Abstract
The Aloe vera factory has been known and used for centuries for its health, beauty, medicinal and skin care parcels. The name Aloe vera derives from the Arabic word “Alloeh” meaning “shining bitter substance,” while “vera” in Latin means “true.” 2000 times agone, the Greek scientists regarded Aloe vera as the universal nostrum. The Egyptians called Aloe “the factory of eternity.” moment, the Aloe vera factory has been used for colorful purposes in dermatology. Aloe vera is a popular herbal drug and worldwide appreciated for its remedial eventuality. From ancient time, it has been used as a home remedy for different health issues A wide range of bioactive composites have been characterized from Aloe vera. It has a wide range of antimicrobial, antioxidant, and antidiabetic parcels. Aloe vera can also give support for carbohydrate and lipid metabolism by maintaining the position of cholesterol and sugar in blood and it can also help to maintain body weight. Due to the presence of advanced number of bioactive composites and fat remedial parcels, it's extensively used in drug, cosmetics and food sector. Aloe vera, a succulent imperishable and failure defying factory, is well known for its remedial eventuality. A number of salutary goods of Aloe vera have been reported, including immunomodulatory, crack and burn mending, hypoglycemic, anticancer, gastro-defensive, antifungal, andanti-inflammatory parcels Aloe vera has colorful medicinal parcels like anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiviral, and antitumor which accelerates crack mending and helps in treating colorful lesions in oral depression. Benefits associated with Aloe vera have been attributed to the polysaccharides contained in the gel of the leaves. Conclusion. The pharmacological attributes of Aloe vera have been revalidated in ultramodern lores through colorful in vivo and in vitro studies. The condiment has immense eventuality as a dental remedial. Indeed, though Aloe vera is a promising condiment with colorful clinical operations in drug and dentistry, more clinical exploration needs to be accepted especially to validate and explain the action of acemannan hydrogel in accelerating the mending of aphthous ulcers and to validate the efficacity of Aloe gel on shrine and gingivitis, so that it can be established in the field of dentistry.
Keywords
Aloe vera factory, care parcels, dermatology, carbohydrate and lipid.
Introduction
The use of natural products in the forestallment and treatment of oral conditions has increased lately and could be of benefit to low socioeconomic position in civic and pastoral communities. Among the colorful presently available herbal agents the most popular and presently entering a lot of scientific attention is Aloe vera. The name Aloe vera is deduced from the Arabic word “ Alloeh ” meaning “ shining bitter substance, ” while “ vera ” in Latin means “ true ”. The factory Aloe vera has a history dating back to biblical times. It's a imperishable succulent xerophyte, which develops water- storehouse towel in the leaves to survive in dry areas of low or erratic downfall. The factory has stiff slate-green shaft- shaped leaves containing clear gel in a central mucilaginous pulp. Benefits associated with Aloe vera have been attributed to the polysaccharides contained in the gel of the leaves. There are over 250 species of Aloe grown around the world. Only two species are grown commercially Aloe barbadensis Miller and Aloe arborescens. The Aloe factory is grown in warm, tropical areas and can not survive nipping temperatures similar as during layoffs. In the United States, utmost of the Aloe is grown in the Rio Grande Valley of South Texas, Florida and Southern California. Internationally, Aloe can be set up in Mexico, the Pacific Rim countries, India, South America, Central America, the Caribbean, Australia, and Africa.
Botany of Aloe Vera -
The cactus- suchlike juicy aloe Vera has a place to the kind of the liliaceous shops. The factory is eitherstem-less or exceptionally suddenly- stemmed( stem up to 25 cm long) with an normal roughly 20 takes off in a straight, thick ensign. The clears out develop to over to 40 – 50 cm long and 6 – 7 cm wide. The takes off are or perhaps thick, hefty, water holding; concave on the beat side, slate-green constantly sanguine and immature shops are constantly dotted. The underpart of the splint is twisted with a pale pink edge that is dressed with 2 mm long prickly teeth dispersed at each 10 – 20 mm. One splint can weigh as important as 1.5 to 2 kg. The juicy splint of the aloe is an adaptation to the exceptionally dry conditions of its living space. The roots of the aloe are generally brief and lay flat implanted within the earth.
Plant

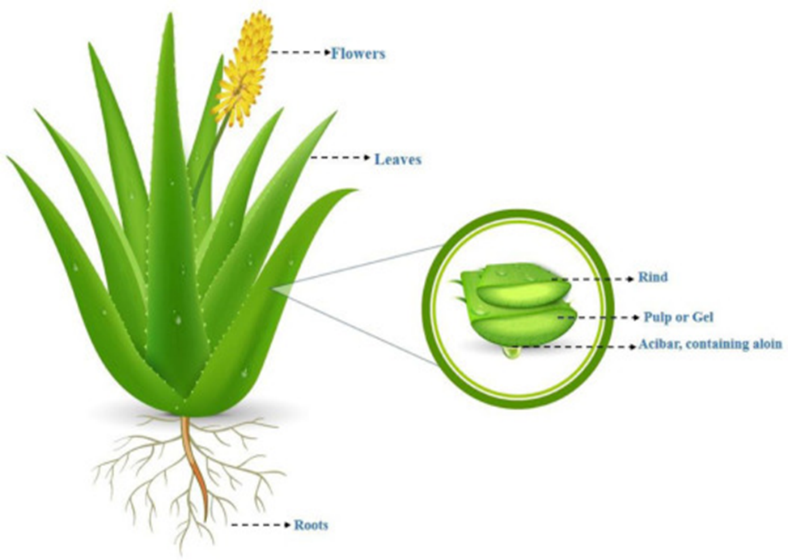
The botanical title of Aloe Vera is Aloe barbadensis shop driver. It has a place to Asphodelaceae( Liliaceae) family, and may be a shrubby or arborescent, perpetual, xerophytic, juicy, pea-green colour factory. It develops primarily within the dry locales of Africa, Asia, Europe and America. In India, it's set up in Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.

Aloe Vera takes off are lance-shaped with serrated edges.
The clears out are:
1. Beefy thick.
2. Green or grey-greenish.
3. Waxy coated on the surface.
4. Value juicy, meaning they can keep their shape due to the moist.
The clears out contain water (the gel) and are flat on the beat side, and adjusted at the foot side. In youthful clears out of Aloe Vera spots are pale green to white. When the Aloe Scle Vera develops up, the spots vanish. Be that as it may, a few species will not free their spots, which is due to hereditary factors.
Toxiconomy -
Kingdom- Plantae
Order- Asparagales
Division- Spermatophyte
Subdivision- Angiospermae
Class- Monocotyledoneae
Specis - Aloe
Species- Barbadensis Mill
Synonyms -
Aloe, Musabbar, Kumari
Biological source
Aloe is the dried latex of leaves of various species of Aloes, namely:
Aloe barbadensis Miller (or Curacao Aloe);
Aloe ferox Miller (or Cape Aloe);
Aloe perryi Baker (or Socotrine Aloe);
Aloe Africana Miller and Aloe spicata Baker (or Cape Aloe)
All these species belong to the family Liliaceae.
Aloe Vera is Comprising of the new juice collected by entry point, from the bases of the clears out of distinctive species of aloe. Aloe perryi, or Aloe Barbadensis Mil and Aloe ferox.
Family - It's belonging to the Liliaceae family
Aloe perryi Bread cook is found in Socotra and Zanzibar islands and in there neighbouring ranges and so the aloes get from this species is known as Socortrine or Zanzibar aloe.
Aloe Vera Linn is something else called Aloe vulgarise Lamarek, or Aloe barbadensis Mil. Aloe officinalis Forskal.
Geographical Source -
Aloe vera are innate to East and South Africa, however have been brought into the West Indies and into topical countries, and will indeed flourish within the countries skirting on the Mediterranena. In India, it is found in Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, UK, Himachal Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu, It is financially created in Aruba, Bonaire, Haiti,
India, South Africa, the Joined together of America and Venezula.[20]
Morphology -
Taste : - Bitter
Odour : - None
Size & Shape : Plant growing to 60-100cm in lance- shaped with elongated.
Strands Colour : Leaves are green to grey- green flower.
Flower : - Yellow tubular in 25-35cm in a slender loose staments.
Root : - Root fibbers that can reach 30-40 cm in length. [21]
Parts of Aloe vera Plant
The Aloe barbadensis factory consists of two different corridor, each of which produces substances with fully different compositions and remedial properties. The parenchymal towel makes up the inner portion of the aloe leaves and produces the Aloe vera gel( or gum), a clear, thin, tasteless, jelly- suchlike material. This towel is recovered from the splint by separating the gel from the inner cellular debris. The other part of the factory is a group of technical cells known as the pericyclic tubules, which do just beneath the external green ring of the splint. These cells produce an exudate that consists of bitter unheroic latex with important laxative- suchlike conduct. This exudate, which is n't to be confused with the gel/ gum from the parenchymal splint towel, is available commercially for systemic ingestion to produce catharsis
Active Ingredient of Aloe vera -
More than 75 active ingredients from inner gel have been identified including vitamins, minerals, enzymes, sugars, anthraquinones or phenolic compounds, lignin, saponins, sterols, amino acids, and salicylic acid. Active ingredients of Aloe vera leaf pulp and exudates.
|
Class
|
Compound
|
|
Vitamins
|
B1, B2, B6, C, ? (??- carotene), choline, folic acid, aa-tocopherol
|
|
Enzymes
|
Alkaline phosphatase, amylase, carboxypeptidase, catalase, bradykinase, cyclooxidase, peroxidase, carboxypeptidase, cyclooxygenase, lipase, oxidase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, superoxide dismutase
|
|
Anthraquinones
|
Aloe emodin, aloetic acid, anthranol, aloin A and B (or collectively known as barbaloin), isobarbaloin, emodin, ester of cinnamic acid
|
|
Inorganic compounds
|
Calcium, chlorine, chromium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese, selenium, zinc, potassium, phosphorous, sodium
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
Pure mannan, acetylated mannan, acetylated glucomannan (acemannan), galactan, glucogalactomannan, galactogalacturan, galactoglucoarabinomannan, arabinogalactan, pectic substance, xylan, cellulose
|
|
Saccharides
|
Mannose, glucose, L-rhamnose, aldopentose
|
|
Organic compounds and lipids
|
Arachidonic acid, yy-linolenic acid, steroids (campesterol, cholesterol, ??-sitosterol), triglycerides, triterpenoid, gibberellin, lignins, potassium sorbate, salicylic acid, uric acid
|
|
Chromones
|
8-C-glucosyl-(2'-O-cinnamoyl)-7-0-methylaloediol A, 8-C-glucosyl-(S)-aloesol, 8-C-glucosyl-7-O-methyl-(S)- aloesol, 8-C-glucosyl-7-0- methylaloediol, 8-C-glucosyl- noreugenin, isoaloeresin D, isorabaichromone
|
|
Nonessential and essential amino acids
|
Alanine, arginine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid, glycine, histidine, hydroxyproline, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, threonine, tyrosine, valine
|
Biological & Pharmacological Actions of Aloe vera Gel
A number of investigations have attempted to relate the chemical constituents in the gel to specific biological effects.
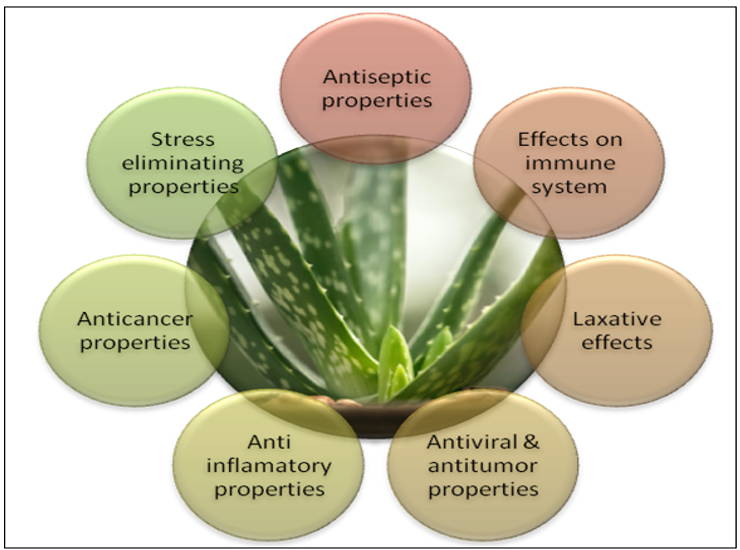
1. Wound-Healing Effects
Different mechanisms have been proposed for the crack- mending goods of Aloe gel, which include keeping the crack wettish, adding epithelial cell migration, more rapid-fire development of collagen, and reduction in inflammation. A 1996 study reported that a high molecular weight polypeptide element from the gel demonstrated a mending effect on excisional injuries in rats. Glucomannan, a mannose-rich polysaccharide, and gibberellin, a growth hormone, interact with growth factor receptor on the fibroblast, thereby stimulating its exertion and proliferation, which in turn increases collagen conflation after topical and oral operation. Yagi et al. reported that Aloe vera gel contains a glycoprotein with cell proliferating- promoting exertion, while Davis et al. noted that Aloe vera gel bettered crack mending by adding blood force( angiogenesis), which increased oxygenation as a result. Angiogenesis is the growth of new blood capillaries and is a part of towel rejuvenescence. A 1993 study showed that topical operation of Aloe vera gel reestablished vascularity of burn towel for a guinea gormandizer, although no specific ingredients were linked. The Aloe vera gel polysaccharide acemannan was shown to spark macrophages, an effect that bettered crack mending in a rat model. Two times latterly, Davis et al. reported that the low molecular weight element of snap- dried Aloe vera gel stimulated blood vessel conformation in a juvenile chorioallantoic membrane( i.e., a vascular membrane deduced from developing funk eggs); in addition, a methanol-answerable bit of the gel which contains a glycoprotein with substantially cell proliferating- promoting exertion stimulated the proliferation of roadway endothelial cells in an in vitro assay and convinced them to foray a collagen substrate.
2. Skin Hydration Effect
It was proposed that the Aloe vera gel phrasings with advanced attention( 0.25 w/ w and 0.5 w/ w) bettered skin hydration conceivably by means of a humectant medium. Humectant medium means that the Aloe gel works by attracting water from the dermis below and by helping to keep this water bound in the stratum corneum.
3. Anti-Aging Effect
Aloe has excellentanti-aging effect by producing the collagen and elastin fibres making the skin more elastic and less wrinkled as reported in an in vivo study conducted on mouse cognizance by Davis et al. One of the main reasons for this lies in the factory’s unique capability to increase product of mortal fibroblast cells between six and eight times faster than normal cell product. Fibroblast cells are set up in the dermis of the skin and are responsible for the fabrication of collagen, the skin’s support protein which keeps skin establishment, supple, and immature looking. It was set up that Aloe vera not only bettered fibroblast cell structure but also accelerated the collagen product process.
4. Anti-Inflammatory goods
It inhibits the cyclooxygenase pathway and reduces prostaglandin E2. lately, the newanti-inflammatory emulsion called C- glucosyl chromone was insulated from gel excerpts. In addition, the peptidase bradykinase was insulated from Aloe and shown to break down the bradykinin, an seditious substance that induces pain.
5. Antibacterial Property
The exertion of Aloe vera inner gel against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria has been demonstrated by several different styles. Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus faecalis are two microorganisms that have been inhibited by Aloe vera gel. Aloe vera gel reportedly was bactericidal against Pseudomonas aeruginosa while acemannan averted it from clinging to mortal lung epithelial cells in a monolayer culture.
6. Antifungal Property
A reused Aloe vera gel medication reportedly inhibited the growth of Candida albicans.
7. Antiviral Property
This action may be direct and circular circular due to stimulation of vulnerable system, and direct due to aloe emodin. Aloe emodin in Aloe vera makes it so that certain contagions are n't suitable to serve. thus, Aloe vera is virucidal to Herpes simplex contagion type 1 and type 2, Varicella zoster contagion, pseudorabies contagion, and influenza contagion according to the exploration of Thomson. During the course of these studies it was set up that the virucidal exertion was due to the anthraquinones uprooted from the inner splint of Aloe and the roots, dinghy, or leaves of a number of other anthraquinone- containing shops. The results indicated that aloe emodin directly affected both DNA- and RNA- containing enveloped contagions but had no effect on naked( unenveloped) contagions. It was concluded that under the conditions tested, the anthraquinones acted directly on the envelope of the anthraquinone-sensitive contagions, performing in the forestallment of contagion adsorption and posterior replication.
8. Immunomodulating goods
Aloe vera, a great vulnerable goad, contains 90 rhodium and iridium( trace minerals) in the acemannan which is one of the polysaccharides which dramatically increases the white blood cells or macrophages and T cells. therefore, immunomodulating goods do via activation of macrophage cells to induce nitric oxide, cache cytokines( e.g., excrescence necrosis factor, interleukin- 1, interleukin- 6, and interferon- ?), and present cell face labels. It helps enlarge the thymus gland in size by 40. The thymus is what produces the T cells of the vulnerable system.
9. Antioxidant Property
Aloe vera has veritably strong antioxidant nutrients. Glutathione peroxide exertion, superoxide dismutase enzymes, and a phenolic antioxidant were set up to be present in Aloe vera gel, which may be responsible for these antioxidant goods. piecemeal from these, it also contains A, C, and E vitamins. These free revolutionary factors get relieve of the poisons and carcinogenic parcels we've in our bodies from the pollution and poor quality foods we eat. We acquire these free revolutionaries in our bodies through immersion of our skin and through digestion.
10. Antitumor Effect
The two fragments from Aloes that are claimed to have anticancer goods include glycoproteins( lectins) and polysaccharides. Different studies indicated antitumor exertion for Aloe vera gel in terms of reduced excrescence burden, excrescence loss, excrescence necrosis, and dragged survival rates. Crack mending and preventative goods of Aloe vera have been reported in several studies.16 Topical operation of Aloe vera to help ulcers and enhance the mending process of dermal injuries( e.g., becks, frostbite, skin infections, surgical injuries, inflammation, herpes ulcers, diabetic bottom ulcers, pressure blisters, and habitual injuries) has been reported.17 Aloe vera is largely suitable for crack dressings.18 utmost of the studies were conducted on burn injuries. Aloe vera is considered as the traditional remedy for beck Five studies delved burn crack mending. In these studies, Aloe vera was more effective than petroleum jelly reek dressing, tableware sulfadiazine 1 ointment, and framycetin cream. also, it reduced the recovery time, averted infection in the crack area, and averted greenishness and- 21 In these studies, Aloe vera was more effective in first- and alternate- degree burn injuries than in the other degrees. As described in Table 1, it's concluded that Aloe vera can reduce the mending time of first- and alternate- degree becks to 9 days( P = 0.006).15
Table 1. Analysis of studies using Aloe vera for first- and second-degree burns
|
Authors
|
Year
|
Sample size
|
Methods
|
Result
|
|
Malek Hosseini
|
2013
|
64 patients with second-degree burns
|
32 patients were dressed with Aloe vera gel and 32 other patients were dressed with silver sulfadiazine 1% cream, daily. Parameters of the wound on the 1st, 7th, and 15th days were studied using Bates-Jensen wound assessment tool
|
By comparing the average improvement in both groups at baseline and on the 15th day, a significant difference was found between the two groups (P<0>
|
|
Khorasani
|
2009
|
30 patients with burns on two areas of the body
|
In each patient, one part of the body was randomly used to apply Aloe vera cream 0.5% and the other part with sulfadiazine 1%. In both groups, Aloe vera and sulfadiazine were applied twice a day. The healing time was 19 days.
|
80% of the SSD group and 100% of the AV group were cured after 19 days. The mean days of recovery in the AV and SSD groups were 15.9±2 and 18.73±2.56 days, respectively. In addition, no infection was observed in both groups (P<0>
|
|
Moghbel
|
2007
|
30 patients with second-degree burn wounds
|
The patients applied Aloe vera dressing and silver sulfadiazine 1% ointment on each hand as the experimental and control groups, symmetrically.
|
They reported improvements within 10 days in 90.6% of the experimental group and 28.7% of the control group (P<0>
|
|
Akhtar
|
1996
|
100 patients with burns
|
100 patients were divided into two groups. The AV group applied Aloe vera dressing three times a day and the control group applied framycetin ointment.
|
The average improvement for the AV group was 18 days versus 30.9 days
|
|
Tamlikikal
|
1991
|
38 patients with first- to third-degree burns in which less than 30% of their body surface area was burned
|
The samples were assigned into two groups by random allocation; in SSD group silver sulfadiazine was applied twice a day and in the AV group Aloe vera was applied twice a day.
|
55% (11/20) with mucilage AV and 39% (7/18) with SSD were recovered
|
Table 2. Analysis of studies using Aloe vera on postoperative wounds
|
Authors
|
Year
|
Sample size
|
Methods
|
Result
|
|
Malazem
|
2015
|
90 women undergoing cesarean section
|
Aloe vera gel dressing was used in the intervention group and a simple dressing on the wound immediately after cesarean section was applied in the other group. The pain and improvement in the first 24 hours and the 8th day were compared
|
In the Aloe vera group, wound healing was faster than the control group in the first 24 hours (P=0.003). However, no difference was observed on the 8th day (P=0.283). Finally, the positive effect of Aloe vera treatment was confirmed
|
|
Sabz Ali Gol
|
2014
|
84 women undergoing nulliparous episiotomy
|
In the intervention group, Aloe vera gel was used twice a day for 10 days and betadine bath was used for the control group twice a day for 10 days.
|
In the Aloe vera group, 57.1% on the 7th day and 30% on the 10th day had complete remission. The pain intensity average was 2.3 on the 7th day and 1.21 on the 10th day.
|
|
Eghdam Poor
|
2013
|
74 women undergoing nulliparous episiotom
|
Aloe vera ointment every 8 hours for 5 days was applied in the intervention group and the control group used betadine bath every 4 hours for 5 days.
|
The average improvement in the Aloe vera group was 1.62, which was significantly high (P<0>
|
|
Jahdi
|
2011
|
74 women undergoing nulliparous episiotomy
|
In the intervention group, Aloe vera ointment (3 cc) was applied every 8 hours for 5 days and betadine bath used in the control group every 4 hours for 5 days.
|
Regarding pain intensity, the average pain score was 1.86 in the Aloe vera group, which was significantly low (P<0>
|
|
Khorasani
|
2011
|
45 skin graft donor sites
|
A group using Aloe vera cream (three times daily), a placebo group (three times daily), and the other group without any topical agent were studied. Dressing was applied daily in all three groups
|
It was concluded that the effect of Aloe vera gel on the donor sites resulted in a significant improvement in recovery time between the control group (without any topical agent: 17±8.6), the placebo group (without Aloe vera cream: 8.8±2.8), and the experimental group (cream without Aloe vera: 9.7±2.9). However, there was no difference in the placebo and experimental group, which can be due to the moisturizing effect of both creams.
|
|
Eshghi
|
2010
|
49 patients after hemorrhoidectomy
|
Aloe vera gel 0.05% was used in the intervention group and placebo was used in the control group 12 hours after hemorrhoidectomy three times a day for 28 days.
|
The complete time of remission was considered as 14 days. 100% of the intervention group and only 4% of the control group cured after 14 days
|
|
Philips
|
1995
|
49 patients undergoing skin shave biopsy
|
The intervention group used Aloe vera gel dressing and the control group used the combined dressing (hydrogel parkside, antibiotic ointment, and absorbent dressing) twice a day.
|
After 14 days, no difference was observed between the two groups in terms of the healing and 24/24 in the AV group and 23/23 in the control group recovered.
|
As described in Table 3, Aloe vera was used for healing of cracked nipples in 2 studies and it reduced the pain and discharge in the area.29,30
Table 3. Analysis of studies using Aloe vera for healing of cracked nipples
|
Authors
|
Year
|
Sample size
|
Methods
|
Result
|
|
Alamolhoda
|
2013
|
110 nulliparous lactating women
|
In one group, after each breastfeeding, lactating women applied 0.5 ml of Aloe vera gel on their nipples and around the areola. The control group applied 4 drops of their breast milk. Both groups were evaluated at days 10 and 14 postpartum
|
The pain and damage of the nipple and discharge in the Aloe vera group were much less than the control group and Aloe vera improved the fissure (P<0>
|
|
Tafazoli
|
2009
|
100 lactating women with breast fissure
|
Two groups were divided into lanolin ointment or Aloe gel groups (three times a day for 1 week).
|
There was a statistically significant difference between the two groups on the 3rd day (P=0.048) and 7th day (P=0.003). Aloe vera gel was more effective than lanolin ointment in healing cracked nipples.
|
REFERENCES
-
-
-
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6330525/#:~:text=Due to anti-inflammatory, increased,considered as the ideal dressing
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334123567_Review_on_Aloe_Vera
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1155/2014/210463
- Malek Hosseini A, Ghaffarzadegan R, Alizadeh SA, Ghaffarzadegan R, Haji Agaei R, Ahmadlou M. Effect of aloe vera gel, compared to 1% silver sulfadiazine cream on second-degree burn wound healing. Complementary Medicine Journal of faculty of Nursing and Midwifery. 2013;3:418–28. [Google Scholar]
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328413306_The_Effect_of_Aloe_Vera_Clinical_Trials_on_Prevention_and_Healing_of_Skin_Wound_A_Systematic_Review
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0305417906007029
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6330525/#:~:text=Due to anti-inflammatory, increased,considered as the ideal dressing
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4452276/
- Maenthaisong R, Chaiyakunapruk N, Niruntraporn S, Kongkaew C. The efficacy of aloe vera used for burn wound healing: a systematic review. Burns. 2007;33:713–8. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2006.10.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabzaligol M, Safari N, Baghcjeghi N, Latifi M, Bekhradi R, Taghizadeh M, et al. The effect of Aloevera gel on prineal pain & wound healing after episiotomy. Complementary Medicine Journal of faculty of Nursing and Midwifery. 2014;4:766–75. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Radha MH, Laxmipriya NP. Evaluation of biological properties and clinical effectiveness of Aloe vera: A systematic review. J Tradit Complement Med. 2015;5:21–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2014.10.006. [ PMC Free Article] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tafazoli M, Saeedi R, Gholami Robatsangi M, Mazloom R. Aloevera gel Vs. lanolin ointment in the treatment of nipple sore: a randomized clinical trial. Tehran University Medical Journal. 2010;67:699–704. Persian. [Google Scholar]
- Eshgizade M, Basiri Moghaddam M, Mohammadzadeh Moghaddam H, Mahmoudian A, Mesbah M. Comparison of the Effect of Olive Oil, Aloe Vera Extract and Breast Milk on Healing of Breast Fissure in Lactating Mothers: A Randomized Clinical Trial (Clinical Trial Article) Qom Univeresity of Medical Sciences. 2016;10:19–27. Persian. [Google Scholar]
- Baby J, Justin SR. Pharmacognostic and phytochemical properties of Aloe Vera linn –an overview. International journal of pharmaceutical sciences review and research 2010; 4:106
- Benefits of Aloe Vera Plant, Aloe Vera Juice & Aloe Vera Products. Knowledge Base Script.2009; 1-7. Available from: www.knowledgepublisher.com. Das N, Chattopadhay RN. Commercial cultivation of Aloe. Natural product radiance 2004; 3:85-87.
- Perkins, Cyndi. "Is Aloe a Tropical Plant?". SFgate.com. Retrieved 13 February 2016.


 Ankita Gadekar *
Ankita Gadekar *
 Gauri Gite
Gauri Gite




 10.5281/zenodo.14843534
10.5281/zenodo.14843534