Abstract
Dysmenorhea characterized by menstrual pain, is a common condition affecting many women worldwide. This study aimed to standardize the formulation of Moringa oleifera soup powder, assessing its physical and chemical parameters to ensure quality and adherence to standards. The methodology involved grinding the ingredients into a fine powder, sieving, shade drying, and mixing them before storage. Evaluation parameters included sensory evaluation, determination of ash value, pH measurement, moisture content analysis, and rheological testing for flow characteristics Results indicated optimal moisture content within standard ranges, suitable for storage, and adequate mineral composition as evidenced by ash value. pH levels fell within acceptable ranges, ensuring stability and compatibility for consumption. Sensory evaluations confirmed palatability, visual appeal, aroma, and texture met standard specifications. Chemical evaluation revealed consistent bulk and tapped densities across formulations, with angle of repose falling within the 'Good' flowability category. The Moringa oleifera soup powder formulations met required physical and chemical parameters, indicating quality and adherence to standards. This study contributes to the standardization of Moringa oleifera soup powder formulation, ensuring its quality and suitability for consumption. Further research could explore additional quality parameters or investigate the efficacy and health benefits of the formulated product.
Keywords
Dysmenorrhea, Formulation, Moringa oleifera, Menstural cramps
Introduction
Dysmenorrhea
Dysmenorrhea refers to the medical condition of experiencing pain and discomfort during menstruation, commonly known as menstrual cramps. There are two main types of dysmenorrhea:[5,6]
Primary Dysmenorrhea:
This is the more common type and is not associated with any other medical condition. It usually begins 1-2 days before menstruation and may last from 2 to 4 days. The pain is typically lower abdominal and can be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and diarrhea[5,6].
Secondary Dysmenorrhea:
This type is associated with an underlying reproductive health issue, such as endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease. The pain in secondary dysmenorrhea often starts earlier in the menstrual cycle and lasts longer than primary dysmenorrhea. It tends to worsen with age.[5,6]
Symptoms:
Primary Dysmenorrhea:
Common symptoms include cramping pain in the lower abdomen, which can be accompanied by lower back pain and radiating pain in the thighs. Other symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fatigue.[5,6]
Secondary Dysmenorrhea:
In addition to menstrual cramps, secondary dysmenorrhea is associated with symptoms related to the underlying condition causing the pain. For example, conditions like endometriosis or fibroids may cause additional pelvic pain.[5,6]
Causes:
Primary Dysmenorrhea:
The exact cause is not well understood, but it is thought to be related to the release of prostaglandins, hormone-like substances that play a role in the contraction of the uterus.
Secondary Dysmenorrhea:
Underlying reproductive health issues such as endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), fibroids, or adenomyosis can contribute to menstrual pain.[5,6]
Factors:
Several factors can contribute to an increased risk of experiencing dysmenorrhea (menstrual cramps). Common risk factors include:[6]
Age:
Dysmenorrhea often starts during adolescence when menstruation begins and tends to be more common in younger individuals. The prevalence tends to decrease with age.
Early Menarche:
Starting menstruation at an early age may be associated with a higher risk of dysmenorrhea.
Heavy Menstrual Flow:
Women who experience heavier menstrual bleeding may be at an increased risk of developing dysmenorrhea.
Family History:
A family history of dysmenorrhea may suggest a genetic predisposition to experiencing menstrual cramps.
Smoking:
As we know smoke contain nicotine and that constrict the vessels that results in dysmenorrhea.
Nulliparity:
Women who have not given birth (nulliparous) may be at a higher risk of dysmenorrhea compared to those who have had children.
Psychological Factors:
Stress, anxiety, and depression may contribute to the perception of pain and could exacerbate menstrual cramps.
Irregular Menstrual Cycles:
Women with irregular menstrual cycles may be more prone to dysmenorrhea.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID):
In cases of secondary dysmenorrhea, underlying conditions such as PID can increase the risk of experiencing menstrual pain.
Endometriosis or Fibroids:
Conditions like endometriosis or the presence of uterine fibroids can be associated with more severe menstrual cramps.
Menstrual Cramp Severity:
Discomfort that is tolerable and does not significantly interfere with daily activities.
Pain that is noticeable and can affect daily activities but is manageable.
Intense pain that can be debilitating, requiring rest and possibly medication for relief.
Plant profile
Moringa oleifera
Moringa oleifera is often referred to as miracle tree that belongs to Moringaceae family. Moringa oleifera is plant which is recognised for its therapeutic attributes. Moringa oleifera is rich in essential phytochemicals found in its leaves, flowers, pods, and seeds, contributing to its diverse array of health-promoting compounds. It is proven in a study that it contain 7 times more vitamin c than orange , 10 folds more Vitamin A than carrots, 17 folds more calcium than milk , 9 folds more protein than yoghurt, 15 folds more potassium than banana, 25 folds more iron than Spinach.[13,17,32]
Common name –
Miracle tree, horseradish tree.
Location –
Moringa oleifera, originating from regions in Africa and Asia, is characterized by its rapid growth and ability to thrive in arid conditions, making it a resilient and drought-resistant tree.
Cultivation –
It is cultivated in tropical and sub-tropical areas. Moringa oleifera can grew in any soil condition but prefer drained, loamy and sandy soil with the temperature range for growing Moringa oleifera is 21-35°C. The pH of Moringa oleifera typically falls within the range of slightly acidic to neutral, approximately ranging from pH 5 to 9.
Pharmacognostic Studies -
Vernacular names of Moringa oleifera in different states of India.
Table 1- Vernacular names[10]
Table 2: Taxonomy [10]
Table 3: Morphology

Fig 1 Moringa oliefera[37]
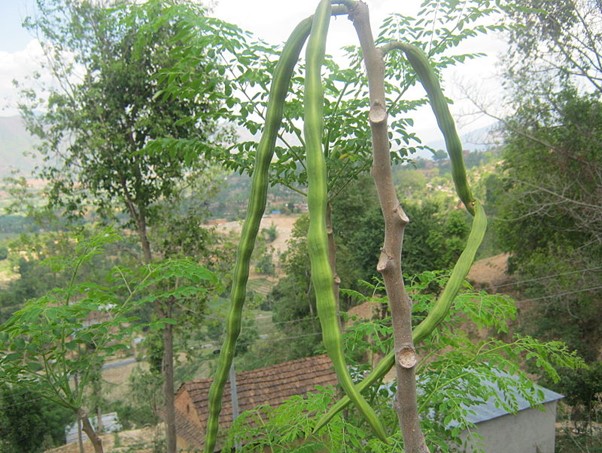

Fig. 2 Moringa oliefera pods[37]

Fig. 3 Moringa oliefera flower[37]

Fig. 4 Moringa oliefera pollens[37]

Fig. 5 Moringa oliefera seeds[37]
Chemical constituents
Moringa oleifera consists of numbers of chemical which can use as a health promoter also and these are vitamins (Vitamin A, Vitamin B, Vitamin C) Carotenoids, Tannins, Saponin, phenolic acid, Isothiocyanates, Minerals( Calcium, Iron, Potassium and magnesium).[20] Compounds like isothiocynates, nitriles and thiocarbamates these compounds are recognized for their potent spasmolytic effects, which means they exhibit strong muscle relaxant properties, which can help in menstrual cramps as well.[10] Thiocarbamates, Glycosides & Nitriles present in this plant contribute to its ability to reduce blood pressure. Moringa oleifera is a rich source of iron which Increase the hemoglobin which can ease the mensuration cramps and also helps in during the pregnancy. The presence of the flavonoids, phenols, antioxidants can give the analgesic as well as anti-inflammatory effects.[8]
Pharmacological Properties :-
Anti-inflammatory activity:-. Inflammation is the innate reaction of the body to injury, infection, or irritation, serving as a natural response mechanism. Common signs of inflammation include redness, swelling, heat, and pain at the affected site. Moringa oleifera posses anti-inflammatory property because of the presence of Isothiocyanates. Research has explored the potential anti-inflammatory effects of Moringa oleifera, attributing this property to its abundance of bioactive compounds such as polyphenols and isothiocyanates. These compounds may help reduce inflammation in the body, providing potential benefits for various conditions.[9,11,12,13]
Antidiabetic activity:-
Moringa oleifera has been explored for its potential antidiabetic effects. Research indicates that elements in Moringa oleifera, including quercetin, chlorogenic acid, kaempferol, glucomoringin and isothiocyanates might contribute to reducing blood sugar levels by enhancing insulin sensitivity. Additionally, Moringa oleifera may have antioxidant properties that protect pancreatic beta cells, which play a crucial role in insulin production.[23,28]
Antimicrobial activity :-
Moringa oleifera has demonstrated antimicrobial properties, attributed to its various bioactive compounds, including alkaloids, flavonoids, and phenolic acids. These components may exhibit antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral activities. Moringa oleifera has been studied for its potential to inhibit the growth of certain bacteria and fungi, showing promise as a natural antimicrobial agent. However, while it shows potential in lab studies, more research is needed to understand its effectiveness in real-world applications and its impact on different types of microorganisms. The chemical entity which is isolated from the methanol extract of Moringa oleifera that is 4-(a-L-rhamnopyranosyloxy) benzyl Isothiocyanate, gave the antimicrobial activity.[9,12]
Antihypertensive activity:-
Moringa oleifera has been investigated for its potential antihypertensive (blood pressure-lowering) effects. Compounds like quercetin, chlorogenic acid, and isothiocyanates found in Moringa may contribute to its ability to relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure.[9,34]
Ocular activity:-
Moringa oleifera has been studied for potential ocular (eye-related) benefits. The plant contains nutrients like Beta-carotene, Vitamin A, Vitamin C, and Zinc, which are important for eye health. These nutrients contribute to the maintenance of the cornea, prevention of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), and overall support for good vision.
Antilipidemic activity:-
Moringa oleifera has been investigated for its potential antilipidemic effects, referring to its ability to lower lipid levels in the blood. Some studies suggest that Moringa oleifera may have a positive impact on lipid profiles by reducing levels of cholesterol and triglycerides. This effect is attributed to bioactive compounds like quercetin, beta-sitosterol, and chlorogenic acid found in Moringa oleifera.[28]
Analgesic activity:-
Moringa oleifera has been explored for potential analgesic effects. Some studies suggest that certain compounds in Moringa, such as alkaloids and flavonoids, may have mild analgesic properties.[9,11,13]
Anti-cancer activity:-
Moringa oleifera has been studied for its potential anti-cancer properties. Compounds found in moringa, namely thiocarbamate and isothiocynate, exhibit properties that hinder the growth of cancerous cell. These effects could potentially play a role in impeding the growth of cancer cells and preventing the spread of tumors.[23]
Antiulcer activity:-
Moringa oleifera has been investigated for its potential antiulcer activity. Some studies suggest that its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties may help protect the gastric mucosa and alleviate symptoms associated with ulcers. Compounds like quercetin and chlorogenic acid found in Moringa have been implicated in these protective effects.[9,12,19]
Cardiovascular activity:-
Moringa oleifera has been studied for its potential cardiovascular benefits. The presence of niazirmin A, niazirimin B, and niazimincin in Moringa appears to be associated with its favorable impact on cardiovascular health. These compounds may contribute to benefits such as blood pressure reduction, cholesterol level decrease, and enhancement of overall heart well-being.[1,19]
Antispasmodic activity:-
Moringa oleifera has been suggested to possess antispasmodic activity, meaning it may have the ability to alleviate muscle spasms. This potential benefit is attributed to certain bioactive compounds found in Moringa, including flavonoids and alkaloids. Extensive pharmacological research on moringa leaves reveals that the ethanol extract and its components demonstrate antispasmodic properties, likely by blocking calcium channels.[8,12]
Ginger
Synonym
Ginger root, zingiberic, zingiber, rhizome
Biological source
It is obtained from the rhizome of gingiber officinale.
Family
Zingiberaceae
Pharmaceutical uses
- Used in the treatment of some types of “stomach problems,” including motion sickness, morning sickness, colic ,upset stomach, gas ,diarrhea, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Pain relief from rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Osteoarthritis
- Menstrual pain
- Upper respiratory tract infection
- Cough
- Respiratory problems
- Migraine headache
- Used as a flavoring agent
Carom seed
Synonym
Ajwain
Biological source
It is obtained from the dried ripe seeds of Trachyspermum ammi (L.) Sprague
Family
Apiaceae
Pharmacological uses
- Antispasmodic
- Stimulant
- Tonic
- Carminative
Other uses
- Used as a spice
- Used as a flavoring agent.
Corn flour
It is a starch that is obtained from the endosperm of the kernel.
Uses
Anticaking agent
Thickening agent
MATERIAL AND METHOD
All the ingredients i.e moringa oleifera, ginger, carom seed and corn flour were collected and purchased from the local market near Paltan market Dehradun, Uttarakhand (Shop Name- Arya Vastu Bhandar).
Table 4: Ingredients with their properties
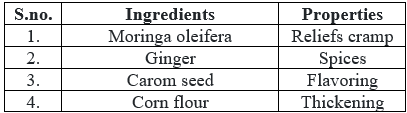
Table 5: Ingredients

Methodology
Table 6: Formulation
Procedure
- All the ingredients were collected from the local market.
- Weigh all the ingredients one by one accordingly.
- Grind the ingredients into fine powder.
- Pass the powder with Sieve no.85
- Shade dry all the ingredients.
- After weighing, pour it in a mortar and pestle.
- Mix all the ingredients carefully.
- Store it in a well closed container.
- Now, the evaluation parameters were performed.

Fig 6: Weighing & mixing of ingredients
Evaluation Parameters:
Sensory evaluation
- Taste
- Color
- Texture
- Odor
Determination of ash value
To ascertain the ash content, the process began with drying and grinding the sample. This prepared sample was then heated at 600°C in a furnace for 4 hours to remove all organic components. Meanwhile, crucibles were dried at 100°C for 2 hours, then cooled in a desiccator. Once cooled, 2.0g of the prepared sample was carefully weighed into the crucible. The crucible, now containing the sample, was then subjected to the same 600°C heat treatment for 4 hours. Following this, the resulting residue (ash) was weighed.[3]
Weight of ash, g = [{(weight of crucible + ash) ? (weight of the crucible)}/ weight of the sample] × 100
pH
1gm of powder was weighed in a beaker, 10ml of water was added into a beaker and then mix it, stand the solution for 5-10min and determine the ph of the solution by using pH strip or pH meter.
Determination of moisture content
To determine the moisture content, a sample was subjected to drying in an oven at 105°C for duration of 5 hours. The weight loss experienced during this process was then utilized for calculation.[3]
Moisture content (%) = (weight loss on drying/weight of the sample) × 100
Flow characteristic of powder (Rheology)
The rheological properties of the formulated powder were investigated using various methods to understand its behavior.[11]
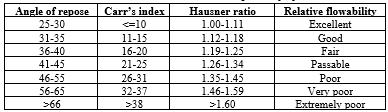
Angle of repose
This is how steeply the powder piles up when poured onto a flat surface. We measured this by pouring the powder through a funnel onto a flat surface and then calculating the angle formed by the pile.
?=tan?1h/r
Bulk density
This is how much mass of the powder fills a given volume. We determined this by measuring the mass of a known volume of powder. A higher bulk density indicates a denser powder.
Bulk density= Mass of powder/ True volume of powder
Tapped density
It measured after tapping or vibrating the powder to settle it. This gives us an idea of how the powder compacts under mechanical agitation.
Tapped density= Mass of powder/ Tapped volume of powder

Table 7. Flow characteristic of powder[11]
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
As a vital aspect of the standardization procedure, a comprehensive evaluation of the finished product, the Moringa oleifera soup powder, was conducted. Various physical and chemical parameters were meticulously tested to ensure its quality and adherence to standards. The moisture content of the Moringa oleifera soup powder was analyzed to ascertain its dryness and stability. The results revealed that the moisture content fell within the prescribed standard ranges, indicating optimal dryness and suitability for storage. The ash value, which provides insights into the inorganic content of the product, was determined. The findings demonstrated that the ash value of the Moringa oleifera soup powder met the specified standards, confirming its adequate mineral composition. The pH level of the soup powder was measured to assess its acidity or alkalinity. The results indicated that the pH fell within the acceptable range, ensuring optimal stability and compatibility with consumption. Sensory evaluations were conducted to assess the taste, color, odor, and texture of the soup powder. These attributes were found to align with the standard specifications, indicating palatability, visual appeal, pleasant aroma, and desirable texture.
Through rigorous testing and analysis, it was confirmed that the Moringa oleifera soup powder met the required physical and chemical parameters, signifying its quality and adherence to standards.
Table 8: Sensory evaluation
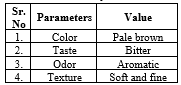
Table 9. Chemical evaluation
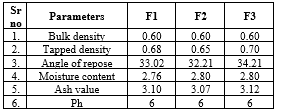
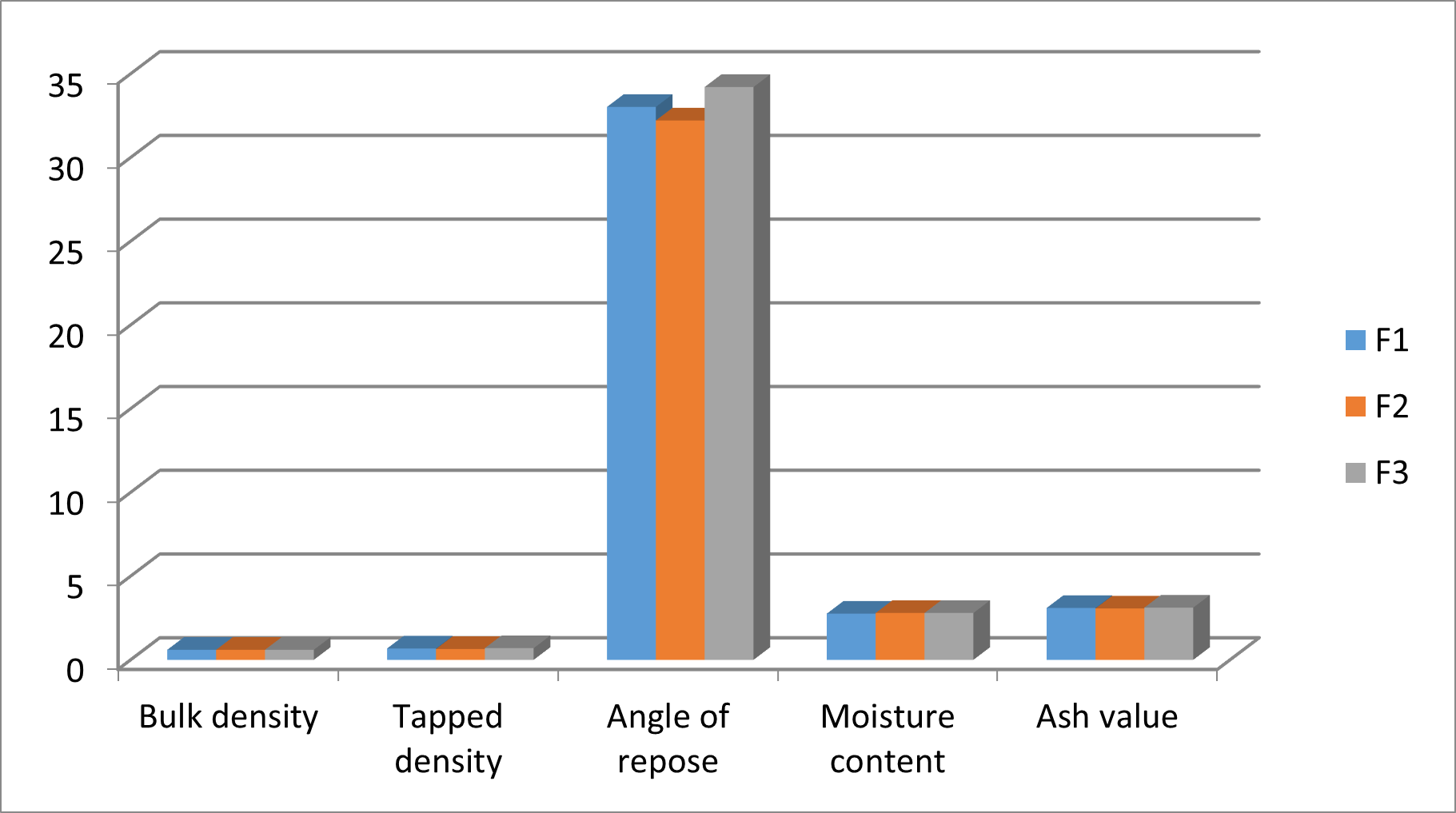
Fig 7: Gaphical Representation Of Result

Fig 8: Final formulation
CONCLUSION
The formulation and evaluation of Moringa oleifera leaves powder soup for dysmenorrhea yielded promising results, indicating its potential as a natural remedy for alleviating menstrual cramps and associated symptoms. Through a comprehensive analysis of various physical and chemical parameters, the quality and adherence to standards of the soup powder were confirmed. The sensory evaluation revealed favorable attributes, including a pale yellow color, bitter taste, aromatic odor, and soft, fine texture, all of which contribute to its palatability and consumer acceptance. Additionally, the pH level fell within the acceptable range, ensuring optimal stability and compatibility for consumption. Further analysis of moisture content and ash value demonstrated suitable dryness and mineral composition, respectively, aligning with standard specifications and indicating the product's quality and stability. Overall, the Moringa oleifera leaves powder soup exhibited promising characteristics, making it a potentially effective and natural option for managing dysmenorrhea. However, further studies and clinical trials may be warranted to validate its efficacy and safety in real-world applications.
REFERENCES
- Ashutosh Pareek, Malvika Pant, Madan Mohan Gupta, Pushpa Kashania, Yashumati Ratan, Vivek Jain, Aaushi Pareek, and Anil A. Chuturgoon(2023) national library of medicine Moringa oleifera: An Updated Comprehensive Review of Its Pharmacological Activities, Ethnomedicinal, Phytopharmaceutical Formulation, Clinical, Phytochemical, and Toxicological Aspects.
- Xinyue Su, Guanzheng Lu, Liang Ye, Ruyu Shi, Maomao Zhu, Xinming Yu, Zhiyong Li, Xiaobin Jia and Liang Feng (2023) Moringa oleifera Lam.: a comprehensive review on active components, health benefits and application School of Traditional Chinese Pharmacy, China Pharmaceutical University.
- Vibhuti batra, abhijit ganguli (2023) physiochemical, sensory and quality attributes of fermented vigna mungo soup fortified with moringa oleifera for leveraging affordable nutritional benefits.
- Patil, S., Mohite, B.V., Marathe, K.R. et al. Moringa Tree, Gift of Nature: a Review on Nutritional and Industrial Potential. Curr Pharmacol Rep 8, 262–280 (2022).
- Ana Abreu-Sánchez, María Laura Parra-Fernández, María Dolores Onieva-Zafra, Juan Diego Ramos-Pichardo, and Elia Fernández-Martínez (2020) national centre for biotechnology infotmation Type of Dysmenorrhea, Menstrual Characteristics and Symptoms in Nursing Students in Southern Spain.
- Inês Guimarães Ana Margarida Póvoa(2020) Primary Dysmenorrhea: Assessment and Treatment.
- Hervé Fernandez, Anthony Baread, Isabella Chanavaz-Lacheray (2020) journal of gynecology obstetrics and human reproduction Prevalence, intensity, impact on quality of life and insights of dysmenorrhea among French women: A cross-sectional web survey.
- Ahmad Faizal Abdull Razis, Muhammad Din Ibrahim, Saie Brindha Kntayya (2020) health benefits of moringa oleifera asian pac cancer prev.
- Muhammad kamran, shabbir hussain, muhhamad amin abid, shahzada khurram syed(2020) Postepy Biologii Komorki 47 (3), 321-334, 2020 Phytochemical composition of Moringa oleifera its nutritional and pharmacological importance.
- Mallenakuppe R, Homabalegowda H, Gouri MD, Basavaraju PS, Chandrashekharaiah UB(2019). History, Taxonomy and Propagation of Moringa oleifera- A Review. SSR Inst. Int. J. Life Sci., 2019; 5(3): 2322-2327. Namra Aziz,
- P. Wal, Ankita Wal and Monika S. Saxena (2019) Evaluation of a Polyherbal Powder for Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus Indian journal of pharmaceutical sciences
- V. N. Pandey1 , Vandana Chauhan1 , V. S. Pandey1 , P. P. Upadhyaya1 & Olga R. Kopp2 1Experimental Botany and Nutraceutical Laboratory, Department of Botany, DDU Gorakhpur University, Gorakhpur, India 2Utah Valley University, 800 West University Parkway MS 299. Orem, UT, USA (2018) Moringa oleifera Lam.: A Biofunctional Edible Plant from India, Phytochemistry and Medicinal Properties.
- Claudia Lizbeth Martínez-González , Laura Martínez, Efraín J Martínez-Ortiz , María Eva González-Trujano , Myrna Déciga-Campos, Rosa Ventura-Martínez , Irene Díaz-Reval (2017) national library of medicine Moringa oleifera, a species with potential analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities.
- Ma riagiulia Bernardi, Lucia Lazzeri, Federica Perelli, Fernando M. Reis, and Felice Petragliaa, (2017) national library of medicine Dysmenorrhea and related disorders.
- J.W. Fahey International Symposium on Moringa 1158, 209-224, 2015 Moringa oleifera: A review of the medicinal potential.
- Birendra kumar paikra, hemant kumar j. dhongade, bina gidwani (2017) national library of medicine phytochemistry and pharmacology of Moringa oleifera lam.
- Ramesh Kumar Saini, Iyyakkannu Sivanesan, and Young-Soo Keum (2016) national library of medicine Phytochemicals of Moringa oleifera: a review of their nutritional, therapeutic and industrial significance.
- Lakshmipriya gopalakrishnan, kruthi doriya, devarai santhosh kumar (2016) food science and human wellness, Moringa oleifera: a review on nutritive importance and its medicinal application.
- Dr. khursheed ansari(2016) journal of pharmacognosy and phytochemistry Sahjana (Moringa oleifera), pharmacognosy and pharmacology: A review.
- Sidney J. Stohs, Michael J. Hartman(2015) Phythotherapy Research Review of the Safety and Efficacy of Moringa oleifera.
- Alemayehu Toma and Serawit Deyno(2014) International Journal of Pharmacognosy Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activities of Moringa oleifera.
- Abdull Razis, Ahmad Faizal(2014) Health benefits of Moringa oleifera, Asian journal of cancer prevention.
- Lae Jung (2014) Soluble extract from Moringa olifera leaves with a new anticancer activity.
- Fatima H. M. EL- Massry; Mohamed E. Mossa; Saad M. Youssef(2013) Egyptian Journal of Agriculture Research Moringa oleifera plant “ Value and Utilization in Food Processing”.
- Durgesh Kumar Dubey, Jyotsna Dora, Anil Kumar and Rattan Kumar Gulsan(2013) International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Chemical Sciences A Multipurpose Tree- Moringa oleifera.
- Y. Singh and k. Prasad(2013) International Journal of Agriculture and Food Science Technology. Moringa oleifera leaf as functional food powder: Characterization and Uses.
- Madukwe E. U., Ugwuoke A. L. and Ezeugwu J. O.(2013 ) Department of Home Science, Nutrition and Dietetics, University of Nigeria Nsukka, Enugu State, Nigeria.
- Majambu Mvikay (2012) Front. Pharmacology Sec. Ethnopharmacology Therapeutic Potential of Moringa olifera leaves in Chronic Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia; A Review.
- M. Mbikay (2012) Therapeutic potential of Moringa oleifera leaves in chronic hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia: a review ethnopharmacology.
- Dr. Ritu Paliwal Veena Sharma Dr. Pracheta(2011) Asian Journal of Biotechnology A review on horse radish tree (Moringa oleifera): A multipurpose tree with high economic and commercial importance.
- J.N. Kasolo, G.S. Bimenya, L. Ojok, J. Ochieng, J.W. Ogwal-okeng(2010), Phytochemicals and uses of Moringa oleifera leaves in Ugandan rural communities Journal of Medicinal Plants Research.
- Mahmood, Khawaja Tahir, Mugal, Tahira, Haq, Ikram Ul(2010) Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research Moringa oleifera: a natural gift- A review.
- P Sudhir Kumar, Devasis Mishra, Gotum Ghosh, Chandra S Panda (2010) International Journal of Phytomedicine Medicinal uses and Pharmacological properties of Moringa olifera.
- S.Y. Dangi, C.I. Jolly & S. Narayanan (2008) Antihypertensive Activity of the Total Alkaloids from the Leaves of Moringa oleifera, Pharmaceutical Biology, 40:2, 144-148,
- Lawrence Onyango Arot Manguro & Peter lemmen(2006) Natural product research phenolics of Moringa olifera leaves
- Shradha saxena, neelam painuly, ashutosh kumar tiwari (2024) review on moringa oleifera dev bhoomi institute of pharmacy and research, dehradun.
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moringa_oleifera#cite_note-ted-13

 Shradha Saxena*
Shradha Saxena*
 Neelam Painuly
Neelam Painuly
















 10.5281/zenodo.12736962
10.5281/zenodo.12736962