Abstract
Enzalutamide's bulk and mixed dosage forms may now be quantitatively estimated using a new, sensitive, and straightforward UV approach. Enzalutamide is an androgen-receptor signalling pathway inhibitor as well as a competitive inhibitor of dihydrotestosterone, the active metabolite of testosterone. At 240 nm, the drug's maximum absorption was discovered. Since methanol was identified to dissolve enzalutamide, it was utilized as a solvent to perform the work. The method's ultimate linearity range was determined to be 3-11 µg/ml, with an R2 value of 0.9996. A %RSD of less than 2, which is well within, denotes a strong and precise approach. The 100–101% recovery rate was discovered, demonstrating the accuracy of the procedure. The approach was validated in accordance with the ICH criteria, and good findings were obtained. The values for LOD and LOQ were found to be 0.1288 and 0.390, respectively. Studies on the drug's stability reveal that it is unstable in a variety of stress situations, including oxidation, base, acid and water.
Keywords
Enzalutamide, castration-resistant prostate cancer, Androgen receptor, Methanol, ICH guidelines, Stress condition
Introduction
Spectroscopy is a branch of science that studies the interaction between EMR and matter. The basic law that relates absorbance and concentration is the Beer-Lambert law.
Beer-Lambert Law:
Beer-Lambert's law is an essential relationship in spectroscopy that describes the connection between the concentration of a solution and the amount of light absorbed by that solution. The law states that the absorbance (A) of a sample is directly proportional to the concentration (c) of the absorbing species in the sample and the path length of the light through the sample. (1-9) Enzalutamide is a competitive inhibitor of dihydrotestosterone, the active metabolite of testosterone, and an inhibitor of the androgen-receptor signalling pathway. (10)
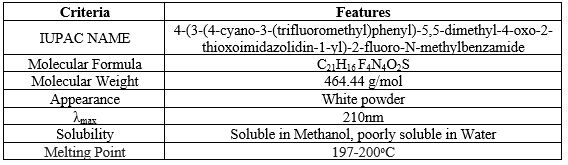
Table 1: Drug profile of Enzalutamide
Figure 1: Structure of Enzalutamide
A search through the literature revealed that the drug has been examined with a variety of analytical approaches, notably HPLC, RP-UPLC, UPLC-MS-MS, and LC-tandem mass spectrometry. The development of a basic, precise, reliable, and repetitive Visible Spectrophotometric method for the quantification of Enzalutamide in bulk and in combined dosage form is described in the current work. According to ICH Guidelines, the developed approach was validated. (11-25)
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
Chemicals and reagents:
Instrumentation:
The proposed work was carried out on a UV Spectrophotometer, which is a double beam double detector configuration with a 1 cm quartz cuvette cell. All weighing was done on PGB-200 model weighing balance.
Selection of Solvents:
On the basis of solubility study Methanol was selected as the solvent for dissolving Enzalutamide.
METHOD DEVELOPMENT:
Preparation of Standard Stock Solutions of Enzalutamide:
Stock Solution A (1mg/ml):
Accurately weighed 10mg of Enzalutamide into a 10ml volumetric flask, dissolved in 5ml methanol and made up the volume to 10ml with distilled water.
Stock Solution B (100µg/ml):
1ml of stock solution A was taken in 10ml volumetric flask and added 4ml of methanol and made up the volume with water.
Dilutions:
Further serial dilutions were done by taking 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9, 1.1ml of stock B and made up the volume with Methanol and water up to 10ml to give concentrations 3,5,7,9,11µg/ml.
Selection of Analytical Wavelength:
An appropriate aliquot portion of 0.7ml from stock solution B was transferred to 10 mL volumetric flasks; the volume was made up to the mark using Methanol and water (7µg/ml working standard). Drug solution was scanned against a Methanol blank between 200 nm to 400 nm range. The drug showed ?max at 240nm.
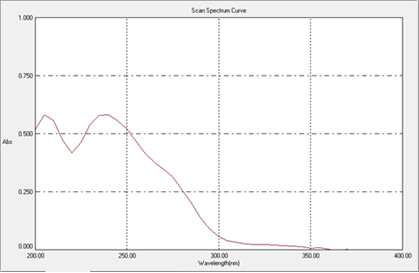
Figure 2: UV spectrum of Enzalutamide (240nm)
METHOD VALIDATION:
The suggested approach has undergone rigorous validation in terms of linearity, accuracy, precision, limits of detection (LOD) and quantification (LOQ), robustness, ruggedness and assay.
Determination of Linearity:
A working standard solution of the drug was divided into five separate 10 mL volumetric flasks using an appropriately measured proportionate fraction. Methanol and water were used to make up the volume to the required level in order to produce concentrations (3–11µg/mL). The absorbance of these solutions was measured at 240nm. The calibration curve was displayed in a concentration versus absorbance graph.
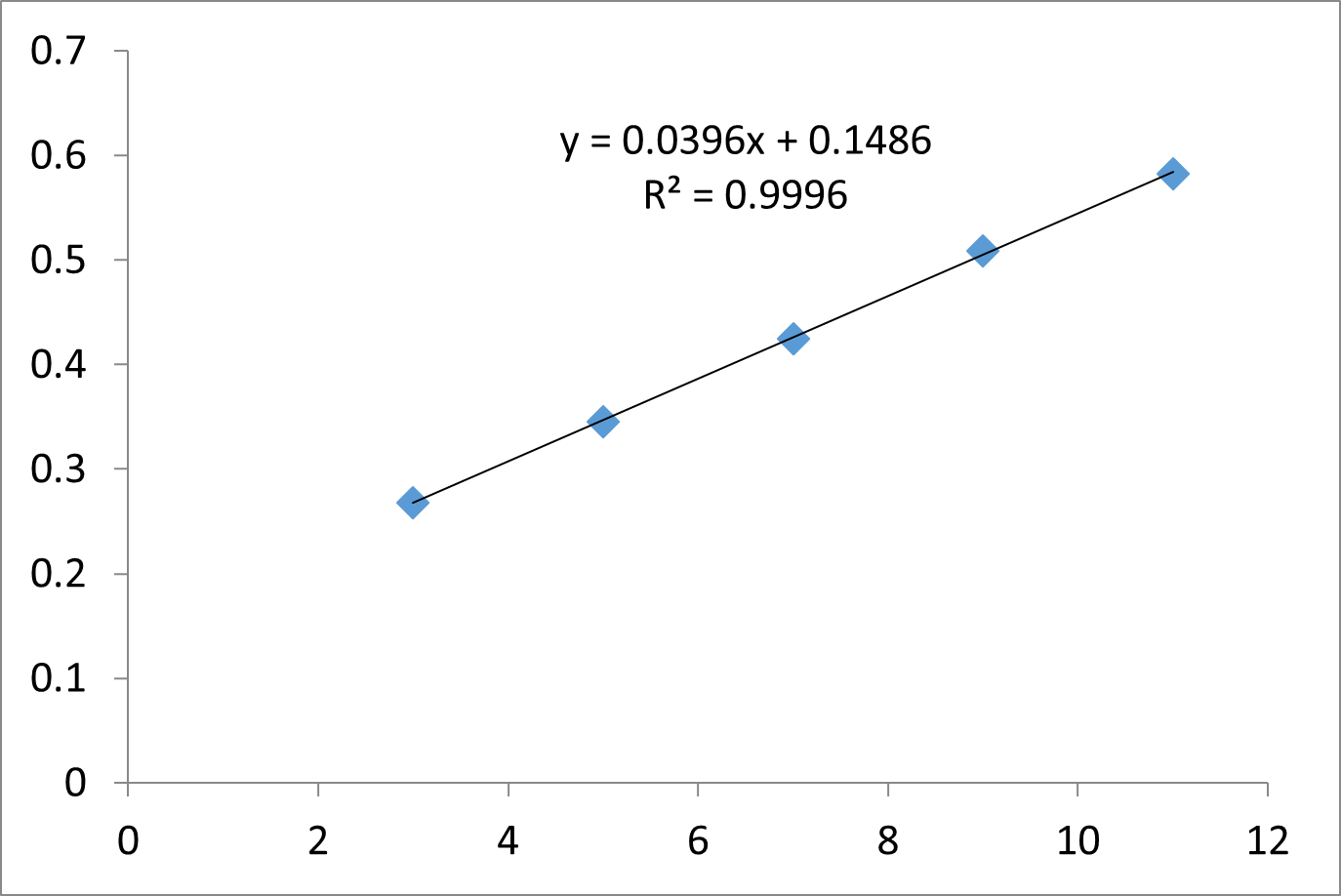
Figure 3: Calibration Curve of Enzalutamide
On the basis of a recovery, research carried out using the conventional addition approach, the proposed method's accuracy was determined. The tablet powder was re-analysed using the recommended method after being mixed with a known quantity of standard medication solutions to make final concentrations of 50%,100%, and 150%. The absorbance recorded and the % recoveries were calculated.
Precision:
Precision was determined as intra-day and inter-day variations. The results of the intra-day and inter-day precision research were determined by calculating absorbance at the same drug concentrations (7 ppm) three times on the same day and three different days over the course of a week at a wavelength of 240nm. The results were reported.
Ruggedness:
The suggested method's durability was assessed through the analysis of portions from uniform slots by two different analysts under similar operational and environmental circumstances. The results were reported accordingly.
Robustness:
Robustness was obtained by performing the analysis at two different wavelengths (±5 nm). The results were reported.
LOD & LOQ:
LOD & LOQ gives information about the sensitivity of the method. The values reported indicate that the method is highly sensitive.
DEGRADATION STUDIES:
Stock preparation:
Prepared 7µg/ml stock solution by taking 0.7ml ml of stock B solution and dissolving in methanol and water (5:5) in 10ml volumetric flask.
Acid degradation:
Added 1ml of 1N HCl to 1 ml of working standard and made up the volume to 10 ml with solvent and kept the prepared solution aside for 24 hrs.
Alkaline degradation:
To 1 ml of working standard solution, 1 ml of 1N NaOH was added and made up the volume to 10 ml with solvent and kept aside for 24hrs.
Oxidative degradation:
To 1 ml of the working standard solution added 1 ml of H2O2 and made up the volume to 10 ml with solvent.
Degradation by hydrolysis: To 1 ml of the working standard solution added 1 ml of water and made up to the mark with solvent.
Assay:
Table no 2 Assay Results
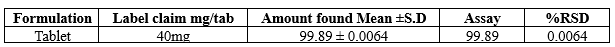
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION:
Method Validation:
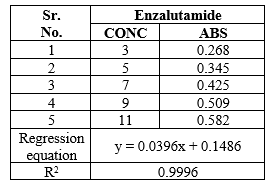
Linearity:
The calibration curve has a regression coefficient of 0.9996 and displayed linearity in the 3–11 µg/ml range.
Table 3: Linearity of Enzalutamide
Accuracy:
The % RSD of the present work was found to be within and less than 2. The %
recovery was between 99-100%.
Table 4: Accuracy data of the UV method
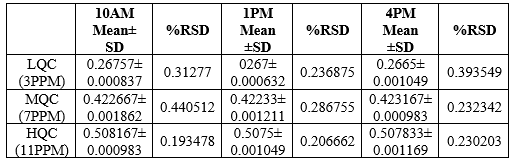
Precision:
The % RSD of Enzalutamide was found to be 0.232 for intraday precision and. 0.232 for interday precision, respectively.
Table 5: Intraday Precision Results
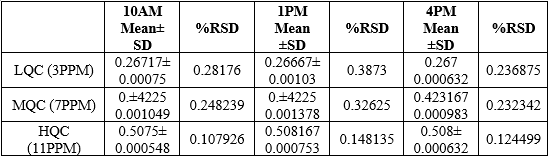
Table 6: Interday precision Values

Robustness:
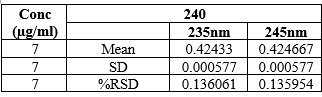
A small variation of the wavelength (±5nm) was applied to the presented method and it was found that the %RSD was within the limits and the values were 0.136061and 0.135954.
Table 6: Robustness Values
Ruggedness:
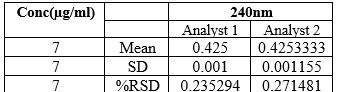
Two different analysts performed the ruggedness studies under same conditions and it was found that the % RSD was within the limits
Table 7: Ruggedness Result
LOD & LOQ:
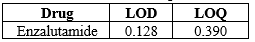
The study for LOD & LOQ was carried out and the obtained results are described in the table below.
Table 8: LOD & LOQ Values
Stability Studies:
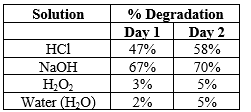
A 7µg/ml solution of Enzalutamide was obtained and its stability was tested (24hours) in 0.1N HCl, 0.1N NaOH, Hydrogen Peroxide, and water. The results are shown in below table.
Table 9: Stabilities Studies of Enzalutamide
DISCUSSION:
Using UV spectroscopy, we created a method in this work for estimating Enzalutamide in both bulk and pharmaceutical combined dosage forms. With the use of various techniques like HPLC, RP-UPLC, and others, there have been numerous methods. We used UV spectroscopy to carry out the method's development and validation.
CONCLUSION:
Based on the aforementioned findings, it can be said that the suggested method is straightforward, sensitive, exact, repeatable, and affordable to determine enzalutamide in bulk and combined dosage form. The drug's R2 value is 0.9996, and an %RSD of less than 2 suggests the method is robust and precise. The lowest LOD value can be used to determine the method's sensitivity. ?gradation indicates high level of degradation that means the drug is highly unstable in different stress conditions.
REFERENCES:
- G.R. Chatwal, S.K. Anand, Instrumental method of Chemical Analysis, 5th ed, Himalaya Publishing House, New Delhi, 2011, 2.108-2.110p.
- D.A. Skoog, F.J. Holler, T.A. Nieman, Principal of Instrumental Analysis,5th ed, Thomson (Brook/Cole), 2004, 378p.
- Davidson AG (2002) Ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrophotometry. In BeckettAH, Stenlake JB, (4thedn), Practical Pharmaceutical chemistry. CBS Publishers and distributors, New Delhi, 275-278.
- A.H. Beckett, J.B. Stenlake, Practical Pharmaceutical Chemistry, 4th ed, Part 2, CBS Publisher and Distributor New Delhi, 2004, 275-278p.
- Patil KM, Bodhankar SL (2005) High-performance thin-layer chromatographic determination of lamotrigine in serum. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 823: 152-157.
- K.A. Connors, A textbook of pharmaceutical analysis, 3rd ed, John Wiley and Sons, 2007, 179-185p.
- D.G. Watson, A textbook for pharmacy students and pharmaceutical chemists, 2nd ed, Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, 2005, 89-91p.
- H.H. Willard, L.L. Merritt, J.A. Dean, F.A. Settle, Instrumental methods of Analysis,7th edn, CBS Publishers New Delhi 1986.159-161p.
- Dr. B.K. Sharma, Instrumental Method of Chemical Analysis, 28th ed, Goel Publishing house, 2012, S-72-S-74p.
- Tran C, Ouk S, Clegg NJ, Chen Y, Watson PA, Arora V, Wongvipat J, Smith-Jones PM, Yoo D, Kwon A, Wasielewska T. Development of a second-generation antiandrogen for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Science. 2009 May 8;324(5928):787-90.
- Song JH, Kim TH, Jung JW, Kim N, Ahn SH, Hwang SO, Kang NS, Yoo SE, Koo TS. Quantitative determination of enzalutamide, an anti?prostate cancer drug, in rat plasma using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry, and its application to a pharmacokinetic study. Biomedical Chromatography. 2014 Aug;28(8):1112-7.
- Ma X, Zhou W, Zou Q, Ouyang P. Structural elucidation of the impurities in Enzalutamide bulk drug and the development, validation of corresponding HPLC method. Journal of Pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. 2016 Nov 30; 131:436-43.
- Katakam LN, Dongala T, Ettaboina SK. Quality by design with design of experiments approach for development of a stability?indicating LC method for enzalutamide and its impurities in soft gel dosage formulation. Biomedical Chromatography. 2021 May;35(5): e5062.
- van Nuland M, Hillebrand MJ, Rosing H, Schillings JH, Beijnen JH. Development and validation of an LC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of abiraterone, enzalutamide, and their major metabolites in human plasma. Therapeutic drug monitoring. 2017 Jun 1;39(3):243-51.
- Gungor S, Akbel E, Bulduk ?. Development, Optimization, and Validation of HPLC Method for Quantification of Enzalutamide in Bulk and Pharmaceuticals. Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal. 2023 Jun;57(3):451-9.
- Puszkiel A, Plé A, Huillard O, Noé G, Thibault C, Oudard S, Goldwasser F, Vidal M, Alexandre J, Blanchet B. A simple HPLC-UV method for quantification of enzalutamide and its active metabolite N-desmethyl enzalutamide in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Journal of Chromatography B. 2017 Jul 15;1058:102-7.
- Suresh PS, Srinivas NR, Mullangi R. Review of HPLC and LC–MS/MS assays for the determination of various nonsteroidal anti?androgens used in the treatment of prostate cancer. Biomedical Chromatography. 2018 Jan;32(1):e4034.
- Nerkar PP, Ansari S, Chalikwar S. Development and Validation of Stability Indicating RP-HPLC Method for Determination of Enzalutamide. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Nanotechnology (IJPSN). 2019 Sep 30;12(5):4635-45.
- Sulochana SP, Saini NK, Daram P, Polina SB, Mullangi R. Validation of an LC–MS/MS method for simultaneous quantitation of enzalutamide, N-desmethylenzalutamide, apalutamide, darolutamide and ORM-15341 in mice plasma and its application to a mice pharmacokinetic study. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. 2018 Jul 15;156:170-80.
- Sitamahalakshmi DS, Bharath P, Ramachandran D, Ramamurty DS. Development and Validation of Stability Indicating RP-HPLC Method for Quantitative Estimation of Enzalutamide in Enzalutamide Capsules Dosage Form. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation. 2023 Apr 1;13(2).
- Prajapati JD, Chhalotiya KU, Prajapati DM. Quantification of newer anticancer drug enzalutamide by stability indicating RP-LC method and UV-visible spectroscopic method in bulk and synthetic mixture. J Mol Oncol Res. 2017; 1 (2): 65-85. 66 J Mol Oncol Res. 2017 Volume 1 Issue. 2017; 2:3.
- Bennett D, Gibbons JA, Mol R, Ohtsu Y, Williard C. Validation of a method for quantifying enzalutamide and its major metabolites in human plasma by LC–MS/MS. Bioanalysis. 2014 Mar;6(6):737-44.
- Zg K, Ss P, Pk D, Po P. Validated RP -HPLC Method for Determination of Enzalutamide in Bulk Drug and Pharmaceutical Dosage Form. Indian Drugs. 2016 Nov 1;53(11). Soto C, Saavedra R, Toral MI, Nacaratte F, Poza C. Preliminary studies for ciclopirox olamine determination by thermal lens spectrophotometry. Microchemical Journal. 2016 Nov 1; 129:36-40.
- Patel AI, Gosai S, Jadav K, PATEL AB, PATEL NK. Stability indicating analytical method development and validation of Enzalutamide in tablet dosage form by RP-UPLC. Journal of the Turkish Chemical Society Section A: Chemistry. 2020 Oct 10;7(3):845-50.
- Jayagopal B, Murugesh S. QBD-driven HPLC method of Enzalutamide: Degradation pathway proposal, structure elucidation, and in silico toxicity prediction. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis. 2021 Sep 5; 203:114231

 Gangu Sreelatha*
Gangu Sreelatha*




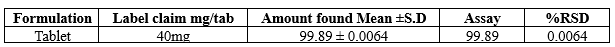







 10.5281/zenodo.11313121
10.5281/zenodo.11313121