Abstract
Digitalis purpurea L. is an important medicinal plant belonging to the family Scrophulariaceae and is an important source of secondary metabolites. The exclusively important digitalis purpurea L. ( Foxglove) Belongs to the family Scrophulariaceae and is distributed throughout the European continent. The phytochemical screening showed the presence of cardiac glucosides, flavonoids, anthraquinones, and also tripenes. But the most important of the phytoconstituents contributed by D.purpurea is the striking presence of numerous cardioactive glycosi6that that have proven to be the most important drugs in treating congestive heart failure. The glucosides of D. purpurea are not only considered to possess cardiac glucosides stimulant but also have wound healing, hepatoprotective, antioxidant, and cytotoxic activities. Many of them exhibit slowing ventricular rate in atrial Fibrillation, atrial flutter, supraventricular tachycardia, and premature extrasystoles. The present review is, therefore, an effort to present a detailed survey of the literature on pharmacognosy, phytochemistry, and pharmacological activities of D . Purpurea.
Keywords
Digitalis purpurea L., phytoconstituents, Foxglove plant, Cardiac glycosides, Cardenolides, Cytotoxic, Antioxidant
Introduction
The plant’s name, Digitalis (from the Latin digit, finger) describes the finger-shaped purple flowers it Bears. The tall flower spikes with charming tubular Flowers of foxglove add both height and vertical Accent to your garden without staking. Perennial Digitalis blooms attract hummingbirds and bees. As a bonus, the deer do not like the foliage Digitalis purpurea contains cardiac glycosides, Volatile oil, fatty matter, starch, gum, and sugars. They possessed cardiovascular, cytotoxic, anti-diabetic, antioxidant, insecticidal, immunological, hepatic, neuro, and cardioprotective effects. The use of herbs as medicine is the oldest form of healthcare known to humanity and has been used in all cultures throughout history(Barnes et al., 2007). Medicinal plants are Widely distributed throughout the world but most abundantly in tropical countries. It is estimated That about 25% of all modern medicines are Directly or indirectly derived from higher plants(WHO, 2005; De Smet, 1995).
Profile plant:-
Taxonomic Classification of Digitalis purpurea
Plant:Kingdom : Plantae
Subkingdom : Viridiplantae
Infrakingdom : Streptophyta
Superdivision : Embryophyta
Division : Tracheophyta
Subdivision : Spermatophytina
Class : Magnoliopsida
Superorder : Asteranae
Order : Lamiales
Family : Plantaginaceaek
Genus : Digitalis
Species : D. purpurea


Pharmacognostic account of digitalis:
Synonyms:- Digitalis Leaves, Foxglove Leaves
Part used: It consists of dried leaves of Digitalis purpurea
Family:- Scrophulariaceae Ii is collected from 2 nd year—growth of the plant in June before the opening of the flower. Drying is done. By applying artificial heat (temperature not more than 65°C). Leaves should contain NLT 5% of Moisture.
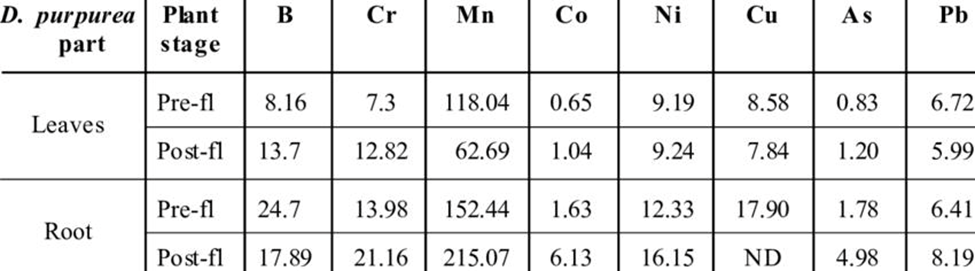
The concentration of mineral elements in D. purpurea Concentration of Elements (µg/g).
Antiproliferative effect of digitoxin and digoxin

Digoxin
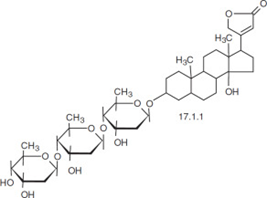
Digitoxin
Morphology
Digitalis purpurea is an herbaceous biennial also called a short-lived Perennial plant. The leaves of digitalis are spirally arranged, simple, 15–35 cm (4.0–13.8 in) long and 5–15 cm (2–5 in) broad, and are covered with grey-white pubescent and glandular hairs, also they have Imparted a woolly texture. Digitalis purpurea is a native European Foxglove woodland plant with spikes of tubular purple flowers with a Spotted throat. Digitalis lanata is an erect perennial forming a rosette of Evergreen lance-shaped leaves, with cream or pale-yellow flowers 2.5cm Long, veined with brown, in a long spike in summer.
Macroscopic Characteristic:

- Colour – Green, Dark Greyish-green
- Odour – Slight
- Taste – Bitter
- Size – 10-40 cm long & 4-20 cm wide
- Shape – Ovate-Lanceolate to broadly ovate; with irregularly crenate Or serrate or occasionally dentate margin.
Microscopic Characteristics:
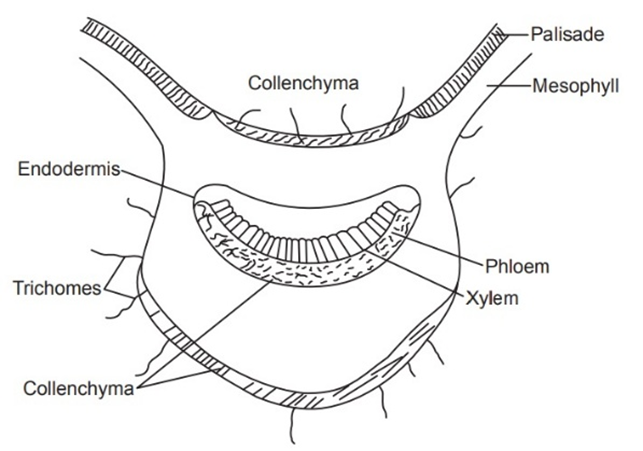
Dorsiventral Leaf; Amniocytic Stomata; uniseriate stomata; Multicellular(3-5 cells); Bluntly Points; Glandular Trichomes; Collapsed Celled covering trichomes; Free from Calcium Oxalate and Sclerenchyma; Starch grain; collenchyma.
Traditional use:
Digitalis is used to treat heart rhythm problems (atrial arrhythmias) and Also treat congestive Digitalis is used to treat heart rhythm problems (atrial arrhythmias) and heart failure (CHF). Digitalis also increases blood flow throughout your body and reduces swelling in your hands and Ankles. Earlier Digitalis was used for the treatment of peptic ulcers, Headaches, boils, and paralysis Externally, digitalis species were used For the granulation of poorly healing wounds and to cure ulcers. After William Withering’s work, the digoxin is isolated from the digitalis Species as a life-saving cardiac drug.
Chemical Constituents :
0.2-0.45% of primary and secondary glycosides, digitoxin, gitoxin, Glucogitaloxin, genotoxin, cardiac glycosides, digitoxin, digoxin,
Ouabain, oleandrin and procellariid, volatile oil, fatty matter, starch, gum
And sugars, glucodigifucoside, diacetyl lanatoside C and digoxin];
[Aglycone diginatigenin: lanatoside D, diginatin, diginatigenin
Gitaloside]; [Aglycone gitaloxigenin: lanatoside E, glucoverodoxin (0.01
To 0.14%), glucoverodoxin (0.02 to 0.12%) and gitaloxin]; [Pregnane Derivatives: including digifolein, glucodigifolein, diginin, digipronin,
Lanafolein, and gitonine]; [Steroid saponins: including lanagitosides I
And II, lignin, desglucolanatigonin, aglycones including tigogenin,
Digoxigenin, digitogenin, and gitogenin] [43].Phenylethyl glycosides,
Verodoxin.
Test for Digitalis:
- Killer-kiliani Test for Digitoxose
- Legal Test
- Baljet Test
1.killer-kiliani test :-
Purpose-
Detects the presence of deoxysugars, particularly digitoxose
Reagents-
Glacial acetic acid, 0.1?rric chloride solution, concentrated sulfuric acid
Procedure-
Treat the sample with the reagents, and observe for a blue or green color
Result-
Blue or green color indicates the presence of digitoxose
2. Legal test:-
Alcoholic solution of drug sample + few drops of NaOH + 2 % solution of 3,5- dinitro benzoic acid ?appearance of pink color ? indicates the presence of cardiac glycosides.
3. Baljet test :-
Baljet’s test is a chemical test used to identify cardioactive glycosides.
The test involves:
Adding 1 mL of fraction A to a test tube
Adding 2 drops of picric acid
Making the solution alkaline with sodium hydroxide solution
The resulting color is turbid yellow to orange
Uses
Cardiovascular effects:
Cardiac glycosides possess positive inotropic effects due to the inhibition of Sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase, which allows calcium to Accumulate in myocytes leading to enhanced cardiac contractility. These Drugs also possess some antiarrhythmic activity but will induce Arrhythmias at higher dose levels.
Clinical data:-
Digitalis glycosides have been used clinically for the treatment of heart failure for more than 200 years and remain the source of commercial Digoxin preparations; however, a defined place in therapy remains under Debate. Reviews of the large, multicentre Digitalis Investigation Group Trial and other clinical trials have found no clear effect of digitalis on Mortality in heart failure. Some effects have been demonstrated for Secondary outcomes of decreased hospitalizations and clinical (symptomatic) deterioration.
Contraindications:
Do not allow children to come into contact with the potentially lethal Plant.
Pregnancy/Lactation:
Documented adverse cardiac reactions. Avoid use.
Interactions:
There are numerous interactions with digoxin and digitalis glycosides, Ranging from relatively minor (cimetidine, triamterene) to Life-threatening (amiodarone, furosemide, verapamil).
Adverse Reactions:
Adverse reactions are generally related to toxicity.
Toxicology:
All parts of the plant are toxic. The incidence of digitalis toxicity in Therapeutic use has been estimated to range from 5% to 25%. Ingestion Of extremely small amounts of the plant may be fatal to humans, especially children, and animals. Toxicity is cumulative.
CONCLUSION
According to all the aspects of this topic, we concluded that digitalis is a pharmacokinetically useful drug of choice for modern And traditional use. It is a costly drug but useful in anticancer therapy in A broad manner. We conclude that this review gives you better Information for your next studies and also for research and review
REFERENCES
- Digitalis purpurea L. USDA, NRCS. 2010. The PLANTS Database National Plant Data Center, Baton Rouge, LA 70874-4490 USA.
- Ebaid GM, Faine LA, Diniz YS, et al. Effects of digitonin on Hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia induced by high-sucrose intake. Food Chem Toxicol. 2006;44(2):293-299.16112785.
- Feussner JR, Feussner DJ. Reassessing the efficacy of digitalis: from Routine treatment to evidence-based medicine. Am J Med Sci. 2010;339(5):482-484.20228671.
- Gavidia I, Tarrío R, Rodríguez-Trelles F, Pérez-Bermúdez P, Seitz HU. Plant progesterone 5beta-reductase is not homologous to the animal Enzyme. Molecular evolutionary characterization of P5betaR from Digitalis purpurea. Phytochemistry. 2007;68(6):853-864.17184799.
- Hauptman PJ, Kelly RA. Digitalis. Circulation.1999;99(9):1265-1270.10069797.
- Antman EM, Wenger TL, Butler VP Jr, Haber E, Smith TW. Treatment Of 150 cases of life-threatening digitalis intoxication with Digoxin-specific Fab antibody fragments: final report of a multicenter Study. Circulation.1990; 81:1744–1752.
- Hickey AR, Wenger TL, Carpenter VP, Tilson HH, Hlatky MA, Furberg CD, Kirkpatrick CH, Strauss HC, Smith TW. Digoxin immune Fab Therapy in the management of digitalis intoxication: safety and efficacy Results of an observational surveillance study. J Am Coll Cardiol.1991; 17:590–598.
- Packer M, Gheorghiade M, Young JB, Costantini PJ, Adams KF, Cody RJ, Smith LK, Van Voorhees L, Gourley LA, Jolly MK, for the RADIANCE study. Withdrawal of digoxin from patients with chronic Heart failure treated with angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors. N Engl J Med.1993; 329:1–7.
- Withering W. An account of the foxglove and some of its medical uses, With practical remarks on dropsy, and other diseases. In: Willius FA, Keys TE, eds. Classics of Cardiology. New York, NY: Dover Publications Inc; 1941;1:231–252.
- Choi DY, Lee JY, Kim MR, Woo ER, Kim YG, Kang KW. Chrysoeriol potently inhibits the induction of nitric Oxide synthase by blocking AP-1 activation. J Biomed Sci. 2005;12(6):949-959.16228289.
- Dick M, Curwin J, Tepper D. Digitalis intoxication recognition and management. J Clin Pharmacol. 1991;31(5):444-447.2050830.
- Dec GW. Digoxin remains useful in the management of chronic heart failure. Med Clin North Am. 2003;87(2):317-337.12693728.

 Atole S. S
Atole S. S







 10.5281/zenodo.14250300
10.5281/zenodo.14250300