Abstract
Nutraceuticals comprised of two words nutra which means nutrition and pharmaceuticals. Nutraceuticals, in broad are food or part of food playing a significant role in modifying and maintaining normal physiological action that maintains healthy human beings.The term "nutraceuticals" was coined in 1989 by the foundation for innovation in medicine {newyork,us}, to provide a name for this rapidly growing area of bimedical research. Nutraceutical may range from isolated nutrients dietary supplements and diets to genetically engineered "designer" foods, herbal products and processed product such as cereals, soups and beverages. These nutraceuticals help in compating some of the major health problems such as obesity, cardiovascular diseases cancer, osteroporosis, arthiritis, diabetes, cholestrol etc. Frequency of nutraceuticals use is 50% to 70% in developed country population and this number is increasing by the age. Ladies use more nutraceuticals than men. The ongoing research will lead to anew generation of foods which will certainly cause the interface between food and drug to become increasingly permeable. The present accumulated knowledge about nutraceuticals represents undoubtly a great challenge for nutritionists, physicians, food technologists and food chemist. The nutraceutical revolution will lead us into new era of medicines and health, become a researchoriented one similar to the pharmaceutical industry.
Keywords
Nutraceuticals, nutrition, dietary supplements, therapeutic effect
Introduction
The quality of life in terms of income, spending and lifestyle has improved with economic development. However, it has also thrown a major challenge in the form of 'lifestyle diseases'. The first victim of this lifestyle change has been food habits. Consumption of junk food has increased number of disease related to nutrition deficiencies [1, 2].
Figure 1 - Nutraceuticals and their importance
Nutraceuticals can play a vital role in controlling them. No wonder more and more people turning to nutraceuticals. Plants are one of the most important resources of human food and medicines [3 - 6]. Increasing knowledge on nutrition, medicine and plant biotechnology has dramatically changed the concept about food, health and agriculture brought a revolution on them[7 – 10]. With recent advance in and nutrition science, natural products and health promoting food have received extensive attention from both health professionals and the public. "Nutraceutical" is a term coined in 1989 by stephen de felice which is defined as "a food or part of food that provide medical or health benefits, including the prevention and treatment of disease." [11 – 14]
The concept of nutraceuticals is rooted in the growing recognition that diet plays a crucial role in maintaining health and preventing illness. Unlike conventional pharmaceuticals which primarily treat symptoms of diseases, nutraceuticals aim to support overall health and well being by targeting underlying physiological processes[15 – 18]. This preventive approach aligns with the increasing consumer interest in natural and holistic solutions, draining the global market for nutraceutical products[19 - 21]. Nutraceuticals exert their effect through diverse mechanisms, including antioxidant properties, modulation in inflammatory pathway, enhancement of immune function and regulation of metabolic processes[22 – 25]. Scientific bioactive compounds responsible for these health promoting effects, paving the way for targeted nutraceutical interventions. Despite their promise, the field of nutraceuticals faces challenges, including regulatory complexities, variability in product quality, and conflicting research findings. Addressing these challenges require rigours scientific inquiry, standardized testing methodologies and transparent regulatory framework to ensure both safety and efficacy [26 -29]. This introduction sets the stage by defining nutraceuticals, discussing their significance, and outlining the structure of the review article. It provide a clear contest for readers to understand the scope and importance of nutraceuticals in contemporary health and nutrition
The Potential Advantages of Nutraceuticals
Food items which provide health advantages beyond basic nutrition are recognised as nutraceuticals, a rapidly growing topic at the junction between nutritional science and medicine. These compounds have bioactive elements that have a variety of physiological effects. They tend to come from natural sources such fruits, vegetables, grains, and herbs. Nutraceuticals have a potential to boost overall health outcomes through supplying the diet with essential nutrients and bioactive substances[30 -32].
Nutraceuticals offer a key benefit of having fewer negative side effects than artificial supplements. Nutraceuticals, which are naturally derived compounds, have been consumed by humans for centuries and are typically well-tolerated[33-35]. Furthermore, nutraceuticals can be customized to address the specific nutritional requirements of different groups. Nutrient-rich foods tailored for older individuals can assist in managing age-related nutritional gaps and promoting overall well-being as one ages[36-38].
Moreover, nutraceuticals are easily available and affordable, which makes them a viable option for improving dietary quality among various population groups. The easy accessibility of nutraceutical items such as dietary supplements, functional foods, and fortified beverages makes it convenient for people to integrate them into their everyday schedules. Nonetheless, it is important to understand that the effectiveness and safety of nutraceuticals may differ based on individual health status, dosage, and product quality. It is advised to consult with a healthcare provider before adding nutraceuticals to your diet[39-42].
Classification of nutraceuticals:
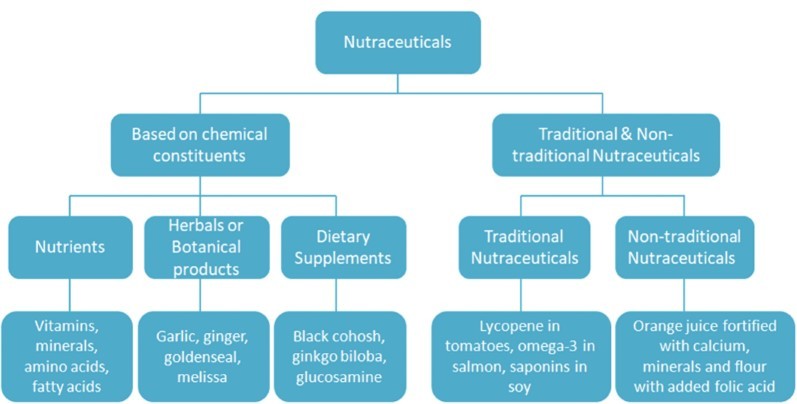
Figure – 2 Classification of Nutraceuticals
Nutraceuticals, an emerging area at the intersection of food science and medicine, can be classified according to their source, chemical structure, and intended uses [43 - 45]. Natural nutraceuticals cover a wide range of bioactive compounds sourced from plants, animals, or microorganisms in nature. Contrary to natural nutraceuticals, synthetic nutraceuticals are created using chemical synthesis or biotechnological methods to mimic natural compounds or develop new bioactive [46-49]. Semi-synthetic nutraceuticals are natural compounds with chemical modifications to improve effectiveness or stability. Nutraceuticals have a diverse chemical makeup, with phytochemicals - bioactive compounds from plants - being common [50 - 53]. Marine-based nutraceuticals, derived from marine organisms, often contain exclusive nutrients and bioactive substances. Vitamins and minerals, which are important for human health, are compounds, both inorganic and organic, that have critical functions in different physiological processes. Moreover, probiotics and prebiotics are live microorganisms and compounds that promote gastrointestinal health and overall wellness [54-58].
Nutraceuticals are used to manage a range of health issues. Omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants are commonly included by individuals focusing on maintaining good cardiovascular health. Nutritional supplements for bone and joint health include calcium, vitamin D, and glucosamine [59- 62]. Probiotics, prebiotics, and dietary fiber can help with digestive health. Nutraceuticals with omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and B vitamins are linked to cognitive health. In conclusion, nutraceuticals can assist with managing weight by promoting metabolism, controlling appetite, or increasing energy expenditure [63 – 67].
TABLE 1 – Various Classifications of Nutraceuticals with Examples

Nutraceuticals in various diseases

Figure 3 - Role of nutraceuticals in various diseases
Nutraceuticals, bioactive compounds derived from foods, have emerged as a promising avenue for managing various health conditions. These natural substances, rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytochemicals, offer potential therapeutic benefits beyond traditional nutrition [68 -71]. This review explores the potential roles of nutraceuticals in different diseases. Nutraceuticals can play a significant role in supporting cardiovascular health. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fatty fish and fish oil supplements, have been extensively studied for their ability to reduce triglycerides, improve endothelial function, and lower blood pressure, thereby reducing the risk of heart disease [ 72 -75 ]. Additionally, coenzyme Q10, an antioxidant involved in energy production, may help support heart function and overall cardiovascular health [76 - 77]. Flavonoids, such as quercetin and resveratrol, abundant in fruits, vegetables, and red wine, possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that can protect against heart disease by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation [78 - 81]. Certain nutraceuticals have shown promise in managing metabolic disorders. Berberine, derived from plants like goldenseal and barberry, has demonstrated potential in improving insulin sensitivity and lowering blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes [82 -84]. Green tea extract, rich in catechins, can enhance metbolism and promote fat oxidation, potentially aiding in weight management [85 -86]. Chromium, a trace mineral, plays a role in glucose metabolism and insulin signaling, and chromium supplementation may be beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes. Essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D are crucial for maintaining bone health and preventing osteoporosis [87 - 90]. Glucosamine and chondroitin, naturally found in cartilage, may help alleviate symptoms of osteoarthritis by supporting joint health and reducing inflammation [91–93]. Curcumin, a polyphenol derived from turmeric, possesses potent anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce joint pain and inflammation associated with arthritis [94-96].Nutraceuticals can also support cognitive health. Omega-3 fatty acids, as previously discussed, can contribute to brain health and may reduce the risk of cognitive decline [97- 98]. Caffeine, found in coffee and tea, has been associated with a reduced risk of Alzheimer's disease and improved cognitive function [99-100]. Ginkgo biloba, a herbal supplement, may enhance blood flow to the brain and provide antioxidant protection, potentially supporting cognitive function [101-102]. Probiotics, beneficial bacteria that can help restore balance to the gut microbiome, may alleviate symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Prebiotics, dietary fibers that act as food for probiotics, can promote their growth and activity in the gut [103- 106]. Peppermint oil may help relieve symptoms of IBS, such as abdominal pain, bloating, and gas [107-108]. Nutraceuticals can also play a role in boosting the immune system. Vitamin C, an antioxidant, is essential for immune function and may help reduce the duration and severity of colds and infections [109- 111]. Zinc, a trace mineral, is crucial for a healthy immune system and may shorten the duration of colds. Echinacea, a herbal supplement, has been traditionally used to stimulate the immune system and may reduce the risk of respiratory infections [112-114]. Nutraceuticals can contribute to skin health as well. Collagen peptides, building blocks of collagen, can help improve skin hydration, reduce wrinkles, and promote youthful skin. Vitamin E, an antioxidant, protects skin cells from damage caused by free radicals and can help promote skin healing [115-118]. Astaxanthin, a carotenoid with potent antioxidant properties, may protect the skin from UV damage and improve skin elasticity. Antioxidants, such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium, can help protect cells from oxidative damage, which is linked to cancer development [119 -122]. Green tea polyphenols, compounds found in green tea, have been shown to have anti-cancer properties and may reduce the risk of certain cancers. Curcumin, a polyphenol derived from turmeric, possesses anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects that may inhibit cancer cell growth and improve outcomes in cancer patients [123-126]. While nutraceuticals offer promising potential benefits, it is important to note that more research is needed to fully understand their efficacy and safety for various health conditions. Consulting with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen is recommended.

Table 2 – Potential benefits of Nutraceuticals in various diseases.
A Comprehensive Exploration of Nutraceutical Considerations
Nutraceuticals, bioactive compounds derived from foods, have emerged as a promising avenue for promoting health and well-being. However, careful consideration is necessary before incorporating nutraceuticals into a healthcare regimen. Adherence to recommended dosages is paramount, as excessive intake can lead to adverse effects. Individuals with existing health conditions or those taking medications should consult with healthcare providers to avoid potential interactions between nutraceuticals and other treatments [127- 129]. Furthermore, the scientific evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of nutraceuticals for specific diseases varies significantly. While many nutraceuticals show promise, it is crucial to prioritize those with a strong scientific foundation and evidence-based support [130-131]. Randomized controlled trials and meta-analyses are considered the gold standard for evaluating the effectiveness and safety of nutraceuticals. Nutraceuticals should be viewed as complementary therapies rather than substitutes for professional medical advice or treatment. They can provide additional support for overall health and well-being, but they should not replace conventional medical interventions when necessary [132-134]. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate use of nutraceuticals in conjunction with other treatments. As research continues to advance, the role of nutraceuticals in healthcare is likely to expand. Emerging technologies and methodologies are enabling scientists to investigate the mechanisms of action of nutraceuticals and identify new potential applications [135-138]. This ongoing research will contribute to a deeper understanding of the benefits and risks associated with nutraceutical use. Individuals considering incorporating nutraceuticals into their healthcare routine should carefully evaluate the available evidence, consult with healthcare professionals, and choose products from reputable manufacturers. By making informed decisions and utilizing nutraceuticals appropriately, individuals can potentially enhance their health and well-being [139- 142].

Table 3 - exploration of nutraceuticals
Ensuring Safety and Quality in the Nutraceutical Industry:
Safety and quality control are paramount in the nutraceutical industry to safeguard consumer health and maintain product integrity. Rigorous measures are implemented throughout the production process to ensure that nutraceutical products are safe, effective, and meet regulatory standards [143-145]. One critical aspect of safety and quality control is ingredient sourcing and verification. Nutraceutical companies must verify the quality and authenticity of raw materials and ingredients used in their products. This involves ensuring that suppliers meet stringent quality standards and conducting thorough testing to assess purity, potency, and the absence of contaminants like heavy metals or pesticides [146-148]. Adherence to good manufacturing practices (GMP) is essential for maintaining consistent product quality. GMP guidelines ensure proper facility design, sanitation, personnel training, and record-keeping to prevent contamination and ensure product uniformity [149- 151]. By following GMP, nutraceutical companies can minimize the risk of product adulteration and maintain high-quality standards . Regular testing throughout the production process is crucial for monitoring product quality and safety [152-154]. This includes in-process testing to assess the quality of raw materials and intermediate products, as well as finished product testing to ensure that the final product meets specified quality standards. Tests may include analysis of ingredient potency, microbial contamination, and stability over time [155-157]. Compliance with regulatory requirements set by agencies like the FDA (in the United States) or equivalent bodies in other countries is another essential aspect of safety and quality control. Adherence to regulations ensures that nutraceutical products are safe for consumption and accurately labelled. Regulatory compliance also helps to maintain consumer trust and confidence in the industry [158-160]. Adverse event monitoring is crucial for ongoing safety evaluation. Companies should have mechanisms in place to monitor and respond to adverse events reported by consumers or healthcare professionals [161-162]. This helps identify potential safety issues and take corrective actions to mitigate risks. Proper packaging and labelling are vital to protect products from contamination and ensure accurate dosing. Clear and accurate labelling informs consumers about ingredients, usage instructions, and potential allergens or interactions [163-166]. Proper packaging also helps to maintain product integrity and prevent tampering. Establishing robust quality control systems involves setting specifications for raw materials and finished products, conducting regular audits, and implementing corrective actions to address any deviations from standards. Quality control systems help to ensure that products consistently meet the highest quality standards [167-169]. By focusing on these aspects of safety and quality control, nutraceutical companies can enhance consumer trust, comply with regulations, and effectively promote the health benefits of their products. A commitment to safety and quality is essential for the long-term success and sustainability of the nutraceutical industry [170-172].

Table 4 – Aspects of safety and quality control of nutraceuticals
By focusing on these aspects of safety and quality control, nutraceutical companies can enhance consumer trust, comply with regulations, and effectively promote the health benefits of their products. A commitment to safety and quality is essential for the long-term success and sustainability of the nutraceutical industry.
Future direction and research
The future of nutraceuticals is set for transformative advancements driven by scientific innovation, technological progress, and evolving consumer demands [173-174]. Key trends include personalized nutrition, facilitated by genetic testing and biomarker analysis, which enables the formulation of individualized supplements tailored to specific genetic profiles and health needs, optimizing efficacy and health outcomes [175- 176]. Concurrently, research into novel ingredients such as botanical extracts, marine compounds, and bioactive peptides, alongside advanced delivery systems like liposomal encapsulation and controlled-release formulations, promises to enhance the bioavailability and therapeutic potential of nutraceuticals. Integration with digital health technologies, such as wearables and health apps, further empowers personalized health management by tracking real-time data to inform supplement regimens [177-179]. In the realm of longevity, nutraceuticals aimed at mitigating age-related conditions, including those with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, are becoming increasingly prominent. The growing understanding of the gut microbiome is also driving the development of prebiotics, probiotics, and postbiotics to support overall health [180-182]. Evidence-based research and clinical trials are gaining emphasis to validate health claims and improve consumer trust, while sustainability concerns are prompting eco-friendly production and ethical sourcing practices [183- 184]. Efforts toward regulatory harmonization across global markets will facilitate international trade and ensure product safety, while increased consumer education and transparency in labeling will empower informed purchasing decisions [185-186]. Finally, as nutraceuticals gain recognition as complementary to conventional medicine, their integration into mainstream healthcare systems, through collaboration with healthcare professionals, is expected to grow, positioning nutraceuticals as a vital component of preventive and integrative health strategies [187-189].

Table 5- Overview of the key trends shaping the future of nutraceuticals
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, nutraceuticals represent a dynamic and evolving sector at the intersection of nutrition, health, and pharmaceuticals. These products encompass a wide range of bioactive compounds, dietary supplements, and functional foods that offer potential health benefits beyond basic nutrition. The growth of nutraceuticals is driven by several factors: increasing consumer awareness and interest in preventive health, advancements in scientific research validating their efficacy, and technological innovations improving ingredient bioavailability and delivery systems. Moreover, the trend towards personalized nutrition and the integration of digital health technologies are shaping the future landscape of nutraceuticals.
However, challenges remain, including regulatory complexities, ensuring product safety and efficacy through rigorous research, and addressing consumer concerns about transparency and sustainability in manufacturing practices. Looking ahead, the nutraceutical industry is expected to continue expanding as a vital component of wellness strategies worldwide. With ongoing scientific inquiry and commitment to quality, nutraceuticals have the potential to contribute significantly to promoting health, supporting healthy aging, and complementing traditional healthcare approaches. As stakeholders collaborate to navigate these opportunities and challenges, nutraceuticals are poised to play an increasingly important role in enhancing public health outcomes and fostering a proactive approach to personal well-being.
REFERENCES
- Egger G, Dixon J. Beyond obesity and lifestyle: a review of 21st century chronic disease determinants. BioMed research international. 2014;2014(1):731685.
- Sharma M, Majumdar PK. Occupational lifestyle diseases: An emerging issue. Indian journal of occupational and environmental medicine. 2009 Sep 1;13(3):109-12.
- Dillard CJ, German JB. Phytochemicals: nutraceuticals and human health. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 2000 Sep 15;80(12):1744-56.
- Das L, Bhaumik E, Raychaudhuri U, Chakraborty R. Role of nutraceuticals in human health. Journal of food science and technology. 2012 Apr;49:173-83.
- Cencic A, Chingwaru W. The role of functional foods, nutraceuticals, and food supplements in intestinal health. Nutrients. 2010 Jun 1;2(6):611-25.
- Gul K, Singh AK, Jabeen R. Nutraceuticals and functional foods: the foods for the future world. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition. 2016 Dec 9;56(16):2617-27.
- Zhao J. Nutraceuticals, nutritional therapy, phytonutrients, and phytotherapy for improvement of human health: a perspective on plant biotechnology application. Recent patents on biotechnology. 2007 Feb 1;1(1):75-97.
- Persley GJ. Agricultural biotechnology and the poor: Promethean science. Agricultural Biotechnology and the Poor: Washington, DC, The World Bank. 2000 Oct.
- Halewood M, Chiurugwi T, Sackville Hamilton R, Kurtz B, Marden E, Welch E, Michiels F, Mozafari J, Sabran M, Patron N, Kersey P. Plant genetic resources for food and agriculture: opportunities and challenges emerging from the science and information technology revolution. New Phytologist. 2018 Mar;217(4):1407-19.
- Kishore GM, Shewmaker C. Biotechnology: Enhancing human nutrition in developing and developed worlds. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 1999 May 25;96(11):5968-72.
- El Sohaimy SA. Functional foods and nutraceuticals-modern approach to food science. World Applied Sciences Journal. 2012;20(5):691-708.
- AlAli M, Alqubaisy M, Aljaafari MN, AlAli AO, Baqais L, Molouki A, Abushelaibi A, Lai KS, Lim SH. Nutraceuticals: Transformation of conventional 27;26(9):2540foods into health promoters/disease preventers and safety considerations. Molecules. 2021 Apr.
- Egbuna C, Dable-Tupas G. Functional foods and nutraceuticals. Springer Nature Switzerland AG. 2020;1:1-632.
- Awuchi CG, Okpala CO. Natural nutraceuticals, especially functional foods, their ma-jor bioactive components, formulation, and health benefits for disease prevention-An overview. Journal of Food Bioactives. 2022 Sep 30;19.
- Nasri H, Baradaran A, Shirzad H, Rafieian-Kopaei M. New concepts in nutraceuticals as alternative for pharmaceuticals. International journal of preventive medicine. 2014 Dec;5(12):1487.
- Adefegha SA. Functional foods and nutraceuticals as dietary intervention in chronic diseases; novel perspectives for health promotion and disease prevention. Journal of dietary supplements. 2018 Nov 2;15(6):977-1009.
- Rajasekaran A, Sivagnanam G, Xavier R. Nutraceuticals as therapeutic agents: A Review. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 2008;1(4):328-40.
- Makkar R, Behl T, Bungau S, Zengin G, Mehta V, Kumar A, Uddin MS, Ashraf GM, Abdel-Daim MM, Arora S, Oancea R. Nutraceuticals in neurological disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020 Jun 22;21(12):4424.
- Bagchi D, editor. Nutraceutical and functional food regulations in the United States and around the world. Elsevier; 2014 Feb 25.
- Daliu P, Santini A, Novellino E. From pharmaceuticals to nutraceuticals: Bridging disease prevention and management. Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology. 2019 Jan 2;12(1):1-7.
- Basu SK, Thomas JE, Acharya SN. Prospects for growth in global nutraceutical and functional food markets: a Canadian perspective. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. 2007;1(4):637-49.
- Yahfoufi N, Alsadi N, Jambi M, Matar C. The immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory role of polyphenols. Nutrients. 2018 Nov 2;10(11):1618.
- Wu D, Lewis ED, Pae M, Meydani SN. Nutritional modulation of immune function: analysis of evidence, mechanisms, and clinical relevance. Frontiers in immunology. 2019 Jan 15;9:3160.
- AlAli M, Alqubaisy M, Aljaafari MN, AlAli AO, Baqais L, Molouki A, Abushelaibi A, Lai KS, Lim SH. Nutraceuticals: Transformation of conventional foods into health promoters/disease preventers and safety considerations. Molecules. 2021 Apr 27;26(9):2540.
- Clarke JO, Mullin GE. A review of complementary and alternative approaches to immunomodulation. Nutrition in clinical practice. 2008 Feb;23(1):49-62.
- Biesalski HK, Aggett PJ, Anton R, Bernstein PS, Blumberg J, Heaney RP, Henry J, Nolan JM, Richardson DP, van Ommen B, Witkamp RF. 26th Hohenheim Consensus Conference, September 11, 2010 Scientific substantiation of health claims: evidence-based nutrition. Nutrition. 2011 Oct 1;27(10):S1-20.
- Sorkin BC, Kuszak AJ, Bloss G, Fukagawa NK, Hoffman FA, Jafari M, Barrett B, Brown PN, Bushman FD, Casper S, Chilton FH. Improving natural product research translation: From source to clinical trial. FASEB journal: official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology. 2020 Jan;34(1):41.
- Heinrich M, Appendino G, Efferth T, Fürst R, Izzo AA, Kayser O, Pezzuto JM, Viljoen A. Best practice in research–overcoming common challenges in phytopharmacological research. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 2020 Jan 10;246:112230.
- Ghosh D, Das S, Bagchi D, Smarta RB, editors. Innovation in healthy and functional foods. CRC press; 2012 Sep 24.
- Biesalski HK, Dragsted LO, Elmadfa I, Grossklaus R, Müller M, Schrenk D, Walter P, Weber P. Bioactive compounds: Definition and assessment of activity. Nutrition. 2009 Nov 1;25(11-12):1202-5.
- Hamed I, Özogul F, Özogul Y, Regenstein JM. Marine bioactive compounds and their health benefits: a review. Comprehensive reviews in food science and food safety. 2015 Jul;14(4):446-65.
- Samtiya M, Aluko RE, Dhewa T, Moreno-Rojas JM. Potential health benefits of plant food-derived bioactive components: An overview. Foods. 2021 Apr 12;10(4):839.
- Nasri H, Baradaran A, Shirzad H, Rafieian-Kopaei M. New concepts in nutraceuticals as alternative for pharmaceuticals. International journal of preventive medicine. 2014 Dec;5(12):1487.
- Santini A, Tenore GC, Novellino E. Nutraceuticals: A paradigm of proactive medicine. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2017 Jan 1;96:53-61.
- Williamson EM, Liu X, Izzo AA. Trends in use, pharmacology, and clinical applications of emerging herbal nutraceuticals. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2020 Mar;177(6):1227-40.
- Bernstein M, Munoz N. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: food and nutrition for older adults: promoting health and wellness. Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. 2012 Aug 1;112(8):1255-77.
- Calvani R, Miccheli A, Landi F, Bossola M, Cesari M, Leeuwenburgh C, Sieber CC, Bernabei R, Marzetti E. Current nutritional recommendations and novel dietary strategies to manage sarcopenia. The Journal of frailty & aging. 2013;2(1):38.
- Shao A, Drewnowski A, Willcox DC, Krämer L, Lausted C, Eggersdorfer M, Mathers J, Bell JD, Randolph RK, Witkamp R, Griffiths JC. Optimal nutrition and the ever-changing dietary landscape: a conference report. European journal of nutrition. 2017 May;56(1):1-21.
- Eussen SR, Verhagen H, Klungel OH, Garssen J, van Loveren H, van Kranen HJ, Rompelberg CJ. Functional foods and dietary supplements: products at the interface between pharma and nutrition. European journal of pharmacology. 2011 Sep 1;668:S2-9.
- Keservani RK, Sharma AK, Kesharwani RK, editors. Nutraceuticals and dietary supplements: Applications in health improvement and disease management. CRC Press; 2020 Nov 5.
- Žuntar I, Petric Z, Bursa? Kova?evi? D, Putnik P. Safety of probiotics: functional fruit beverages and nutraceuticals. Foods. 2020 Jul 17;9(7):947.
- Bagchi D, Nair S, editors. Developing new functional food and nutraceutical products. Academic Press; 2016 Sep 19.
- Santini A, Cammarata SM, Capone G, Ianaro A, Tenore GC, Pani L, Novellino E. Nutraceuticals: Opening the debate for a regulatory framework. British journal of clinical pharmacology. 2018 Apr;84(4):659-72.
- Aronson JK. Defining ‘nutraceuticals’: Neither nutritious nor pharmaceutical. British journal of clinical pharmacology. 2017 Jan;83(1):8-19.
- El Sohaimy SA. Functional foods and nutraceuticals-modern approach to food science. World Applied Sciences Journal. 2012;20(5):691-708.
- Joana Gil?Chávez G, Villa JA, Fernando Ayala?Zavala J, Basilio Heredia J, Sepulveda D, Yahia EM, González?Aguilar GA. Technologies for extraction and production of bioactive compounds to be used as nutraceuticals and food ingredients: An overview. Comprehensive reviews in food science and food safety. 2013 Jan;12(1):5-23.
- de Morais MG, Vaz BD, de Morais EG, Costa JA. Biologically active metabolites synthesized by microalgae. BioMed research international. 2015;2015(1):835761.
- Kiuru P, D?Auria MV, Muller CD, Tammela P, Vuorela H, Yli-Kauhaluoma J. Exploring marine resources for bioactive compounds. Planta medica. 2014 Sep;80(14):1234-46.
- Rani A, Saini KC, Bast F, Mehariya S, Bhatia SK, Lavecchia R, Zuorro A. Microorganisms: a potential source of bioactive molecules for antioxidant applications. Molecules. 2021 Feb 20;26(4):1142.
- Dillard CJ, German JB. Phytochemicals: nutraceuticals and human health. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 2000 Sep 15;80(12):1744-56.
- da Silva BV, Barreira JC, Oliveira MB. Natural phytochemicals and probiotics as bioactive ingredients for functional foods: Extraction, biochemistry and protected-delivery technologies. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2016 Apr 1;50:144-58.
- Braithwaite MC, Tyagi C, Tomar LK, Kumar P, Choonara YE, Pillay V. Nutraceutical-based therapeutics and formulation strategies augmenting their efficiency to complement modern medicine: An overview. Journal of Functional Foods. 2014 Jan 1;6:82-99.
- Piccolella S, Crescente G, Candela L, Pacifico S. Nutraceutical polyphenols: New analytical challenges and opportunities. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. 2019 Oct 25;175:112774.
- Soltani M, Ghosh K, Hoseinifar SH, Kumar V, Lymbery AJ, Roy S, Ringø E. Genus Bacillus, promising probiotics in aquaculture: aquatic animal origin, bio-active components, bioremediation and efficacy in fish and shellfish. Reviews in Fisheries Science & Aquaculture. 2019 Jul 3;27(3):331-79.
- Gomez-Zavaglia A, Prieto Lage MA, Jimenez-Lopez C, Mejuto JC, Simal-Gandara J. The potential of seaweeds as a source of functional ingredients of prebiotic and antioxidant value. Antioxidants. 2019 Sep 17;8(9):406.
- Caruso G, Floris R, Serangeli C, Di Paola L. Fishery wastes as a yet undiscovered treasure from the sea: Biomolecules sources, extraction methods and valorization. Marine drugs. 2020 Dec 7;18(12):622.
- Ghosh S, Sarkar T, Pati S, Kari ZA, Edinur HA, Chakraborty R. Novel bioactive compounds from marine sources as a tool for functional food development. Frontiers in Marine Science. 2022 Feb 10;9:832957.
- Hosseini SF, Rezaei M, McClements DJ. Bioactive functional ingredients from aquatic origin: A review of recent progress in marine-derived nutraceuticals. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 2022 Feb 10;62(5):1242-69.
- Ameye LG, Chee WS. Osteoarthritis and nutrition. From nutraceuticals to functional foods: a systematic review of the scientific evidence. Arthritis research & therapy. 2006 Aug;8:1-22.
- Messina OD, Vidal Wilman M, Vidal Neira LF. Nutrition, osteoarthritis and cartilage metabolism. Aging clinical and experimental research. 2019 Jun 1;31:807-13.
- Lopez HL. Nutritional interventions to prevent and treat osteoarthritis. Part II: focus on micronutrients and supportive nutraceuticals. PM&R. 2012 May 1;4(5):S155-68.
- González-Sarrías A, Larrosa M, García-Conesa MT, Tomás-Barberán FA, Espín JC. Nutraceuticals for older people: Facts, fictions and gaps in knowledge. Maturitas. 2013 Aug 1;75(4):313-34.
- El Sohaimy SA. Functional foods and nutraceuticals-modern approach to food science. World Applied Sciences Journal. 2012;20(5):691-708.
- Ballan R, Battistini C, Xavier-Santos D, Saad SM. Interactions of probiotics and prebiotics with the gut microbiota. Progress in molecular biology and translational science. 2020 Jan 1;171:265-300.
- Aluko RE. Functional foods and nutraceuticals. New York, NY, USA:: Springer; 2012 Jun 5.
- J?drusek?Goli?ska A, Górecka D, Buchowski M, Wieczorowska?Tobis K, Gramza?Micha?owska A, Szymandera?Buszka K. Recent progress in the use of functional foods for older adults: A narrative review. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety. 2020 Mar;19(2):835-56.
- Raman M, Ambalam P, Doble M. Probiotics, prebiotics, and fibers in nutritive and functional beverages. InNutrients in beverages 2019 Jan 1 (pp. 315-367). Academic Press.
- Rajasekaran A, Sivagnanam G, Xavier R. Nutraceuticals as therapeutic agents: A Review. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 2008;1(4):328-40.
- Sachdeva V, Roy A, Bharadvaja N. Current prospects of nutraceuticals: A review. Current pharmaceutical biotechnology. 2020 Aug 1;21(10):884-96.
- Shashirekha MN, Mallikarjuna SE, Rajarathnam S. Status of bioactive compounds in foods, with focus on fruits and vegetables. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition. 2015 Aug 24;55(10):1324-39.
- Liu RH. Dietary bioactive compounds and their health implications. Journal of food science. 2013 Jun;78(s1):A18-25.
- Kris-Etherton PM, Harris WS, Appel LJ. Fish consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. circulation. 2002 Nov 19;106(21):2747-57.
- Lavie CJ, Milani RV, Mehra MR, Ventura HO. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and cardiovascular diseases. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2009 Aug 11;54(7):585-94.
- Kris-Etherton PM, Harris WS, Appel LJ. Fish consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology. 2003 Feb 1;23(2):e20-30.
- Siscovick DS, Barringer TA, Fretts AM, Wu JH, Lichtenstein AH, Costello RB, Kris-Etherton PM, Jacobson TA, Engler MB, Alger HM, Appel LJ. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid (fish oil) supplementation and the prevention of clinical cardiovascular disease: a science advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017 Apr 11;135(15):e867-84.
- Littarru GP, Tiano L. Bioenergetic and antioxidant properties of coenzyme Q 10: recent developments. Molecular biotechnology. 2007 Sep;37:31-7.
- Pepe S, Marasco SF, Haas SJ, Sheeran FL, Krum H, Rosenfeldt FL. Coenzyme Q10 in cardiovascular disease. Mitochondrion. 2007 Jun 1;7:S154-67.
- David AV, Arulmoli R, Parasuraman S. Overviews of biological importance of quercetin: A bioactive flavonoid. Pharmacognosy reviews. 2016 Jul;10(20):84.
- Zhang H, Tsao R. Dietary polyphenols, oxidative stress and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Current Opinion in Food Science. 2016 Apr 1;8:33-42.
- Wu JM, Wang ZR, Hsieh TC, Bruder JL, Zou JG, Huang YZ. Mechanism of cardioprotection by resveratrol, a phenolic antioxidant present in red wine. International journal of molecular medicine. 2001 Jul 1;8(1):3-17.
- Perez-Vizcaino F, Duarte J, Andriantsitohaina R. Endothelial function and cardiovascular disease: effects of quercetin and wine polyphenols. Free radical research. 2006 Jan 1;40(10):1054-65.
- Pang B, Zhao LH, Zhou Q, Zhao TY, Wang H, Gu CJ, Tong XL. Application of berberine on treating type 2 diabetes mellitus. International journal of endocrinology. 2015;2015(1):905749.
- Cicero AF, Baggioni A. Berberine and its role in chronic disease. Anti-inflammatory nutraceuticals and chronic diseases. 2016:27-45.
- Derosa G, Maffioli P, Cicero AF. Berberine on metabolic and cardiovascular risk factors: an analysis from preclinical evidences to clinical trials. Expert opinion on biological therapy. 2012 Aug 1;12(8):1113-24.
- Murase T, Haramizu S, Shimotoyodome A, Nagasawa A, Tokimitsu I. Green tea extract improves endurance capacity and increases muscle lipid oxidation in mice. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology. 2005 Mar 1.
- Chen N, Bezzina R, Hinch E, Lewandowski PA, Cameron-Smith D, Mathai ML, Jois M, Sinclair AJ, Begg DP, Wark JD, Weisinger HS. Green tea, black tea, and epigallocatechin modify body composition, improve glucose tolerance, and differentially alter metabolic gene expression in rats fed a high-fat diet. Nutrition research. 2009 Nov 1;29(11):784-93.
- Mehri A. Trace elements in human nutrition (II)–an update. International journal of preventive medicine. 2020 Jan 1;11(1):2.
- Panchal SK, Wanyonyi S, Brown L. Selenium, vanadium, and chromium as micronutrients to improve metabolic syndrome. Current hypertension reports. 2017 Mar;19:1-1.
- Collins JF, editor. Molecular, genetic, and nutritional aspects of major and trace minerals. Academic Press; 2016 Sep 14.
- Petroni ML, Brodosi L, Marchignoli F, Sasdelli AS, Caraceni P, Marchesini G, Ravaioli F. Nutrition in patients with type 2 diabetes: present knowledge and remaining challenges. Nutrients. 2021 Aug 10;13(8):2748.
- Jerosch J. Effects of glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate on cartilage metabolism in OA: outlook on other nutrient partners especially Omega?3 fatty acids. International journal of rheumatology. 2011;2011(1):969012.
- Henrotin Y, Marty M, Mobasheri A. What is the current status of chondroitin sulfate and glucosamine for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis?. Maturitas. 2014 Jul 1;78(3):184-7.
- Zhu X, Sang L, Wu D, Rong J, Jiang L. Effectiveness and safety of glucosamine and chondroitin for the treatment of osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of orthopaedic surgery and research. 2018 Dec;13:1-9.
- Jurenka JS. Anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin, a major constituent of Curcuma longa: a review of preclinical and clinical research. Alternative medicine review. 2009 Jun 1;14(2).
- Daily JW, Yang M, Park S. Efficacy of turmeric extracts and curcumin for alleviating the symptoms of joint arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Journal of medicinal food. 2016 Aug 1;19(8):717-29.
- Ramadan G, Al-Kahtani MA, El-Sayed WM. Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant properties of Curcuma longa (turmeric) versus Zingiber officinale (ginger) rhizomes in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Inflammation. 2011 Aug;34:291-301
- Fotuhi M, Mohassel P, Yaffe K. Fish consumption, long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and risk of cognitive decline or Alzheimer disease: a complex association. Nature Reviews Neurology. 2009 Mar;5(3):140-52.
- Cederholm T, Salem Jr N, Palmblad J. ?-3 fatty acids in the prevention of cognitive decline in humans. Advances in nutrition. 2013 Nov 1;4(6):672-6.
- Eskelinen MH, Kivipelto M. Caffeine as a protective factor in dementia and Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2010 Apr 14;20(s1):S167-74.
- Arendash GW, Cao C. Caffeine and coffee as therapeutics against Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2010 Apr 14;20(s1):S117-26.
- DeFeudis FV, Drieu K. Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) and CNS functions basic studies and clinical applications. Current drug targets. 2000 Jul 1;1(1):25-58.
- Diamond BJ, Shiflett SC, Feiwel N, Matheis RJ, Noskin O, Richards JA, Schoenberger NE. Ginkgo biloba extract: mechanisms and clinical indications. Archives of physical medicine and rehabilitation. 2000 May 1;81(5):668-78.
- Sanders ME, Merenstein DJ, Reid G, Gibson GR, Rastall RA. Probiotics and prebiotics in intestinal health and disease: from biology to the clinic. Nature reviews Gastroenterology & hepatology. 2019 Oct;16(10):605-16.
- Distrutti E, Monaldi L, Ricci P, Fiorucci S. Gut microbiota role in irritable bowel syndrome: New therapeutic strategies. World journal of gastroenterology. 2016 Feb 2;22(7):2219.
- Lee BJ, Bak YT. Irritable bowel syndrome, gut microbiota and probiotics. Journal of neurogastroenterology and motility. 2011 Jul;17(3):252.
- Geier MS, Butler RN, Howarth GS. Inflammatory bowel disease: current insights into pathogenesis and new therapeutic options; probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics. International journal of food microbiology. 2007 Apr 1;115(1):1-1.
- Khanna R, MacDonald JK, Levesque BG. Peppermint oil for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of clinical gastroenterology. 2014 Jul 1;48(6):505-12.
- Cappello G, Spezzaferro M, Grossi L, Manzoli L, Marzio L. Peppermint oil (Mintoil®) in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: A prospective double blind placebo-controlled randomized trial. Digestive and liver Disease. 2007 Jun 1;39(6):530-6.
- Jayawardena R, Sooriyaarachchi P, Chourdakis M, Jeewandara C, Ranasinghe P. Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: A review. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews. 2020 Jul 1;14(4):367-82.
- Wintergerst ES, Maggini S, Hornig DH. Immune-enhancing role of vitamin C and zinc and effect on clinical conditions. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism. 2006 Feb 27;50(2):85-94.
- Mrityunjaya M, Pavithra V, Neelam R, Janhavi P, Halami PM, Ravindra PV. Immune-boosting, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory food supplements targeting pathogenesis of COVID-19. Frontiers in immunology. 2020 Oct 7;11:570122.
- Jayawardena R, Sooriyaarachchi P, Chourdakis M, Jeewandara C, Ranasinghe P. Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: A review. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews. 2020 Jul 1;14(4):367-82.
- Roxas M, Jurenka J. Colds and influenza: a review of diagnosis and conventional, botanical, and nutritional considerations. Alternative Medicine Review. 2007 Mar 1;12(1).
- Davison G, Kehaya C, Wyn Jones A. Nutritional and physical activity interventions to improve immunity. American journal of lifestyle medicine. 2016 May;10(3):152-69.
- Michalak M. Plant-derived antioxidants: Significance in skin health and the ageing process. International journal of molecular sciences. 2022 Jan 6;23(2):585.
- Michalak M, Pierzak M, Kr?cisz B, Suliga E. Bioactive compounds for skin health: A review. Nutrients. 2021 Jan 12;13(1):203.
- Reilly DM, Lozano J. Skin collagen through the lifestages: Importance for skin health and beauty. undefined. 2021 Jan 8;8:N-A.
- Vollmer DL, West VA, Lephart ED. Enhancing skin health: By oral administration of natural compounds and minerals with implications to the dermal microbiome. International journal of molecular sciences. 2018 Oct 7;19(10):3059.
- Michalak M. Plant-derived antioxidants: Significance in skin health and the ageing process. International journal of molecular sciences. 2022 Jan 6;23(2):585.
- Michalak M, Pierzak M, Kr?cisz B, Suliga E. Bioactive compounds for skin health: A review. Nutrients. 2021 Jan 12;13(1):203.
- Addor FA. Antioxidants in dermatology. Anais brasileiros de dermatologia. 2017 May;92:356-62.
- Ekpe L, Inaku K, Ekpe V. Antioxidant effects of astaxanthin in various diseases—A review. J. Mol. Pathophysiol. 2018;7(1):1-6.
- Basnet P, Skalko-Basnet N. Curcumin: an anti-inflammatory molecule from a curry spice on the path to cancer treatment. Molecules. 2011 Jun 3;16(6):4567-98.
- Niedzwiecki A, Roomi MW, Kalinovsky T, Rath M. Anticancer efficacy of polyphenols and their combinations. Nutrients. 2016 Sep 9;8(9):552.
- Perrone D, Ardito F, Giannatempo G, Dioguardi M, Troiano G, Lo Russo L, De Lillo A, Laino L, Lo Muzio L. Biological and therapeutic activities, and anticancer properties of curcumin. Experimental and therapeutic medicine. 2015 Nov 1;10(5):1615-23.
- Griffiths K, Aggarwal BB, Singh RB, Buttar HS, Wilson D, De Meester F. Food antioxidants and their anti-inflammatory properties: a potential role in cardiovascular diseases and cancer prevention. Diseases. 2016 Aug 1;4(3):28.
- Miller LG. Herbal medicinals: selected clinical considerations focusing on known or potential drug-herb interactions. Archives of internal medicine. 1998 Nov 9;158(20):2200-11.
- Mouly S, Lloret-Linares C, Sellier PO, Sene D, Bergmann JF. Is the clinical relevance of drug-food and drug-herb interactions limited to grapefruit juice and Saint-John’s Wort?. Pharmacological research. 2017 Apr 1;118:82-92.
- Péter S, Navis G, de Borst MH, von Schacky C, van Orten-Luiten AC, Zhernakova A, Witkamp RF, Janse A, Weber P, Bakker SJ, Eggersdorfer M. Public health relevance of drug–nutrition interactions. European journal of nutrition. 2017 Aug;56:23-36.
- Wallace TC, Bailey RL, Blumberg JB, Burton-Freeman B, Chen CO, Crowe-White KM, Drewnowski A, Hooshmand S, Johnson E, Lewis R, Murray R. Fruits, vegetables, and health: A comprehensive narrative, umbrella review of the science and recommendations for enhanced public policy to improve intake. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition. 2020 Jul 19;60(13):2174-211.
- Santini A, Cammarata SM, Capone G, Ianaro A, Tenore GC, Pani L, Novellino E. Nutraceuticals: Opening the debate for a regulatory framework. British journal of clinical pharmacology. 2018 Apr;84(4):659-72.
- Santini A, Tenore GC, Novellino E. Nutraceuticals: A paradigm of proactive medicine. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2017 Jan 1;96:53-61.
- Andrew R, Izzo AA. Principles of pharmacological research of nutraceuticals. British Journal of Pharmacology. 2017 Jun;174(11):1177.
- AlAli M, Alqubaisy M, Aljaafari MN, AlAli AO, Baqais L, Molouki A, Abushelaibi A, Lai KS, Lim SH. Nutraceuticals: Transformation of conventional foods into health promoters/disease preventers and safety considerations. Molecules. 2021 Apr 27;26(9):2540.
- Joana Gil?Chávez G, Villa JA, Fernando Ayala?Zavala J, Basilio Heredia J, Sepulveda D, Yahia EM, González?Aguilar GA. Technologies for extraction and production of bioactive compounds to be used as nutraceuticals and food ingredients: An overview. Comprehensive reviews in food science and food safety. 2013 Jan;12(1):5-23.
- Zhao J. Nutraceuticals, nutritional therapy, phytonutrients, and phytotherapy for improvement of human health: a perspective on plant biotechnology application. Recent patents on biotechnology. 2007 Feb 1;1(1):75-97.
- El Sohaimy SA. Functional foods and nutraceuticals-modern approach to food science. World Applied Sciences Journal. 2012;20(5):691-708.
- Barreca D, Trombetta D, Smeriglio A, Mandalari G, Romeo O, Felice MR, Gattuso G, Nabavi SM. Food flavonols: Nutraceuticals with complex health benefits and functionalities. Trends in Food Science & Technology. 2021 Nov 1;117:194-204.
- Gul K, Singh AK, Jabeen R. Nutraceuticals and functional foods: the foods for the future world. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition. 2016 Dec 9;56(16):2617-27.
- Ronis MJ, Pedersen KB, Watt J. Adverse effects of nutraceuticals and dietary supplements. Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology. 2018 Jan 6;58(1):583-601.
- AlAli M, Alqubaisy M, Aljaafari MN, AlAli AO, Baqais L, Molouki A, Abushelaibi A, Lai KS, Lim SH. Nutraceuticals: Transformation of conventional foods into health promoters/disease preventers and safety considerations. Molecules. 2021 Apr 27;26(9):2540.
- Mechanick JI, Brett EM, Chausmer AB, Dickey RA, Wallach S, Bergman DA, Garber JR, Hamilton CR, Handelsman Y, Holdy KE, Kukora JS. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists Medical Guidelines for the Clinical Use of Dietary Supplements and Nutraceuticals: 2. Physicians specializing in clinical nutrition, nutrition support, and metabolic disorders. Endocrine Practice. 2003 Oct 1;9(5):417-70.
- Galanakis CM, editor. Nutraceutical and functional food components: Effects of innovative processing techniques. Academic Press; 2021 Oct 24.
- Sarkar DK. Quality systems and controls for pharmaceuticals. John Wiley & Sons; 2008 Jul 31.
- Travis J, Lattimore LG, Harvey M, Frey T. NSF International’s role in the dietary supplements and nutraceuticals industries. InNutraceutical and functional food regulations in the United States and around the World 2019 Jan 1 (pp. 147-158). Academic Press.
- Bandaranayake WM. Quality control, screening, toxicity, and regulation of herbal drugs. Modern phytomedicine: turning medicinal plants into drugs. 2006 Sep 20:25-57.
- Abdel-Rahman A, Anyangwe N, Carlacci L, Casper S, Danam RP, Enongene E, Erives G, Fabricant D, Gudi R, Hilmas CJ, Hines F. The safety and regulation of natural products used as foods and food ingredients. Toxicological Sciences. 2011 Oct 1;123(2):333-48.
- Mukherjee PK, Bahadur S, Chaudhary SK, Kar A, Mukherjee K. Quality related safety issue-evidence-based validation of herbal medicine farm to pharma. InEvidence-based validation of herbal medicine 2015 Jan 1 (pp. 1-28). Elsevier.
- Heinz HJ. Principles and practices for the safe processing of foods. Elsevier; 2013 Oct 22.
- Gouveia BG, Rijo P, Gonçalo TS, Reis CP. Good manufacturing practices for medicinal products for human use. Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences. 2015 Apr 1;7(2):87-96.
- Patel KT, Chotai NP. Documentation and records: harmonized GMP requirements. Journal of young pharmacists. 2011 Apr 1;3(2):138-50.
- Bagchi D, editor. Nutraceutical and functional food regulations in the United States and around the world. Elsevier; 2014 Feb 25.
- Salgueiro L, Martins AP, Correia H. Raw materials: the importance of quality and safety. A review. Flavour and Fragrance Journal. 2010 Sep;25(5):253-71.
- Wang H, Chen Y, Wang L, Liu Q, Yang S, Wang C. Advancing herbal medicine: enhancing product quality and safety through robust quality control practices. Frontiers in Pharmacology. 2023 Sep 25;14:1265178.
- Yu LX, Amidon G, Khan MA, Hoag SW, Polli J, Raju GK, Woodcock J. Understanding pharmaceutical quality by design. The AAPS journal. 2014 Jul;16:771-83.
- Jenkins NE, Grzywacz D. Quality control of fungal and viral biocontrol agents-assurance of product performance. Biocontrol Science and Technology. 2000 Dec 1;10(6):753-77.
- Niazi SK. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Formulations: Volume Two, Uncompressed Solid Products. CRC press; 2019 Nov 25.
- Johnson R. Food fraud and economically motivated adulteration of food and food ingredients.
- Martirosyan DM, Singharaj B. Health claims and functional food: The future of functional foods under FDA and EFSA regulation. Functional foods for chronic diseases. 2016;1:410-7.
- Hobbs JE, Malla S, Sogah EK. Regulatory frameworks for functional food and supplements. Canadian Journal of Agricultural Economics/Revue Canadienne d'Agroeconomie. 2014 Dec;62(4):569-94.
- Leape LL, Berwick DM, Bates DW. What practices will most improve safety?: evidence-based medicine meets patient safety. Jama. 2002 Jul 24;288(4):501-7.
- Zhou W, Pool V, Iskander JK, English-Bullard R, Ball R, Wise RP, Haber P, Pless RP, Mootrey G, Ellenberg SS, Braun MM. Surveillance for safety after immunization: vaccine adverse event reporting system (VAERS)—United States, 1991–2001. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2003 Jan 24;52(1):1-24.
- Wallace CA, Sperber WH, Mortimore SE. Food safety for the 21st century: Managing HACCP and food safety throughout the global supply chain. John Wiley & Sons; 2018 Aug 8.
- Noah L. The imperative to warn: Disentangling the right to know from the need to know about consumer product hazards. Yale J. on Reg.. 1994;11:293.
- Muraro A, Hoffmann?Sommergruber K, Holzhauser T, Poulsen LK, Gowland MH, Akdis CA, Mills EN, Papadopoulos N, Roberts G, Schnadt S, Van Ree R. EAACI Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Guidelines. Protecting consumers with food allergies: understanding food consumption, meeting regulations and identifying unmet needs. Allergy. 2014 Nov;69(11):1464-72.
- Cohen MR. The role of drug packaging and labeling in medication errors. Medication errors. 2007:111-52.
- Montgomery DC. Introduction to statistical quality control. John wiley & sons; 2019 Dec 30.
- Guideline IH. Good manufacturing practice guide for active pharmaceutical ingredients. Q7A, Current step. 2000 Nov;4.
- Guideline IH. Development and manufacture of drug substances (chemical entities and biotechnological/biological entities) Q11. London: European medicines agency. 2011 May.
- Sanders ME, Huis in't Veld J. Bringing a probiotic-containing functional food to the market: microbiological, product, regulatory and labeling issues. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 1999 Nov;76:293-315.
- Bagchi D, editor. Nutraceutical and functional food regulations in the United States and around the world. Elsevier; 2014 Feb 25.
- Basu SK, Thomas JE, Acharya SN. Prospects for growth in global nutraceutical and functional food markets: a Canadian perspective. Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. 2007;1(4):637-49.
- Ashraf SA, Siddiqui AJ, Abd Elmoneim OE, Khan MI, Patel M, Alreshidi M, Moin A, Singh R, Snoussi M, Adnan M. Innovations in nanoscience for the sustainable development of food and agriculture with implications on health and environment. Science of the Total Environment. 2021 May 10;768:144990.
- Goyal N, Jerold F. Biocosmetics: technological advances and future outlook. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. 2023 Feb;30(10):25148-69.
- de Toro-Martín J, Arsenault BJ, Després JP, Vohl MC. Precision nutrition: a review of personalized nutritional approaches for the prevention and management of metabolic syndrome. Nutrients. 2017 Aug 22;9(8):913.
- Di Renzo L, Gualtieri P, Romano L, Marrone G, Noce A, Pujia A, Perrone MA, Aiello V, Colica C, De Lorenzo A. Role of personalized nutrition in chronic-degenerative diseases. Nutrients. 2019 Jul 24;11(8):1707.
- Liu Y, Zeng S, Ji W, Yao H, Lin L, Cui H, Santos HA, Pan G. Emerging theranostic nanomaterials in diabetes and its complications. Advanced Science. 2022 Jan;9(3):2102466.
- Sharma P, Srivastava P, Singh A. Rishabha Malviya. Education. 2008 Oct;2010.
- Differding E. Biotechnology in India: An Analysis of ‘Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council’(BIRAC)?Supported Projects. ChemBioChem. 2023 Nov 2;24(21):e202300302.
- Noce A, Marrone G, Di Daniele F, Ottaviani E, Wilson Jones G, Bernini R, Romani A, Rovella V. Impact of gut microbiota composition on onset and progression of chronic non-communicable diseases. Nutrients. 2019 May 14;11(5):1073.
- AlFadhly NK, Alhelfi N, Altemimi AB, Verma DK, Cacciola F, Narayanankutty A. Trends and technological advancements in the possible food applications of Spirulina and their health benefits: A Review. Molecules. 2022 Aug 30;27(17):5584.
- Zhang T, Gao G, Kwok LY, Sun Z. Gut microbiome-targeted therapies for Alzheimer’s disease. Gut microbes. 2023 Dec 18;15(2):2271613.
- Ottman JA, Stafford ER, Hartman CL. Avoiding green marketing myopia: Ways to improve consumer appeal for environmentally preferable products. Environment: science and policy for sustainable development. 2006 Jun 1;48(5):22-36.
- Steinberg E, Greenfield S, Wolman DM, Mancher M, Graham R, editors. Clinical practice guidelines we can trust. national academies press; 2011 Jul 16.
- Wallach LM. Accountable governance in the era of globalization: The WTO, NAFTA, and international harmonization of standards. U. Kan. L. Rev.. 2001;50:823.
- Thow AM, Jones A, Hawkes C, Ali I, Labonté R. Nutrition labelling is a trade policy issue: lessons from an analysis of specific trade concerns at the World Trade Organization. Health promotion international. 2018 Aug 1;33(4):561-71.
- Maizes V, Rakel D, Niemiec C. Integrative medicine and patient-centered care. Explore. 2009 Sep 1;5(5):277-89.
- Hechtman L. Clinical naturopathic medicine-eBook. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2013 Jun 3.
- Cohen MH. Beyond complementary medicine: legal and ethical perspectives on health care and human evolution. University of Michigan Press; 2000


 Sakshi Kumari *
Sakshi Kumari *
 Sonu Sharma
Sonu Sharma
 Vikram Kumar
Vikram Kumar
 Nitish Kumar
Nitish Kumar
 Amit Kumar Yadav
Amit Kumar Yadav
 Manish Kumar Chandravanshi
Manish Kumar Chandravanshi
 Gaurav Kumar
Gaurav Kumar
 Shubhankar Kumar
Shubhankar Kumar
 Subham Nandi
Subham Nandi
 Neeraj Kumar Mandal
Neeraj Kumar Mandal
 Chandan Pal
Chandan Pal








 10.5281/zenodo.13995210
10.5281/zenodo.13995210