Abstract
Device’s disease, also known as neuromyelitis optica (NMO), is a rare autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the optic nerves and spinal cord. It is characterized by severe inflammation and damage to these areas, leading to sudden vision loss, weakness, and sometimes paralysis of the limbs. Unlike multiple sclerosis (MS), another autoimmune disorder affecting the nervous system, Device’s disease tends to spare the brain. The exact cause is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve immune system dysfunction that targets proteins in the optic nerves and spinal cord. Diagnosis typically involves MRI scans, spinal fluid analysis, and antibody testing. Treatment aims to suppress immune activity with medications such as corticosteroids, immunosuppressant, and plasma exchange. Ongoing research seeks to improve understanding of the disease mechanisms and develop more effective therapies.
Keywords
Device disease, AQP4-Abs, neuromyelitis optica, history of neurology, multiple sclerosis, MOG –Abs, Immunosuppressant.
Introduction
Another name for Device’s illness is neuromyelitis optica (NMO), a rare autoimmune disease mostly affecting the optic nerves and spinal cord. Its distinctive characteristics include damage and inflammation to the myelin sheath, which shields nerve fibres.
Terminologies
Even though there were numerous various terminologies used to describe the relationship between optic neuritis myelitis, numerous instances report from the 20th century were referred to as "Device disease/ Device’s syndrome” : neuroopticomyélite (device), neuro-myelitis diffuse aiguë (Gault), neuro-optic myelitis, neuromyelitis optic (Erwin Stransky), acute neuro-optic myelitis, neuromielite optic, opthalmo-Pneuromyélite, oftalmomielitis, neuromielitis optics, andmielitis oftálmica.(1)
AIM OF DEVIC’S DISEASE
- Controlling Inflammation: The primary goal is to suppress the immune system's attack on the optic nerves and spinal cord. This is typically achieved through immunosuppressive therapies such as corticosteroids, plasma exchange (plasmapheresis), and medications that target specific immune cells or molecules involved in the autoimmune process.
- Preventing Relapses: Device’s disease tends to have a relapsing-remitting course, where patients experience episodes of neurological symptoms followed by periods of remission. Treatment aims to reduce the frequency and severity of these relapses.
- Managing Symptoms: Depending on the extent of nerve damage and disability, symptomatic treatment may involve physical therapy, pain management, and supportive care to improve quality of life.

Figure 1.1 Device’s disease affecting the optic nerves and spinal cord.
HISTORY

The English terms "acute optic neuromyelitis" and "neuromyélite optical acute" are translations of the French term "neuro-myélite optique aiguë," which was first used by Eugene Device (1858–1930) in a paper presented at the Congrès Francis de Medicine in Lyon in 1894.2. Device meant the phrase to refer to a new syndrome that combines optic neuritis and acute myelitis: "Ces seis cas de myélite aiguë accompanist de névrite optique sont suffisants pour légitimer la création d'un type Clinique, ou pluton d'un syndrome auquel on pourrait donner le nom de neuro-myélite optique." (2)
TYPES:
There are 2 types of NMO
- Relapsing form
- Monophasic form
It has phases of resolution interspersed with irregular flare-ups.It is more uncommon to find this type. Women are considerably more likely to have this form than males are.
Monophasic form
This means there will probably be a long period without any attacks succeeding a single, perhaps month-long attack. Similar situations are had by both sexes. (3)
CAUSES OF DEVIC’S DISEASE
- Mainly due to the attack on the body’s own cells by the immune system.
- When you have non-motor neuropathy (NMO), your immune system destroys the protective layer of myelin that shields your neurons, particularly in the optic and vertebral nerve myelin cells. People who have non-motor neuropathy (NMO) usually have flare-ups that happen months or years apart. Between these flare-ups, people might recover. (3)
- It is still unsure as to the cause Devic illness. The theory of an infectious etiology has been identified by the temporal correlation of the disease onset with particular infectious illnesses. (4)
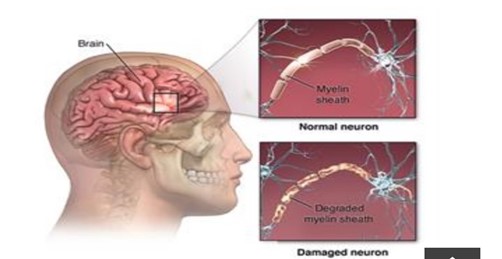
Figure 1.2 Normal neuron Vs Damaged neuron
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS
- Headache , Dizziness , Vision problem
- Bladder dysfunction ,numbness and weakness
- Depression, fatigue , tremor
- Itching , seizures , emotional change Dizziness
- Swallowing problems
- Sexual dysfunction
- Cognitive dysfunction
- Pain
- Hearing loss
- Bowol dysfunction
- Walking difficulty
- Breathing problems(5)
COMPLICATION OF DEVIC’S DISEASE
Visual impairment or blindness
Women with neuromyelitics optica have high risk of miscarriage
Difficulty in making a correct diagnosis(6)
Paralysis or weakness of 1 or more limb(7)
HOW TO SPREAD NEUROMYELITIS OPTICA
The neuromyelitis optica can spread to damage the tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic neurons(8)
The neuromyelitis optica can spred the edema spreds into the surrounding
retina may be of diagnostic aid (9)
The neuromyelitis optica can spread from human to human (10)
Foods good for NMO
- Vitamin D(11)
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Whole grains
- Lean protein
- Supplements
Use of Vitamin –D in NMO
Vitamin-D
? Repair myeline
?
Coats and protects nerves(12)

DIAGNOSIS AND TEST OF DEVIC’S DISEASES
- Blood tests
- Magnetic resonance imaging scans(MRI)
- Physical and neurological examinations
- Personal and medical history
- Neurological exam
- Lumbar puncture(spinal tab)
- Stimuli response test
- Optical coherence tomography
- Eye test
Blood test
- One of the most essential diagnostic methods that doctors employ to diagnose NMO is a blood test for AQP4 or MOG antibodies. Although blood testing cannot always prove the condition, it is helpful in determining NMO, as 13.5% of cases do not have detectable antibodies.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans
MRI scans are especially helpful for identifying NMO. The spinal cord and other parts of the brain that are affected can be scanned using an MRI to detect changes caused by the condition. Medical professionals are usually able to rule out multiple sclerosis and separate them from changes linked to multiple sclerosis
Physical and Neurological Examinations
These examinations search for indications and manifestations that may result from NMO. Because it can detect issues with the senses, reflexes, muscles, balance, and facial functions, the neurological exam is particularly crucial.
Personal and medical history
This includes inquiring about the symptoms, general health, and specific medical and personal history from the healthcare practitioner.
The may also be offered more testing, as the physician may think it's necessary to rule out any other diseases. The can get more information about the tests the provider suggests, as well as their reasoning for doing so, from them.
Neurological exam
A neurologist assesses speech, vision, memory, coordination, strength, feeling, and movement. The examination may involve an eye physician.
Lumber Puncture (Spinal tab)
A tiny amount of spinal fluid is extracted by the neurologist using a needle inserted into the lower back during this procedure. The results of this test show how many immune cells, proteins, and antibodies are present in the fluid. NMO and MS may be distinguished by this test. During NMO episodes, the spinal fluid may exhibit abnormally high levels of white blood cells. Though it doesn't always happen, this is higher than what is often observed in MS.
Stimuli Response Test
The purpose of the evoked potentials test, also known as the evoked response test, is to determine how well the brain reacts to stimuli like sights, sounds, or touch. Electrodes, which are wires, are affixed to the head, neck, arm, leg, and back in certain situations. The electrodes are equipped with equipment that records the brain's reactions to stimuli. These examinations aid in the detection of lesions or damaged regions in the brain, brainstem, spinal cord, optic nerve, or nerves.
Optical coherence tomography
This test assesses the thickness of the retinal nerve. Compared to those with MS, patients with an inflamed optic nerve from NMO experience more significant vision loss and retinal nerve weakening
Eye Test
An eye exam by ophthalmologist it help to look for optic nerve damage
- Visual acuity
- Visual field
- Ability to see colour
- Pupil reflexes
- Slit lamp exam
- The retinal nerve’s thickness is assessed by this test.Individuals with NMO related optic nerve inflammation experience more severe vision loss
SURVEY OF DEVIC’S DISEASE ACCORDING TO AGE

Fig1.3: In general, NMO is uncommon. Between 0.3 and 4.4 people per 100,000 have NMO on average? This indicates that there are between 2,400 and 350,600 cases globally, and between 1,000 and 14,600 cases in the US.(13)
TREATMENT AND MANAGEMENT:
Treatment for acute effects: This addresses inflammation in particular as well as the immediate consequences of an NMO assault. The most prevalent medication for this is corticosteroids or other prescription anti-inflammatory drug types. Since acute treatment lowers the chance of long-term damage from an attack, it is crucial.
The immune system accidentally targets the neurological system, which results in NMO. Handling that entails reducing or adjusting the immune system to lessen its potential to harm the nervous system. This can stop NMO attacks altogether, or at least lessen their intensity or duration. Professionals advise both those with and without AQP4 antibodies to follow these treatments.
DRUGS USED IN THE TREATMENT OF DEVIC’S DISEASE
These medications lessen nerve system's inflammation. Corticosteroids, including prednisone, are the most prevalent medicines that cause this effect. Healthcare professionals frequently administer these drugs intravenously (IV), putting them directly into the bloodstream. IV medication is used while receiving care in a hospital. The doctor can move them to similar medications that the take orally in the form of pills after the leave the hospital.
When steroids aren’t helpful, plasma exchange procedure is followed. This procedure removes blood plasma from body and replaces it with a matching amount of donor plasma. Swapping out some of the plasma for donor plasma removes some of the immune cells and chemical markers (which strengthen immune response) circulating in the plasma. That helps reduce body’s immune response, which reduces inflammation.
- Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)
Immunoglobulin, is a type of plasma that has donor antibodies in it. These antibodies won't attack the body. During this patients will get an IV infusion of plasma.
These drugs are taken on a regular basis. Some are administered intravenously (IV) in an infusion clinic or other comparable medical setting. Some are available as pills that can be taken at home. The majority of people will take these medications for a year or maybe forever.
DRUGS USED TO TREAT DEVIC’S DISEASE
- Eculizumab
Eculizumab is a complement inhibitor, the eculizumab is sold under the brand name Solaris.
Mechanism of action
The eculizumab drug complement inhibition of anti C5 monoclonal antibody.
Route of administration
Only administer as an intravenous infusions
Dosing level:
Initial dosage; 900mg IV infusion weekly for 4weeks, then 1,200mg for 1 week
Maintains; 1,200 mg every 2 weeks
Uses;
It is used to treatment of paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria
The eculizumab is a medication that suppresses the immune system.
The eculizumab is a first line therapy when the diagnosis of a HUS is unequivocal.
2. Inebilizumab
This medication is used to treatment a certain nervous system disorder, the lnebailizumab sold under the brand name Uplizna, in this drug is used in the treatment of device’s disease.
Mechanism of action
Inebilizumab binds to CD19 and through one of several potential mechanism leads to cell
Route of administration
UPLIZNA is administered as an IV infusion
Dosing level
Initial dosage ; 300 mg IV infusion followed 2 weeks later by a 2nd 300mg IV infusion dose.
2.Satralizumab
The satralizumab drug is used in the treatment of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder; an autoimmune disorder of the nervous system that affects eye nerves and spinal cord.
Mechanism of action
Interleukin-6 inhibition of anti-interleukin-6 receptor monoclonal a
Rout of administration: The satralizumab drug is administration in intravenous rout
Dosing level
Initial loading dosage; 120 mg SQ at weeks 0, 2, and 4 maintenance dosage 120 mg SQ every 4 weeks
Ayurveda medicine use in treatment of device’s disease.
- Brahmi
Brahmi is proven to have neuroprotective, antioxidant, adapt genic, analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antidepressant properties which make it an useful drug in neuroinflammatory condition like NMO.(14)
PREVENTION DEVIC’S DISEASE.
There is no way to prevent or lower the risk of developing non-motor neuropathy (NMO) because it occurs randomly and for reasons that professionals are still learning about.
REFERENCE
- Arias M. the knowledge sharing in the history of neuromyelitis optica spectrum an unfinished tale bridging three centuries.spain; springe,
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articales/PMC3599417/
- Device’s disease. Knowledge sharing in johns Hopkins medicine. Identifying sharing barriers in neuromyelitis optic.https:// www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/neuromyelitis-optica.
- Jarius S, wildemann B, Paul F. Neuromyelitis optica: clinical features immunopathogenesis and treatment; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3992027/). Clin EXP lmmunoi.2014; 176(2):149-164.Accessed 11/25/2022
- Steven alexander j, Rogar E Kelley, Anna C Long. Clinical course, pathophysiology, and management, October 2002, volume 9, Issue 1, pages 33-40
- Karina maciak, Sylwia pietrasik, Michal bijak biohazard prevention centre, Th 17 related cytokines as potential discriminatory markers between neuromyelitis optic (device’s disease and multiple sclerosis. Poland. 20 August 2021.
- Device’s disease. Knowledge sharing in johns Hopkins medicine. Identifying sharing barriers in neuromyelitis optic.https:// www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/neuromyelitis-optica
- Sidik.M, Synitia nusanti, karim s, Majithia v. knowledge sharing in complication of device’s disease diagnosis and management. (Case report). Indonesia, Jakarta: ophthalmol Ina 2015:41 (31): 219-228.
- Rosales D, Kister I common and rare manifestations of neuromyelitics optica spectrum disorder, New York; springer science+ business media :( 2016) 16:42.
- Monika bradi, Hans’s lass Mann, Neuromyelitis Optic: Pathogenicity of Patient Immunoglobulin in Vivo. American published, in Wiley inter-science (www.interscience.wiley .com), 2009.
- Coyle PK, dissecting the immune component of neurologic disorders a grand change for the 21st century; stony brook, NY, USA.2011.
- Dimitrov V, White JH. Species –specific regulation of innate immunity by vitamin D signalling .J steroid biochem Mol Biol. 2016; 164:246-253.
- Desrina, Syntia Nusanti, M Sidik Diagnosis and Management of Device’s Disease; Universitas Indonesia; 2015; 41(3):219-228.
- Neuromyelitis optic.https:// www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/neuromyelitis-optica

 Daphne Sherine*
Daphne Sherine*






 10.5281/zenodo.13143291
10.5281/zenodo.13143291