Abstract
Many advantages of gels a major limitation is in the delivery of hydrophobic drugs. So to overcome this limitation an emulsion based approach is being used so that even a hydrophobic therapeutic moiety can enjoy the unique properties of gels. When gels and emulsions are used in combined form the dosage form are referred as emulgel. In recent years, there has been great interest in the use of novel polymers. A unique aspect of dermatological pharmacology is the direct accessibility of the skin as a target organ for diagnosis and treatment. The combination of hydrophilic cornified cells in hydrophobic intercellular material provides a barrier to both hydrophilic and hydrophobic substances. Within the major group of semisolid preparations, the use of transparent gels has expanded both in cosmetics and in pharmaceutical preparations. Polymer can function as emulsifiers and thickeners because the gelling capacity of these compounds allows the formulation of stable emulsions and creams by decreasing surface and interfacial tension and at the same time increasing the viscosity of the aqueous phase. In fact, the presence of a gelling agent in the water phase converts a classical emulsion into an emulgel. These emulgel are having major advantages on novel vesicular systems as well as on conventional systems in various aspects. Various permeation enhancers can potentiate the effect, So emulgels can be used as better topical drug delivery systems over present systems. The use of emulgels can be extended in analgesics and antifungal drugs.
Keywords
Emulgel, Topical, Hydrophilic, Hydrophobic, Analgesics.
Introduction
Topical drug delivery system is the dosage form which is administered on the skin and other routes of drug delivery get failed or for skin disorders. The topical drug delivery system has the advantage of negotiating the first pass metabolism. It also helps to avoid the risk and inconvenience of i.v route therapy. Topical formulations are prepared in different consistency such as solid, semisolid, and liquid. The topical delivery system is failed in the administration of hydrophobic drug. In each formulation with the active ingredients many excipients are used. Sometimes more than one formulation can be combined to enhance the drug delivery; emulgel is such type of combination. It is the combination of emulsion and gel. Emulgel is prepared both in oil- in- water and water- in- oil type emulsion mixed with gel. Oil- in- water type is used for lipophilic drugs and water- in- oil type is used for hydrophobic drugs' delivery Emulgel have many advantages like thixotropic, greaseless, easily spreadable, easily removable, emollient, non-staining, bio-friendly, pleasing appearance, transparent and cosmetically acceptable, which also have a good skin The emulsion and gel preparations have their own properties. But the gels show some limitations as hydrophobic drug delivery. This limitation is overcoming by emulgel. By the use of gelling agent classical emulsion can be converted in to emulgel.
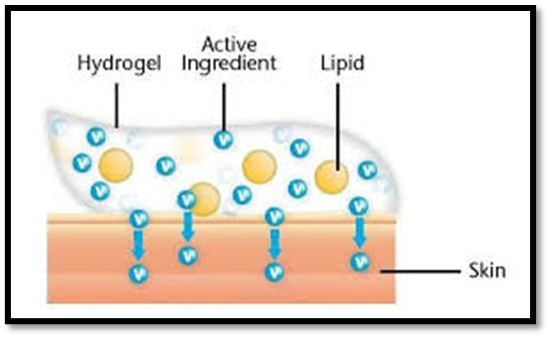
Fig.1 Emulgel Structure
Two types of topical delivery products are available. They are external and internal products. As their name indicates, the external products are applied by spreadingor spraying, and the internal products are applied orally, vaginally or rectally. The topical preparation can be classified by their consistencies, which are solid preparation, liquid preparation, semi-solid preparation and miscellaneous preparation. factors will affect the absorption of drug through every route. Some factors like skin thickness, skin pH, hydration, inflammation, partition coefficient, molecular weight and other factors affect topical route.
The topical delivery system has many advantages and also disadvantages. The main advantage is avoidance of first pass metabolism and gastrointestinal incompatibility. Nearly all topical preparations are applied on the skin. They penetrate through the skin and give the action in right site.
The skin is the largest sense organ in our body, which consist of approximately 2 m2 of surface area and pH of skin is 4.0 to 5.6. The skin contains four layers; non- viable epidermis, viable epidermis, viable dermis and subcutaneous connective tissue.
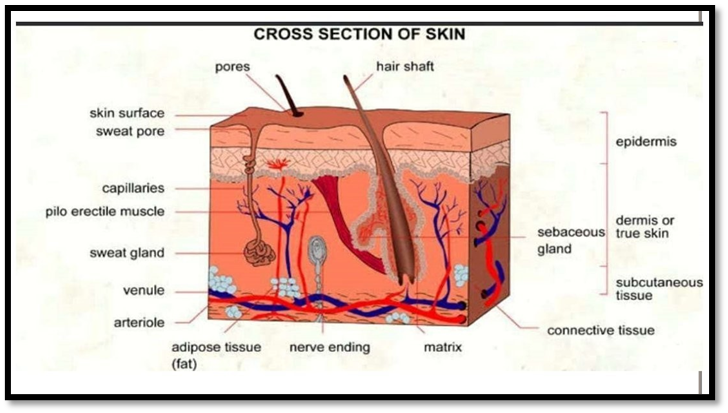
Non- viable epidermis [stratum corneum]: It is the outer layer of skin, which is 10-20 cell thick. The cells are 34-44 µm long, 25-36 µm wide, 0.5- 0.20 µmthick with surface area of 750-1200 µm.
Viable epidermis thickness. It lies between stratum corneum and dermis with 1050 µm
The tonofibrils help for joining the cells.
Dermis: It is seen under the viable epidermis, and it is a structural fibrin. Thickness of the dermis ranges from 2000-3000 µm and contains loose connective tissue.
Mechanism of Skin Penetration
Skin penetration enhancers are the molecules which reversible to remove the barrier resistance of the stratum corneum. They allow drugs to penetrate more readily to the viable tissues and hence enter the systemic circulation.
The intercellular routes accelerants may interact at the polar head groups of the lipids, within aqueous region between lipid head group and between the hydrophobic tails of the barrier.
The common mechanism is to protect the body for unwanted particles from the environment. The main barrier of the skin is located in the outermost layer of skin that is epidermis.
Since the lipid regions in the stratum corneum forms the only continuous structure, substance applied on to the skin always have to pass these region.
The major obstacle for topical drug delivery is the low diffusion rate of drug across the stratum corneum. Several methods have been assessed to increase the permeation rate of drugs temporarily.
Defination:
Emulgel is oil in water or water in oil emulsion carrying drug to be incorporated in gel base to obtain gellified emulsion. Emulgel shows the controlled and better release effect of drug by virtue of combined effect of gel and emulsion with increased stability.Normally the emulgels are used as anti-inflammatory drugs. In the coming years, topical drugs delivery will be used extensively to impart better patient compliance.
Examples of Emulgel: Miconz-H-emulgel, Isofen emulgel, Diclon emulgel,etc.
ADVANTAGES
• Incorporation of hydrophobic drugs
• Better loading capacity
• Better stability
• Controlled release
• No intensive sonication
• Avoiding first pass metabolism
• Avoiding gastrointestinal incompatibility
• More selective for a specific site
• Improved patient compliance
• Convenient and easy to apply
• Improve bioavailability and even the low doses can be effective in comparison with other conventional semi solid preparation.
DISADVANTAGES
• Skin irritation on contact dermatitis
• The possibility of allergenic reactions
• The poor permeability of some drugs through the skin
• Drugs of large particle size are not easy to absorb through the skin
• The occurrence of the bubble during formulation of emulgel
Can be used only for drugs which require very small plasma concentration for action. 6.
Enzyme in epidermis may denature the drugs
Emulsions are of different types depending on the size of droplets or nature of distribution
1) Macroemulsion gel
2) Nanoemulsion gel
3) Microemulsion gel
1) Macroemulsions gel
These are most common type of emulgels where the particle size of droplets of emulsion is more than 400nm. They are visually opaque but the individual droplets can be easily observed under microscope. Macroemulsion are thermodynamically unstable, but can be stabilized using surface active agents. E.g. Khullar R. et al, mefenamic acid emulgel was prepared using Carbopol 940 as gelling agent. Liquid paraffin was used as oil phase. Mentha oil and clove oil was used as penetration enhancer. Then it was evaluated for rheological studies, spreading coefficient studies, skin irritation test, in-vitro release, etc.
2) Nanoemulsion gel
When nanoemulsion is incorporated into gel it is called as nanoemulgel. Nanoemulsion are thermodynamically stable transparent (translucent) dispersions of oil and water stabilized by an interfacial film of surfactant and co surfactant molecules having a droplet size of less than 100nm. Nanoemulsion formulations possess improved Transdermal and dermal delivery properties in vitro as well as in vivo. This has improved transdermal permeation of many drugs over the conventional topical formulations such as emulsions and gels.
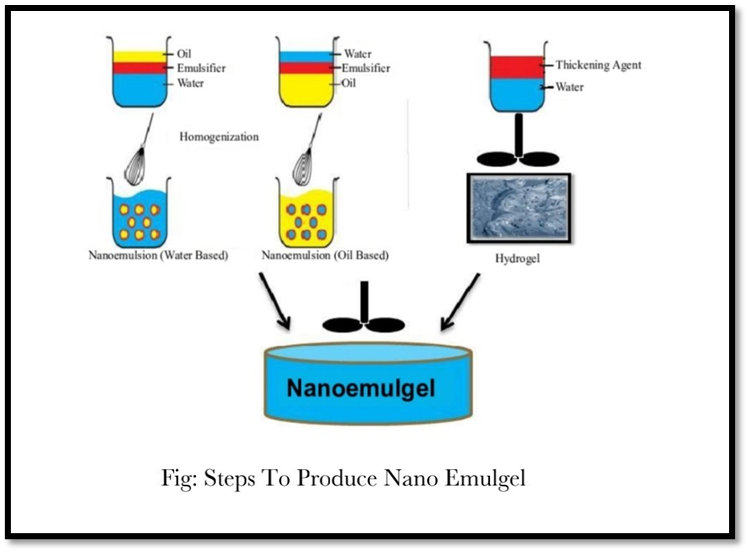
E.g. Singh B. P et al, prepared Carvedilol nanoemulgel using oleic acid and isopropyl myristate (3:1) as oil phase. Tween 20 and Carvedilol were used as surfactant and co surfactant respectively. Carbopol 934 was used as gelling agent.
3)Microemulsion gel:
Microemulsions are transparent and thermodynamically stable as their droplet size range from 10 to 100nm and they do not coalesce. Microemulsions are composed of oil, co-surfactant, and water in specific proportions.
The ingredients of Microemulsion could facilitate the permeation rate of the drug by reducing the diffusion barrier of the stratum corneum. However, due to low viscosity of Microemulsion, their less retention capacity in the skin restrains its application in the pharmaceutical industry To overcome this disadvantage, gelling agents such as
Carbopol 940, xanthan gum and carrageenan have been added into the Microemulsion for forming Microemulsion based gel in order to increase its viscosity which could be suitable for topical application.
Moreover, Microemulsion based gel prevents the absorption of drug in the blood stream and provide higher drug accumulation in the skin for efficient action.
E.g. Bachhav Y. G et al, prepared clotrimazole Microemulsion based vaginal using Carbapol 90 as oil phase and Cremophor EL as surfactant. Carbopol ETD 2020 is used as gelling agent.
FORMULATION OF EMULGEL
For the preparation of emulgel some constituents are used including drug, which are:
1. Vehicle
Properties of vehicles is that
Deliver the drug to target site.
Sustain a therapeutic drug level in the target tissue for a sufficient duration to
provide a pharmacological effect.
Release the drug so it can migrate freely to the site of action.
a) Aqueous material
This forms the aqueous phase of the emulsion. Commonly used agents e.g. water, alcohols.
b) Oils
These agents from the oily phase. For externally applied emulsions, mineral oils, either alone or combined with soft or hard paraffin's are widely used. In oral preparations nonbiodegradable mineral and castor oils that provide a local laxative effect and fish liver oils or various fixed oils of vegetable origin (e.g.: arachis, cottonseed, and maize oils) as nutritional supplements.
Gelling agents
These are used to increase consistency of dosage form and provide gelled behavior. Gelling agent are of 2 types natural and synthetic. Incorporation of gelling agent to a system makes it thixotropic. It is observed that there exist an inverse relationship between concentration of gelling agent and extent of drug released. Then get hydrated and swell. Besides its hydrophilic nature, its cross-linked structure and its insolubility in water makes carbopol a potential candidate for use in controlled release drug delivery system. HPMC emulgel shows better drug release than carbopol. Ex: carbopol-934(1%), HPMC-2910(2.5%).
Penetration enhancers
These are agents that partition into and interact with skin constituents to induce a temporary and reversible increase in skin permeability. E.g: Oleic acid, lecithin, isopropyl myristate, urea, eucalyptus oil, chenopodium oil, pyrrolidone, laurocapran, dimethyl sulphoxide, linoelic acid, menthol.
Properties of penetration enhancer
- They should be non-toxic, non-irritating and non-allergenic.
- They would ideally work rapidly and the activity and duration of effect should be both predictable and reproducible.
- They should have no pharmacological activity within the body i.e. should not bind to receptor sites.
- The penetration enhancers should work unidirectional i.e. should allow therapeutic agents into the body while preventing the loss of endogenous material from the body.
- The penetration enhancers should be appropriate for formulation into diverse topical preparations, thus should be compatable with both excipients and drugs.
- They should be cosmetically suitable with an appropriate skin 'feel'.
Mechanism of penetration enhancer Penetration enhancers may act by one or more of three main mechanisms
1. Disruption of the highly ordered structure of stratum corneum lipid.
2. Interaction with intercellular protein.
3. Improved partition of the drug, co-enhancer or solvent into the stratum corneum.
4. Most of the hydrophobic drugs cannot be incorporated directly into gel base because solubility act as a barrier and problem arises during the release of the drug.
5. Emulgel helps in the incorporation of hydrophobic drugs into the oil phase and then oily globules are dispersed in aqueous phase resulting in o/w emulsion and this emulsion can be mixed into gel base. This may be proving better stability and release of drug than simply incorporating drugs into gel base.
- IDEAL PROPERTIES OF ADDITIVES
- They should be nontoxic.
- They should be easily available.
- They should be cheap.
- They do not be contraindicated.
- They should chemically and physically be stable.
PREPARATION OF EMULGEL
Emulgel are prepared by incorporating gel and emulsion. The emulsion and gel are prepared separately and mixed together. with gentle stirring. The chemicals are used as oil phase are castor oil, clove oil, iquid paraffin, etc. For preparing emulsion, aqueous phase and oil phase are taken separately and mixed together.
Then the gel is prepared by using gelling agent. After preparing gel and emulsion, they are mixed Water and alcohol are used as aqueous phase.
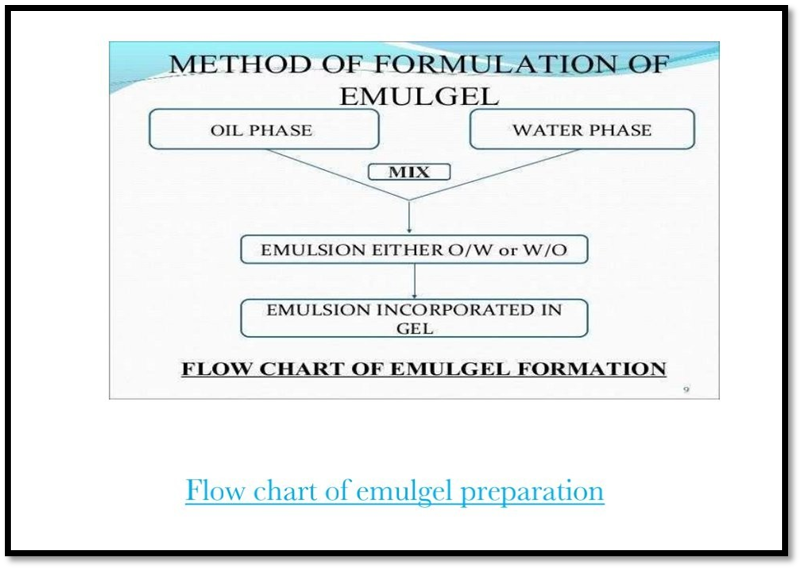
METHOD OF FORMULATION OF EMULGEL
OIL PHASE
MIX
WATER PHASE
EMULSION EITHER O/W or W/O
EMULSION INCORPORATED IN GEL
FLOW CHART OF EMULGEL FORMATION
EVALUATION TECHNIQUES
Physical appearance:
The prepared Emulgel is checked visually for their color, homogeneity, consistency and phase separation.
pH Evaluation:
pH evaluation is the important criteria especially for the topical formulation. The pH of emulgel should be between 5.8 - 6 to mimic the skin condition. If the pH of the prepared emulgel is acidic or basic, it may cause irritation to the patient. PH of the prepared emulgel was measured using digital pH meter by dipping the glass electrode into an emulgel. The measurement of pH of each formulation was done in triplicate and average values were calculated.
Spreadability:
Spreadability of emulgel is measured in terms of diameter of emulgel circle produced when emulgel is placed between two glass plates of definite weight. A weighed quantity (350 mg) of emulgel is taken on one glass plate and another glass plate is dropped from a distance of 5 cm. The diameter of the circle of spread emulgel is measured.
It is calculated by using the formula:
S-M.L/T
Where,
S= spredability
M= weight tied to upper slide.
L= length of glass slide.
T= time taken to separate the slides completely.
Extrudability Study [tube test]:
It is calculated by the force required to extrude the emulgel from the tube. The method applied for determination of applied shear in the region of the rheogram corresponding to a shear rate exceeding the yield value and exhibiting consequent plug flow.
In this study emulgel extruded from lacquered aluminum collapsible tube on application of weight in grams required to extrude at least 0.5cm ribbon of emulgel in 10 seconds. For better extrudability, more quantity is extruded. For the measurement of extrudability, it is done in triplicate and the average values are calculated.
The extrudability is then calculated by using the following formula.
Extrudability = weight applied to extrude emulgel from tube (in gm) / Area (in cm2).
Rheological Studies:
Viscosity of emulgel is determined at 25°C using a cone and plate viscometer with spindle 52 and connected to a thermostatically controlled circulating water bath.
Swelling Index:
It is determined by taking Ig of emulgel in a porous aluminum foil and mixed with 0.1N NaOH kept in a 50ml beaker. Then samples are withdrawn at different time intervals and kept for drying and it is reweighed. Swelling index is calculated as follows:
Swelling Index = {Wt-Wo/Wo}100
Where, (SW) % = Equilibrium percent swelling,
Wt Weight of swollen emulgel after time 't' Wo weight of emulgel at zero time.
Drug Content Determination
Emulgel is mixed in a suitable solvent. Filter it to obtain clear solution. Determine its absorbance using UV spectrophotometer. From the standard equation by putting the absorbance value concentration and drug content can be obtained.
Drug Content (Concentration × Dilution Factor × Volume taken) × Conversion Factor.
Bioadhesive strength measurement
The modified method was used for the measurement of bioadhesive strength. The apparatus consist of two arm balance, both the ends are tied to glass plates using strings. One side contains single glass plate for keeping weight. The right and left pans were balanced by adding extra weight on the left hand pan. The balance was kept in this position for 5 mints.
Procedure: Accurately weighed 1g of emulgel was placed between these two slides containing hair less fresh rat skin pieces, extra weight from the left pan was removed to sandwitch the two pieces of glass and some pressure was applied to remove the presence of air.
The balance was kept in the position for 5 min. weight was added slowly at 200mg/min to the left hand pan until the two glass slides got detached from each others.
The weight required to detach the emulgel from the glass surface gives
the measure of bioadhesive strength by
Bioadhesive strength-weight required (in g) / area(cm?2;)using a formula,
Skin Irritation Test (Patch Test):
For this study emulgel is applied on the shaven skin of rat and its adverse effect like change in color, change in skin morphology are evaluated up to 24 hours. About 8 rats can be used for the study. Test passes if no irritation shown. If it fails the test is repeated with another 2 rats.
Microbiological assay:
Microbiological assay was performed by using ditch plate technique. Previously prepared Sabouraud's agar dried plates were used. 3 grams of the gellified emulsion are placed in a ditch cut in plate. Freshly prepared culture loops are streaked across agar at a anglefrm the edge of the plate. After incubation for 18-24hrs at 25°c, the fungal growth was observed and the percentage inhibition was measured as follows % inhibition = L2 /L1x 100
In-vitro Release Studies:
The in vitro drug release studies were carried out using a modified franz diffusion (FD) cell the formulation was applied on dialysis membrane which was placed between donor and receptor compartment of the FD cell. Phosphate buffer PH 7.4 was used as a donor and receptor compartment of the cell was maintained at 37c by circulating water jacket. This whole assembly was kept on a magnetic stirrer and the solution was stirred continuously using a magnetic bead. A similar bank set was run simultaneously as a control. sample (5 ml) was withdrawn at suitable time intervals and replaced with equal amount of fresh dissolution media. Samples were analysed spectrophotometrically at 318nm and cumulative %drug release was calculated.
PACKAGING OF EMULGELS
Packaging of emulgels are usually done in membrane sealed lacquered aluminum tube with inner coating of a phenoxy-epoxy based lacquer closed with propylene screw cap or an aluminum laminated tubes closed by a moulded seal, with a propylene screw cap.
Material for laminates tubes
1. Foil laminates
It provides light, air and moisture barrier.
2. All plastic laminates
It has a chemical resistant barrier
CONCLUSION
In the coming years, topical drug delivery will be used extensively to impart better patient compliance. Emulgel is a recent technique for topical drug delivery and it is suitable for hydrophobic drugs.
Since it is also capable in enhancing spreadibility, adhesion, viscosity and extrusion. They will become a popular drug delivery system.
Moreover, they will become a solution for loading hydrophobic drugs in a water soluble gel base.
REFERENCES
- Purushottam Sonaje Sumeet, Bhaskarrao Gondkar Sheetal, Bhandudas Saudagar Ravindra., 2013. Gellified Emulsion: A New Born Formulations For Topical Delivery of Hydrophobic Drugs A Review, World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 3(1), pp 233251.
- Shah A. Arpan, Kamdar Kamal, Shah Rushabh, Keraliya A. Rajesh., 2013. Emulgel: A Topical Prepartions for Hydrophobic Drugs. Ph Tech Med, 2(5), pp 370-376.
- Bhatt Preeti, Gnanarajan. G, 2013. Emulgels: A Novel Formulation Approach for the Topical Delivery of Hydrophobic Drugs A Review. International Research Journal of Pharmacy, 4(2), pp 12-16.
- Panwar AS, Upadhyay N, Bairagi M, Gujar S, Darwhekar GN, Jain D, 2011. Emulgel:
- A Review. Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Life Science, 1(3), pp 333-343.
- K.P. Mohammade Haneef, Sherry Easo, P.V. Hafsa, Guru Prasad Mohanta, Chandini Nayar, 2013. Emulgel: An Advanced Review. Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Research, 5(12), pp 254-258.
- Haedenia Anu, Jayronia Sonali and Jain Sanjay, 2014. Emulgel: An emergent tool in topical drug delivery. A review International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Research, 5(5), pp 1653-1660.
- Kute S.B and Saudagar R.B. Emulsified Gel a Novel approach for delivery of hydrophobic drugs, 2013. A review on emulgel. Journal of Advanced Pharm
- Joshi Baibhav, Singh Gurpreet, Rana A.C, Saini Seema, Singla Vikas, 2011, Emulgel: A Comprehensive Review on the Recent Advances in Topical Drug Delivery. A Review International Research Journal of Pharmacy, 2(11), pp 66-70.
- Vikas Singla, Seema Sanil, Baibhav Joshi and A.C. Rana, 2012. Emulgel: A New Platform for Topical Drug Delivery. International Journal of pharmaceutical and biological sciences, 1 (3), pp 485-498.
- Anu Hardenia, Sonali Jayronia and Sanjay Jain, 2014. Emulgel: An emergent tool in topical drug delivery. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science and Research,5(5), pp 1653-1660.
- Pathan, I.B, Setty C.M, 2009. Chemical penetration enhancers for transdermal drug.

 Pawar Chaitanya Vidyasagar*
Pawar Chaitanya Vidyasagar*
 Nishant V. Pote
Nishant V. Pote




 10.5281/zenodo.11582581
10.5281/zenodo.11582581