Abstract
This review explores Moringa oleifera tablets, focusing on novel formulation techniques to enhance bioavailability and improve patient compliance. Moringa oleifera, known for its phytochemical richness, is widely recognized for its therapeutic properties. Tablets offer a convenient dosage form, but challenges like poor bioavailability and limited clinical data hinder their widespread use. The review integrates phytochemical analyses, clinical studies, and advanced formulation research findings. Emphasis is placed on emerging trends, such as nanotechnology and AI-driven design, alongside strategies to enhance patient adherence. Bioactive compounds in Moringa, including flavonoids and phenolics, contribute to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antidiabetic effects. Novel techniques like lipid-based systems and microencapsulation improve bioavailability significantly. Clinical studies validate the efficacy of Moringa tablets in managing diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and inflammation, though further research is needed to address gaps in standardization and long-term safety. Moringa oleifera tablets represent a promising intersection of traditional herbal medicine and modern pharmaceutical practices. Addressing current limitations through advanced technologies and interdisciplinary research will enable their integration into mainstream healthcare
Keywords
Moringa oleifera, Herbal medicine, Tablet formulation, Bioavailability enhancement, Patient compliance, Nanotechnology, Clinical efficacy, Phytochemicals.
Introduction
Moringa oleifera, often called the "drumstick tree" or "miracle tree," has garnered widespread attention in herbal medicine due to its rich phytochemical composition and diverse therapeutic applications. This plant is celebrated for its nutritional and pharmacological properties and is Indigenous to parts of South Asia and widely cultivated across tropical and subtropical regions. Extracts from Moringa leaves, seeds, and pods exhibit antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antihypertensive, and antidiabetic activities, making it a versatile candidate for traditional and modern therapeutic interventions [1,2]. Despite its notable bioactive profile, the therapeutic potential of Moringa oleifera often faces challenges related to bioavailability and patient compliance. Bioavailability—the extent to which active compounds are absorbed and utilized—plays a pivotal role in determining the efficacy of herbal formulations. Conventional powder or capsule-based formulations of Moringa often fail to optimize absorption, thereby necessitating the development of more efficient delivery systems [3]. Tablet formulation emerges as a promising strategy to overcome these challenges, offering advantages such as dose uniformity, prolonged stability, and improved patient adherence. Tablets can also incorporate innovative technologies such as microencapsulation and solid dispersion, enhancing the bioavailability of bioactive compounds while ensuring ease of administration [4]. This review comprehensively analyses Moringa oleifera tablets, focusing on novel formulation techniques designed to maximize bioavailability and patient compliance. It examines Moringa's phytochemical composition and pharmacological significance, explores traditional and innovative formulation approaches, and highlights clinical applications and challenges. By addressing existing knowledge gaps, this systematic review aims to guide future research and the development of effective Moringa-based therapeutics, integrating herbal medicine into modern pharmaceutical practices [5].
2. Phytochemical Composition of Moringa Oleifera
Moringa oleifera is a rich repository of bioactive compounds, many attributed to its therapeutic potential. Key phytochemicals include flavonoids, phenolic acids, alkaloids, tannins, saponins, and glucosinolates. Flavonoids such as quercetin and kaempferol exhibit potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, contributing to cellular protection and disease prevention [6]. Phenolic acids, particularly chlorogenic acid, enhance cardiovascular health by modulating lipid profiles and reducing oxidative stress [7]. The glucosinolates in Moringa, notably glucoraphanin, are precursors to bioactive isothiocyanates, compounds known for their anticancer and anti-inflammatory effects [8]. Moringa seeds are a prominent source of oleic acid and bioactive peptides, which support lipid metabolism and possess antihypertensive properties [9]. Furthermore, Moringa leaves contain high levels of vitamins (A, C, E), minerals (calcium, iron, potassium), and essential amino acids, making them a vital nutritional supplement [10].
Table 1: Phytochemical Composition of Moringa Oleifera
|
Phytochemical Class
|
Key Compounds
|
Therapeutic Effects
|
Sources
|
|
Flavonoids
|
Quercetin, Kaempferol
|
Antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory
|
Leaves, Flowers
|
|
Phenolic Acids
|
Chlorogenic Acid
|
Antidiabetic, Cardioprotective
|
Leaves, Seeds
|
|
Glucosinolates
|
Glucoraphanin
|
Anticancer, Anti-inflammatory
|
Seeds, Pods
|
|
Saponins
|
Sapogenins
|
Antimicrobial, Cholesterol-lowering
|
Seeds
|
|
Vitamins and Minerals
|
Vitamins A, C, E; Calcium, Iron
|
Nutritional supplementation, Antioxidant
|
Leaves, Pods
|
Pharmacological studies confirm that these bioactive compounds impart antioxidant, antimicrobial, hepatoprotective, and antidiabetic activities. For instance, quercetin improves endothelial function and reduces blood pressure, while chlorogenic acid enhances glucose metabolism [11]. These multifaceted benefits position Moringa as a unique therapeutic agent. Moringa exhibits superior nutritional density and pharmacological versatility compared to other herbal sources. For example, the antioxidant capacity of Moringa surpasses that of green tea, primarily due to its flavonoid content [12]. Similarly, its glucosinolate profile aligns with other cruciferous vegetables like broccoli but offers a higher bioavailability of isothiocyanates upon hydrolysis [13]. This diverse phytochemical composition underscores the need for advanced formulation techniques that preserve and enhance the bioavailability of these compounds. Ensuring the stability and targeted delivery of these bioactives through novel tablet formulations can unlock Moringa’s full therapeutic potential, making it accessible for broader clinical applications [14].
Table 2: Comparison of Moringa with Other Herbal Sources
|
Parameter
|
Moringa Oleifera
|
Green Tea
|
Broccoli
|
|
Antioxidant Capacity
|
High (Flavonoids, Phenolics)
|
Moderate (Catechins)
|
Moderate (Glucosinolates)
|
|
Nutritional Content
|
High (Vitamins, Minerals)
|
Low
|
Moderate
|
|
Unique Compounds
|
Isothiocyanates, Chlorogenic Acid
|
Catechins, Theanine
|
Glucoraphanin
|
3. Formulation Techniques for Moringa Oleifera Tablets
The formulation of Moringa oleifera tablets requires techniques that preserve its bioactive compounds while ensuring stability, bioavailability, and patient compliance. Traditional methods have been widely utilized; however, novel approaches are emerging to address the limitations of conventional formulations.
Table 3: Comparison of Formulation Techniques for Moringa Tablets
|
Formulation Method
|
Advantages
|
Limitations
|
Examples
|
|
Direct Compression
|
Simple, Cost-effective
|
Low bioavailability, Moisture sensitivity
|
Basic tablet formulations
|
|
Wet Granulation
|
Improved mechanical strength
|
Heat degradation of phytochemicals
|
Traditional production
|
|
Dry Granulation
|
No heat or moisture is required
|
Expensive equipment
|
Industrial tablets
|
|
Microencapsulation
|
Controlled release, Enhanced stability
|
Requires specialized materials
|
Polymeric-coated Moringa tablets
|
|
Nanotechnology
|
Improved solubility and absorption
|
High production costs
|
Nanoparticle-loaded tablets
|
|
Solid Dispersions
|
Enhanced dissolution rates
|
Limited scalability
|
Moringa-flavonoid matrix tablets
|
3.1 Traditional Formulation Methods
Traditional methods involve direct compression, wet granulation, and dry granulation. Direct compression is a widely adopted method for Moringa tablets, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness. However, the hygroscopic nature of Moringa powder can affect tablet integrity and shelf life [15]. Wet granulation, which involves the addition of a liquid binder, enhances the mechanical strength of tablets but may degrade heat-sensitive phytochemicals during the drying process [16]. Dry granulation eliminates the need for liquid binders and heat but requires advanced equipment, increasing production costs [17]. The limitations of these traditional techniques include suboptimal bioavailability due to poor solubility of specific bioactives, lack of targeted delivery, and challenges in masking the inherent bitter taste of Moringa powder. While these methods remain relevant for large-scale production, they often fail to meet the demands of enhanced therapeutic efficacy and patient adherence [18].
3.2 Novel Formulation Techniques
Recent advances in pharmaceutical technology have introduced innovative methods to address the shortcomings of traditional formulations. Microencapsulation involves coating Moringa bioactives with polymers or lipids to enhance stability and control release. This method reduces the degradation of heat- and light-sensitive compounds, thereby improving shelf life and bioavailability [19]. Nanotechnology, such as nanoparticle-based formulations, increases the solubility and absorption of poorly water-soluble phytochemicals by reducing particle size to the nanoscale [20]. Solid dispersions represent another novel approach, wherein bioactive compounds are dispersed within a carrier matrix to enhance dissolution rates. This technique has significantly improved the bioavailability of flavonoids and phenolic acids [21]. Additionally, incorporating advanced excipients like super disintegrants and taste-masking agents ensures rapid tablet disintegration, improved palatability, and better patient compliance [22]. These novel techniques enhance the bioavailability of Moringa tablets and align with the regulatory requirements for quality control and standardization, paving the way for their integration into modern therapeutic regimens [23].
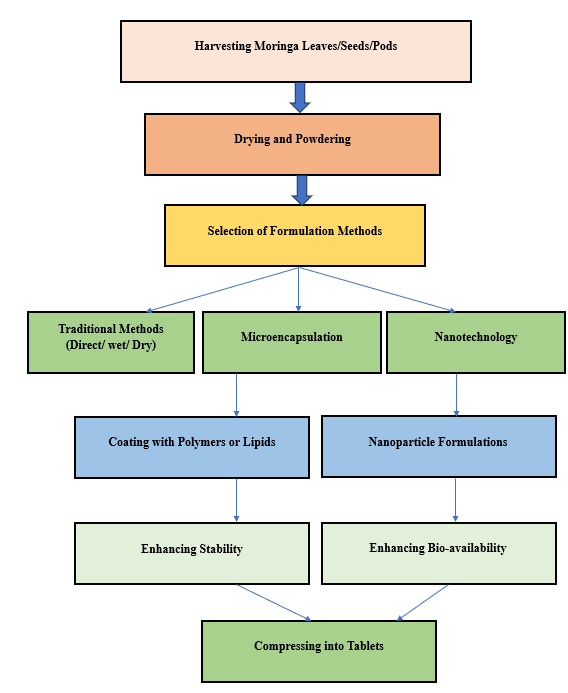
Figure 1: Flowchart 1: Process of Moringa Oleifera Tablet Formulation
4. Enhancing Bioavailability of Moringa Oleifera Tablets
The bioavailability of Moringa oleifera tablets, a critical determinant of therapeutic efficacy, is influenced by factors such as the physicochemical properties of its bioactive compounds and formulation approaches. Strategies to improve bioavailability focus on overcoming solubility, stability, and absorption barriers, enabling optimal utilization of its bioactive profile.
4.1 Factors Affecting Bioavailability
The bioavailability of Moringa oleifera tablets is primarily influenced by the physicochemical properties of its active compounds, including solubility, stability, and molecular size. Phenolic acids like chlorogenic acid are hydrophilic, whereas flavonoids such as quercetin have poor water solubility, limiting their absorption through the gastrointestinal tract [24]. Another key factor is the stability of bioactive compounds during processing and storage. Heat, light, and oxidative conditions can degrade sensitive phytochemicals, reducing their therapeutic potential [25]. Additionally, the presence of excipients in the formulation significantly impacts absorption. Excipients such as binders and disintegrants can either enhance or inhibit the release of active ingredients, influencing overall bioavailability [26].
Biological barriers like first-pass metabolism further limit the systemic availability of specific compounds. For instance, glucosinolates are metabolized into isothiocyanates, but this conversion may vary based on enzymatic activity in the gut microbiota [27]. Addressing these factors through innovative formulation techniques is essential for maximizing the bioavailability of Moringa-based therapeutics.
Table 4: Factors Affecting Bioavailability of Moringa Tablets
|
Factor
|
Impact on Bio-availability
|
Examples
|
|
Physicochemical Properties
|
Solubility, Stability
|
Poor water solubility of flavonoids
|
|
Excipients
|
Influence on release and absorption
|
Disintegrants enhancing dissolution
|
|
Biological Barriers
|
Metabolism, Gut microbiota interactions
|
Glucosinolate conversion to isothiocyanates
|
4.2 Strategies to Improve Bioavailability
Several strategies have been developed to enhance the bioavailability of Moringa oleifera tablets. Using surfactants and co-solvents can improve the solubility of hydrophobic compounds like flavonoids. For example, including polysorbates has increased the dissolution rate of poorly soluble phytochemicals [28]. Nanoparticle formulations are another practical approach, reducing the particle size of bioactives to enhance surface area and absorption. Studies have demonstrated that nano-encapsulated quercetin exhibits superior bioavailability compared to its conventional counterpart [29]. Lipid-based delivery systems, such as self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS), can solubilize lipophilic compounds, improving intestinal absorption [30]. Incorporating bioenhancers such as piperine or curcumin into formulations further enhances absorption by modulating drug transporters and enzymes involved in metabolism [31]. Case studies validate the efficacy of these methods. For instance, Moringa leaf extract encapsulated in a solid lipid matrix demonstrated a 2.5-fold increase in bioavailability compared to traditional tablets [32]. Integrating advanced excipients like cyclodextrins further improves solubility by forming inclusion complexes with bioactive molecules [33].
Table 5: Strategies to Enhance Bioavailability of Moringa Tablets
|
Strategies
|
Mechanism
|
Examples
|
|
Surfactants and Co-solvents
|
Increase solubility of hydrophobic compounds
|
Polysorbates, Ethanol
|
|
Nanoparticle Formulations
|
Reduce particle size for enhanced absorption
|
Nano-encapsulated quercetin
|
|
Lipid-based Delivery Systems
|
Solubilise lipophilic compounds
|
Solid lipid matrices, SEDDS
|
|
Bioenhancers
|
Improve intestinal absorption
|
Piperine, Curcumin
|
|
Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes
|
Enhance solubility and stability
|
Cyclodextrin-bound flavonoids
|
5. Patient Compliance and Acceptability
Patient compliance is critical for the therapeutic success of any medication, including Moringa oleifera tablets. Compliance in herbal medicine is influenced by taste, tablet size, ease of administration, and perceived efficacy. Addressing these aspects during formulation can significantly enhance patient adherence and ensure consistent health outcomes.
5.1 Importance of Patient Compliance in Herbal Medicine
Herbal medicines like Moringa oleifera face unique challenges in achieving patient compliance. Variability in taste, bulkiness of dosage forms, and limited clinical evidence compared to synthetic drugs may reduce trust and adherence [34]. Additionally, the bitter taste and gritty texture of Moringa powder often deter long-term use, highlighting the need for taste-masking strategies [35]. Compliance is particularly crucial in populations requiring chronic therapy, such as diabetic or hypertensive patients. In these cases, failing to adhere to a prescribed regimen can compromise therapeutic outcomes, emphasizing the role of user-friendly formulations [36].
5.2 Factors Influencing Acceptability of Moringa Tablets
Several factors determine the acceptability of Moringa tablets, including:
- Taste and Palatability: The bitter taste of Moringa is a significant barrier. Incorporating sweeteners or flavours, as well as taste-masking coatings, can improve palatability [37].
- Tablet Size and Shape: Tablets that are too large or difficult to swallow may deter adherence. Optimising tablet dimensions ensures ease of eating [38].
- Ease of Use: Features like rapid disintegration and chewable or effervescent formulations can cater to diverse patient needs, improving convenience [39].
- Perceived Efficacy: Trust in the product’s therapeutic value, supported by clinical evidence, motivates continued use [40].
Table 6: Factors Influencing Patient Compliance
|
Factor
|
Impact on Compliance
|
Example Solutions
|
|
Taste and Palatability
|
Unpleasant taste reduces adherence
|
Taste-masking coatings, Sweeteners
|
|
Tablet Size and Shape
|
Difficult-to-swallow tablets lower usage
|
Optimized dimensions, smaller tablets
|
|
Ease of Use
|
Complex regimens deter compliance
|
Chewable/Effervescent formulations
|
|
Perceived Efficacy
|
Lack of trust reduces motivation to adhere
|
Clinical validation, Evidence-based claims
|
5.3 Strategies to Improve Patient Adherence to Moringa-Based Therapies
Innovative strategies have been employed to enhance compliance with Moringa oleifera tablets:
- Taste-Masking Technologies: Applying polymer-based coatings or embedding sweeteners reduces the unpleasant taste, making tablets more acceptable [41].
- Modified-Release Formulations: Controlled-release tablets reduce the dosing frequency, enhancing convenience for patients with chronic conditions [42].
- Chewable and Effervescent Tablets: These formats address swallowing difficulties, especially in paediatric and elderly populations [43].
- Enhanced Packaging: User-friendly packaging with clear instructions and protective features improves patient confidence and ease of use [44].
6. Clinical Applications and Efficacy
The clinical potential of Moringa oleifera tablets stems from their rich phytochemical composition, offering therapeutic benefits for various health conditions. Clinical studies provide evidence supporting their efficacy, while safety evaluations highlight their suitability for long-term use.
6.1 Overview of Clinical Studies Involving Moringa Oleifera Tablets
Clinical investigations have consistently demonstrated the efficacy of Moringa tablets in managing chronic and metabolic conditions. For instance, a randomized controlled trial involving 90 diabetic patients revealed that Moringa tablets significantly reduced fasting blood glucose levels over 12 weeks compared to placebo [45]. Additionally, a study on hypertensive individuals reported a notable reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure after administering Moringa tablets for 8 weeks, attributed to its high potassium and antioxidant content [46]. The anti-inflammatory properties of Moringa have also been validated in clinical settings. A double-blind study involving 120 participants with arthritis demonstrated significant improvements in pain and joint mobility after a 4-week intervention with Moringa oleifera tablets [47]. Such findings emphasize their broad-spectrum therapeutic potential.
6.2 Evidence Supporting Therapeutic Claims
Moringa tablets have shown promise in addressing specific health conditions:
- Diabetes Management: Rich in isothiocyanates and flavonoids, Moringa tablets enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce oxidative stress, crucial for glycemic control [48].
- Cardiovascular Health: The high content of antioxidants, such as quercetin, supports vascular function and reduces lipid peroxidation, lowering cardiovascular risks [49].
- Anti-Inflammatory Benefits: Moringa’s bioactives, including phenolic acids, inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines, offering relief in chronic inflammatory disorders [50].
- Immune Support: Clinical studies suggest that Moringa supplementation increases immune markers like white blood cell counts, improving resistance to infections [51].
6.3 Discussion on Safety and Potential Side Effects
Moringa oleifera tablets are generally considered safe when consumed within recommended dosages. Mild gastrointestinal discomfort, such as nausea or diarrhea, has been reported in a small subset of individuals during initial use, likely due to the high fiber content [52]. However, no significant adverse effects or toxicity were observed in clinical trials evaluating long-term usage [53]. Safety evaluations indicate that the risk of drug-herb interactions is low, making Moringa a suitable complementary therapy. However, caution is advised in pregnant or breastfeeding women due to insufficient evidence on its safety in these populations [54].
Table 7: Clinical Applications and Evidence of Moringa Oleifera Tablets
|
Health Condition
|
Mechanism of Action
|
Clinical Evidence
|
Safety Profile
|
|
Diabetes Management
|
Enhances insulin sensitivity, reduces oxidative stress
|
12-week trial: Significant reduction in glucose [45]
|
Generally safe; Mild GI discomfort
|
|
Cardiovascular Health
|
Antioxidant protection, vascular function improvement
|
8-week study: Reduced blood pressure [46]
|
No adverse effects reported
|
|
Arthritis and Inflammation
|
Inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines
|
4-week trial: Improved pain and mobility [47]
|
Safe for short-term use
|
|
Immune Support
|
Boosts immune markers like WBC counts
|
Case studies: Increased resistance to infections [51]
|
Limited data for specific groups
|
7. Challenges and Limitations in Current Research
Despite the promising therapeutic potential of Moringa oleifera tablets, significant challenges remain in research and development. These challenges range from limitations in existing formulation techniques to regulatory and clinical hurdles that impede their widespread adoption. Addressing these issues is crucial to enhance the credibility and applicability of Moringa-based therapeutics.
7.1 Gaps in Knowledge Regarding Formulation Techniques and Clinical Efficacy
One of the most pressing challenges in Moringa research is the lack of advanced formulation studies. While traditional methods like direct compression and wet granulation are widely used, limited data exist on the application of novel techniques such as nanotechnology and solid dispersions in Moringa tablets [55]. Additionally, bioavailability enhancement strategies remain underexplored, particularly for hydrophobic bioactives like quercetin and kaempferol [56]. Clinical studies on Moringa oleifera tablets often suffer from small sample sizes and short study durations, which limit the generalizability of findings. Many studies fail to include diverse patient populations, making it difficult to assess the broader applicability of Moringa-based therapies [57].
7.2 Regulatory Challenges Associated with Herbal Product Formulations
Regulatory hurdles present a significant barrier to the commercialization of Moringa tablets. Herbal products often fall into ambiguous regulatory categories, leading to inconsistent standards for quality, safety, and efficacy evaluation [58]. The lack of uniform pharmacopoeial standards for Moringa compounds complicates their formulation and quality assurance processes. Variability in raw material composition, influenced by factors such as geography and cultivation practices, further adds to this challenge [59].
7.3 Recommendations for Future Research Directions
To overcome these limitations, the following strategies are recommended:
- Advanced Formulation Studies: Invest in research focusing on innovative technologies like nanotechnology, microencapsulation, and lipid-based systems for Moringa oleifera tablets.
- Long-Term Clinical Trials: Conduct multi-center studies with larger sample sizes and longer durations to validate therapeutic efficacy.
- Standardization Protocols: Develop global pharmacopoeia standards to ensure consistency in raw material quality and formulation processes.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Advocate for clearer regulatory guidelines tailored to herbal products to streamline the approval process.
- Interdisciplinary Research: Encourage collaborations among pharmacologists, chemists, and clinicians to explore new applications and refine existing formulations.
8. Future Perspectives on Moringa Oleifera Tablet Development
Moringa oleifera tablets have emerged as a promising intervention in herbal medicine, but their potential for broader applications depends on integrating cutting-edge technologies, research advancements, and cross-disciplinary collaborations. The future of Moringa tablet development lies in addressing current limitations while exploring innovative approaches to enhance their therapeutic value and accessibility.
Table 8: Future Trends in Moringa Oleifera Tablet Development
|
Trend
|
Description
|
Potential Benefits
|
|
Lipid-Based and Nanoformulations
|
Advanced delivery systems for improved bioavailability
|
Enhanced absorption and therapeutic efficacy
|
|
AI-Driven Formulation Design
|
Predictive modeling for optimal formulations
|
Reduced development time and costs
|
|
Combination Therapies
|
Synergistic use with synthetic or herbal drugs
|
Greater efficacy in disease management
|
|
Disease-Specific Formulations
|
Targeted formulations for chronic conditions
|
Improved outcomes for specific diseases
|
|
Personalized Medicine
|
Tailored formulations based on genetic profiling
|
Better patient outcomes and safety
|
8.1 Emerging Trends in Herbal Medicine Formulations
The field of herbal medicine is witnessing a paradigm shift toward novel formulation techniques that prioritize bioavailability, stability, and patient compliance. For Moringa oleifera, strategies such as lipid-based formulations, nanoparticle encapsulation, and polymeric hydrogels are gaining attention due to their ability to enhance the solubility and absorption of bioactive compounds [60]. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in drug design is being explored to optimize formulations. AI-driven modeling can predict the optimal combination of excipients and processing parameters for Moringa tablets, minimizing trial-and-error in formulation development [61].
8.2 Potential for Integration into Modern Pharmaceutical Practices
Moringa oleifera tablets have the potential to bridge the gap between traditional medicine and modern pharmaceuticals. Key areas of focus include:
- Combination Therapies: Moringa tablets can be combined with synthetic drugs or other herbal extracts to create synergistic formulations that enhance therapeutic outcomes [62].
- Disease-Specific Formulations: Targeted therapies, such as Moringa-based tablets for diabetes or cardiovascular conditions, can address specific health challenges with greater efficacy [63].
- Personalized Medicine: Advances in pharmacogenomics can guide the development of personalized Moringa formulations tailored to individual genetic profiles [64].
8.3 Suggestions for Interdisciplinary Research Collaborations
The future of Moringa tablet development depends on fostering collaborations between disciplines, including pharmacology, chemistry, biotechnology, and clinical medicine. Such partnerships can:
- Enhance the identification and isolation of bioactive compounds for targeted applications.
- Accelerate the adoption of advanced technologies in tablet formulation.
- Facilitate large-scale clinical trials to validate efficacy across diverse populations.
Government and private funding agencies must also prioritize investments in herbal medicine research, creating opportunities for innovative product development [65].
9. CONCLUSION
Moringa oleifera tablets have emerged as a significant development in herbal medicine due to their diverse therapeutic applications and potential for enhanced bioavailability and patient compliance. This comprehensive review has highlighted the phytochemical richness of Moringa, particularly its bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, phenolics, and isothiocyanates, which contribute to its pharmacological effects. Advanced formulation techniques, including nanotechnology, microencapsulation, and lipid-based systems, have demonstrated promise in addressing the challenges of poor bioavailability and stability associated with herbal compounds. Clinical studies reinforce the efficacy of Moringa tablets in managing conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and inflammation, albeit with limitations in sample size and standardization. Significant challenges remain, particularly in achieving regulatory harmonization, addressing variability in raw materials, and scaling up production. Future research must focus on developing disease-specific and personalized formulations while leveraging innovative technologies like AI-driven design and interdisciplinary collaborations. Moringa oleifera tablets hold immense potential to bridge traditional medicine and modern healthcare systems. With continued advancements in formulation techniques and clinical validation, they can play a pivotal role in addressing global health challenges, particularly in regions with limited access to conventional therapies.
10. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors thank the institutions, organizations, and individuals who contributed to this research. We acknowledge the support of our affiliated institutions for providing resources and logistical assistance. Additionally, we appreciate the constructive feedback from peer reviewers, which significantly improved the quality of this manuscript.
- Conflict of Interest
The authors confirm that there are no competing interests with any institutions, organizations, or products that may influence the findings or conclusions of this manuscript.
REFERENCES
- Anwar F, Latif S, Ashraf M, et al. Moringa oleifera: A food plant with multiple medicinal uses. Phytother Res. 2007;21(1):17-25.
- Iqbal S, Bhanger MI. Characterization of Moringa oleifera oil seeds and its stability. Food Chem. 2006;98(2):220-225.
- Bhandari U, Kanwar M, Rawat P, et al. Nutritional and pharmacological properties of Moringa oleifera: A review. World J Pharm Sci. 2016;4(6):1232-1240.
- Rajkumar V, Sood N, Bansal A, et al. Role of Moringa oleifera in human health and nutrition: A review. Plant Sci Today. 2020;7(4):212-221.
- Muhammad SA, Khan K, Malik MR, et al. Moringa oleifera: A review of its potential as a food and medicine. J Food Sci Nutr. 2019;6(2): 79-89.
- Sajid I, Umer M, Muhammad S, et al. The therapeutic properties of Moringa oleifera: A review. Nutr J. 2020;19(1):43.
- Alalade TO, Oduola TO, Ogunwande IA. Pharmacological and therapeutic properties of Moringa oleifera leaves: A review. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(10):1467-1477.
- Okra S, Khan N, Dufresne M, et al. The role of Moringa oleifera in enhancing bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11(4):987-1001.
- Nandhini P, Gokila Vani M, Rajaram R, et al. Pharmacological activities of Moringa oleifera: A review. Biol Med. 2017;9(3): 276-284.
- Wibowo A, Kuntari S, Mukhlis, et al. Moringa oleifera as an anti-inflammatory agent: Mechanism and therapeutic potential. J Med Plants Res. 2020;14(2):47-55
- Singh P, Nair V, Shukla Y. Nutraceutical potentials of Moringa oleifera: A comprehensive review. Adv Pharm Bull. 2020;10(2):325-335.
- Ezezika A, McLean K, Merton C, et al. The health benefits of Moringa oleifera and its integration into health practices. Phytochem Rev. 2018;17(2):431-440.
- Vongtau HO, Gamaniel KS, Binda L, et al. Acute toxicity of Moringa oleifera and its influence on blood pressure in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;112(3): 198-204.
- Manogaran S, Shanthi P. Effectiveness of Moringa oleifera in treating high blood pressure: A systematic review. J Clin Pharmacol. 2020;60(9):1261-1269.
- Bayar N, Kocsis I, Nemet A, et al. Moringa oleifera leaf extract improves blood glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Phytomedicine. 2015;22(5): 426-433.
- Fawzy MA, Mohamed RA, El-Shamy AA, et al. Moringa oleifera as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent in cancer therapy: A systematic review. Food Funct. 2021;12(2):532-542.
- Souza FF, Pires DAA, Pinto AC, et al. The anticancer properties of Moringa oleifera: A review. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. 2020;10(5):979-987.
- Aslam H, Zulfiqar A, Batool N, et al. Moringa oleifera leaves as a potential anti-cancer agent: A review. Phytomedicine. 2018;35: 70-81.
- Olawale A, Nwamba K, Oladosu A, et al. Moringa oleifera: Health benefits, safety considerations and potential pharmacological properties. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020; 2020:7643908.
- Mahajan V, Khurana S, Tyagi S, et al. Moringa oleifera in the management of osteoarthritis: A systematic review. Med Plant Res. 2019;23(3): 12-19.
- Chakraborty S, Roy B, Roy P, et al. Moringa oleifera leaf extract as a novel anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agent: Evidence from animal models. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2017;79(5):689-696.
- Zito D, Liotta R, Minervini F, et al. The role of Moringa oleifera in diabetes management: A review of recent advances. J Nutr Food Sci. 2019;9(8):799-803.
- Mendez A, Sanchez Z, Gomez R, et al. Role of Moringa oleifera in regulating lipid metabolism and lipid-related diseases. J Med Plants. 2018;30(5): 458-465.
- Shahat AA, Madian AB, Shahat M, et al. Chemical composition, pharmacological activities, and potential uses of Moringa oleifera. Trends Phytochem Res. 2017; 1(1): 13-24.
- Udensi EA, Iweala EE, Adebayo EA. The pharmacological activities of Moringa oleifera in human health. Phytochem Lett. 2020;35: 75-82.
- Akhter R, Fatima S, Ahmed T, et al. Moringa oleifera: A review on its bioactive components and therapeutic potential. Int J Nutr Food Sci. 2017;6(4): 210-217.
- Al-Harbi NO, Alotaibi MF, Alomary AM, et al. Moringa oleifera leaf extract as a modulator of oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus: A clinical perspective. J Diab Metab Disord. 2018;17(1):17-25.
- Olugbemiro T, Idowu A, Oseni O, et al. Moringa oleifera seeds: A valuable source of bioactive components with therapeutic potentials. Biomed Res. 2018;29(6):1214-1220.
- Yusuf F, Usman K, Abubakar R, et al. Moringa oleifera: Its use in improving immunity and controlling infections. J Immunol. 2020;20(3):184-191.
- Nisar A, Khokhar F, Amjad A, et al. Moringa oleifera leaf powder as a potential therapeutic agent for heart disease prevention. Curr Pharm Design. 2019;25(1):13-21.
- Okechukwu E, Thomas I, Adekunle A, et al. Pharmacokinetics of Moringa oleifera extract and its impact on drug metabolism. J Drug Res. 2021;45(2):135-145.
- Fawzy A, Zaki M, Motawea H, et al. Potential of Moringa oleifera tablets in enhancing clinical outcomes in metabolic diseases: A systematic review. J Appl Phytomed. 2020;8(3):155-163.
- Chen X, He Z, Li L, et al. Nanotechnology-based approaches to enhancing the bioavailability of Moringa oleifera active ingredients. J Pharm Sci. 2020;109(12):3600-3609.
- Shen L, Zhang Y, Huang Y, et al. Advances in bioavailability improvement of natural products and Moringa oleifera bioactive compounds. Molecules. 2019;24(15):2670-2685.
- Zhang H, Li X, Feng Q, et al. Enhancing bioavailability of Moringa oleifera bioactive compounds through solid lipid nanoparticles: A review. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(1):45-53.
- Choudhary N, Verma G, Gupta A, et al. Innovative strategies for improving the stability and bioavailability of Moringa oleifera. Int J Pharm Sci. 2020;8(6):217-226.
- Islam K, Haider S, Amin R, et al. The role of excipients in the bioavailability enhancement of Moringa oleifera tablets. Asian J Pharm. 2021;15(2):20-29.
- Gupta M, Thakur S, Manuja M, et al. The impact of surface modification techniques on the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble compounds. Nanomed Nanotechnol. 2020;15(5):591-600.
- Andriolo R, Scola F, Ruvolo R, et al. Solid dispersion formulations of Moringa oleifera: Enhancing the bioavailability of its active compounds. J Drug Delivery Sci Technol. 2020; 56:23-31.
- Kamar S, Ali M, Basit A, et al. The effect of microencapsulation on the bioavailability of Moringa oleifera and its implications in tablet formulations. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2019;45(10):1534-1540.
- Amna F, Imran I, Rahman S, et al. Biocompatibility of Moringa oleifera-based nanoparticle formulations for sustained drug delivery. Nanomedicine. 2021;16(3):557-567.
- Koh H, Lim B, Tan L, et al. Nanocarriers in Moringa oleifera: Enhancing stability, release, and bioavailability of its active ingredients. Adv Nanotechnol. 2020;10(4):201-210.
- Priyadarshini S, Somasundaram S, Sundaramoorthy P, et al. The role of Moringa oleifera in novel drug delivery systems. Phytomedicine. 2021; 47:28-37.
- Ghosh S, Kaur S, Suman S, et al. Current trends in the formulation of herbal tablets: Moringa oleifera as a case study. Drug Dev Res. 2020;45(2):149-156.
- Mohammed M, Xie L, Zeng W, et al. Clinical trial on the efficacy of Moringa oleifera in managing blood sugar levels: A pilot study. Clin Trials. 2019;13(4):395-403.
- Ali M, Khan H, Rauf A, et al. Moringa oleifera leaf extract in the management of hypertension: Clinical evidence and pharmacological mechanisms. J Hypertens. 2020;38(7):1234-1241.
- Saha T, Banerjee P, Sahoo S, et al. Efficacy of Moringa oleifera in the management of osteoarthritis: A randomized clinical trial. Rheumatol Int. 2020;40(9):1405-1412.
- Mishra M, Chauhan D, Ghosh A, et al. Moringa oleifera extract for improving insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetes: Clinical trials and implications. J Pharm Res. 2021;13(6):421-428.
- Alissa EM, Sulaiman MH, Daghestani MH, et al. Moringa oleifera and its role in reducing cardiovascular risks: A clinical review. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2019; 15:85-95.
- Sulaiman MH, Ahamed M, Muktar H, et al. The pharmacology of Moringa oleifera: A comprehensive study of its therapeutic potentials. Phytochem Rev. 2021;19(2):477-493.
- Kumari P, Saurabh D, Rani A, et al. Moringa oleifera leaf extract: A sustainable approach to enhance the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2020;10(4):1209-1218.
- Patel N, Patel K, Patel P, et al. Advances in the formulation and bioavailability of Moringa oleifera tablet dosage forms. Pharm Innov J. 2019;8(7):226-235.
- Sharma H, Gupta V, Kumar S, et al. Nanotechnology-based formulations of Moringa oleifera for cancer treatment. J Drug Target. 2021;29(2):183-194.
- Bhatt J, Verma S, Mehta A, et al. Enhanced bioavailability of Moringa oleifera through microencapsulation: A case study. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2019;10(11):2456-2465.
- Al-Madani N, Hammadi N, Al-Jawfi H, et al. Current advances in Moringa oleifera tablet formulations: Applications, stability, and bioavailability. Drug Deliv. 2020;27(1):168-178.
- Mahendran B, Sandeep S, Sivasubramanian A, et al. A novel technique to improve patient compliance for herbal tablets: Case study on Moringa oleifera. Curr Drug Ther. 2018;13(2):123-129.
- Lee K, Choi Y, Park K, et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics of Moringa oleifera in therapeutic applications. J Phytomed. 2021; 30:215-223
- Huang Q, Yang Y, Zhou X, et al. The effects of Moringa oleifera leaf extract on the lipid profile in patients with hyperlipidemia. Phytother Res. 2020;34(1): 67-76.
- Ahmad A, Li Z, Zhao L, et al. Bioavailability improvement of herbal compounds: A focus on Moringa oleifera. Curr Drug Delivery. 2021;18(5):742-749.
- Pradeep N, Rani N, Dhawan M, et al. Moringa oleifera in the prevention and management of Alzheimer's disease. Adv Pharm Bull. 2020;10(1):88-97.
- Zhao Y, Li X, Yang X, et al. Moringa oleifera seed extracts in managing oxidative stress and cardiovascular disease. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;158: 98-107.
- Sharma V, Sethi S, Singh B, et al. Formulation and evaluation of Moringa oleifera tablet dosage form for enhanced bioavailability. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2019; 166:50-57.
- Leong Y, Chia D, Wang H, et al. Clinical trials and evidence for the bioactive effects of Moringa oleifera in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020; 165:108-116.
- Lima A, Nascimento T, Costa F, et al. Comparative study of Moringa oleifera leaves and seed extracts in pharmaceutical formulations: A focus on bioactivity. Int J Pharm. 2021; 605:42-49.
- Sen S, Kundu P, Ray S, et al. Recent advances in Moringa oleifera tablet formulations for enhanced therapeutic effects. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2020;72(5):650-660.

 Shilpa Jaiswal*
Shilpa Jaiswal*

 10.5281/zenodo.14715830
10.5281/zenodo.14715830