding Endurance, values were mainly depending upon the selected independent variables. The regression equations for the responses fitted in quadratic model were generated. ANOVA was used to identify the significant effect. Obtained value of F is larger than critical F-value, the result was found to be significant at that level of probability <0>
Stability Study:
Stability studies were carried out for 30 days at 40°C and 75 % RH. The patch were observed for physical changes, folding endurance, percentage drug content, percentage drug release and other parameters. TDP of Enalapril maleate were found to be physically and chemically stable and showed no significant change in terms of physical characteristics, formulation TDP7 was stable and retained their original properties with minor differences in drug content, %DR and other parameter which are in acceptable limits.
CONCLUSION
The drug was characterized for colour, dour, taste and it matches to the standard value as per melting point of Enalapril Maleate 129.60°C to 158.4°C was found to be 147°C to 154°C by open capillary method and it was found in the standard range. The wavelength of Enalapril Maleate was found 226 nm by using UV Visible Spectrophotometer. The calibration curve showed a linear relationship between concentration and absorbance. It obeys Beer and Lambert's law in the range 5-25 g/ml. The correlation coefficient was 0.9977. The peak obtained by DSC showed the melting point 153.32°C of drug and sharpness of peak indicates the purity of sample. Transdermal patch of enalapril maleate was successfully formulated by using HPMCK4M as polymers and Span80 as penetration enhancer by employing solvent casting method using TDP/ODF Machine. TDP7 was found as optimized batch which shows 85% Drug release for 24 hr. The data obtained from in-vitro diffusion study of batch TDP-7 is fitted to various mathematical models like zero order, first order, Higuchi and Korsemeyer-Peppas model. It is concluded that transdermal patch of enalapril maleate was passed all the evaluation test.
REFERENCE
- M. R. Shivalingam, Arul Balasubramanian, Kothai Ramalingam, Formulation and Evaluation of Transdermal Patches of Pantoprazole Sodium, International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics ISSN- 0975-7058 Vol 13, Issue 5, 2021.
- Suryani, Wa Ode Sitti Musnina, Ruslin, Michrun Nisa, Rima Aprianti, Marganita Hasanah, Firda Rahmania Putri, Andi Nafisah Tendri Adjeng, Nani Yuniar, Muhamad Handoyo Sahumena, Muhammad Aswan, Formulation and Physical Characterization Of Curcumin Nanoparticle Transdermal Patch, International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics , Int J App Pharm, Vol 11, Issue 6, 2019, 217-221.
- Vanessa Raeder, Iro Boura, Valentina Let, Peter Jenner Heinz Reichmann, Claudia Trenkwalder,Lisa Klingelhoefer K. Ray Chaudhuri, Rotigotine Transdermal Patch for Motor and Non-motor Parkinson’s Disease: A Review of 12 Years’ Clinical Experience, CNS Drugs (2021), Published online: 9 February 2021
- Bazigha K. Abdul Rasool , Amira A. Mohammed and Yasmein Y. Salem, The Optimization of Dimenhydrinate Transdermal Patch Formulation Based on the Quantitative Analysis of In Vitro Release Data by DD Solver through Skin Penetration Studies, Scientia Pharmaceutica · July 2021
- Long Mo,a Guijing Lu,a Xiping Ou,a and Dongsheng Ouyang, Formulation and development of novel control release transdermal patches of carvedilol to improve bioavailability for the treatment of heart failure, Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan; 29(1): 266–272.
- Asha Rani M , Lakshmi Csr , Nargund , Design and Evaluation of Quetiapine Fumarate Nanoparticles Loaded Transdermal Patches, International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Research, June 2019 Vol.:15, Issue:3.
- Hemantkumar Bhosale, Pooja Bansude, Vishal Babar and Prajwala Khapale, Design and Evaluation of Polymeric Films (Hpmc) of Enalapril Maleate for Transdermal Use, World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research SJIF Impact Factor 7.523 Volume 7, Issue 3, 1088-1101.
- Priyanka Kriplani, Abhishek Sharma, Aman, Pooja Pun, Bhawna Chopra, Ashwani Dhingra and Geeta Deswal,Formulation and Evaluation of Transdermal Patch of Diclofenac Sodium, Global Journal of Pharmaceutics Sci. 2018.
- Amina L. Mohamed , Heba Elmotasem , Abeer A. A. Salama , Colchicine mesoporous Silica Nano- particles/Hydrogel Composite Loaded Cotton Patches as a New Encapsulator System for Transdermal osteoarthritis management , International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 49-1163 .
- Najmeh Nematpour , Negin Farhadian , Kosar, Elham Arkan a, Faranak Seyedi a, Salar Khaledian a, Mohsen Shahlaei a, Sajad Moradi, Sustained release nanofibrous composite patch for transdermal antibiotic delivery, Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects is an international journal Volume 586, 5 February 2020, 124267.
- Anuradha Patel, Richa Solanki, Saumya Jain, Yuvraj Singh Dangi, Naina Dubey, Formulation, Development and Evaluation of Etoricoxib containing Transdermal patches in Arthritis management, IJRAR- International Journal of Research and Analytical Reviews, VOLUME 5 I ISSUE 4 I OCT – DEC. 2018.
- Jajala Mamatha, Sravya Gadili, Kanagala Pallavi, Formulation and Evaluation of Zidovudine Transdermal Patch using Permeation Enhancers, Journal of Young Pharmacists, Published on:July 2020.
- Nilesh M. Mahajan, Grishma H. Zode , Debarshi Kar Mahapatra, Sonali Thakre , Nitin Dumore , Purushottam S. Gangane1, Formulation development and evaluation of transdermal patch of piroxicam for treating dysmenorrhoea, Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science Vol. 8(11), pp 035-041, November, 2018.
- MayankKumar Malaiya, Ashish Jain, Hurkat Pooja, Anki Jain, Dharmendra Jain, Controlled delivery of rivastigmine using transdermal patch for effective management of alzheimer's disease, Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology Volume 45, June 2018, Pages 408-414 .
- Anroop B. Nair, Sumeet Gupta, Bandar E. Al-Dhubiab, Shery Jacob, Pottathil Shinu, Jigar Shah, Mohamed Aly Morsy, Nagaraja SreeHarsha, Mahesh Attimarad, Katharigatta N. Venugopala, and Sabah H. Akrawi, Effective Therapeutic Delivery and Bioavailability Enhancement of Pioglitazone Using Drug in Adhesive Transdermal Patch, Pharmaceutics ; Published: 23 July 2019
- Sweta Kulkarni, Formulation and Evaluation of Transdermal Patch for Atomoxetine hydrochloride, Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics, Available online 25 April 2019.
- Tamer M. Shehata , Omar M.M. Mohafez, Hamza N. Hanieh ,Pharmaceutical Formulation and Biochemical Evaluation of Atorvastatin Transdermal Patches, Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical Education and Research | Vol 52 | Issue 1 | Jan-Mar, 2018
- Rabinarayan Parhi , Suresh Padilam , In vitro permeation and stability studies on developed drug-in-adhesive transdermal patch of simvastatin, Bulletin of Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo University Volume 56, Issue 1, June 2018, Pages 26-33
- Dharmesh Trivedi, Anju Goyal , Formulation and evaluation of transdermal patches Containing Dexketoprofen Trometamol, International Journal of Pharmaceutical Chemistry and Analysis, Received 25-05-2020 Accepted 04-06-2020.
- Rao Monica, Sonavne Vijay, Kulkarni Sayali , Magar Mayuri, Zope Abhishek, Karanjkar Transdermal Patch of Ketoprofen by Full Factorial Design For Rheumatoid Arthritis, Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics Accepted 09 March 2019; Available Online 15 March 2019.

 Reema J Jagnit *
Reema J Jagnit *
 M. M. Bari
M. M. Bari
 S D. Barhate
S D. Barhate
 Yogesh Sonawane
Yogesh Sonawane
 Abhay Sawant
Abhay Sawant


















 10.5281/zenodo.13193974
10.5281/zenodo.13193974