Abstract
The pharmaceutical industry is currently at its pinnacle. It's important to make sure that pharmaceutical process validations are carried out correctly and that the outcomes are repeatable. Results merely guarantee the uniformity of product products.The significance of objective measurements, statistical tools, and analyses is also emphasized by process validation, which likewise places an emphasis on understanding, detection, and control of variability and provides assurance on consistency of quality and productivity across a product's life cycle. Validation studies are a crucial component of GMP, according to GMP, and they must be completed in accordance with established guidelines. Establishing written proof that offers a high level of assurance that a certain process consistently yields a product that satisfies its set specifications and quality characteristic is known as process validation. In order to guarantee repeatable, high-quality goods, process validation is a systematic method of indenting, measuring, assessing, recording, and reevaluating the crucial steps in the manufacturing process. This article provides a broad introduction and overview of the significance of process validation in the pharmaceutical manufacturing process.
Keywords
Process Validation, cGMPs
Introduction
Among cGMPs, pharmaceutical process validation is considered the most significant and widely accepted criteria. The quality system (QS) regulation contains the standards for process validation. The process of developing a drug product into a dosage form involves several steps, including regulatory registration, animal studies, clinical trials, laboratory testing, and drug discovery. A product must meet a number of quality standards before being put on the market, including identity, chemical composition, physical stability, appropriate preservation against microbial contamination, when necessary, strength, quality, purity, uniformity of drug dosage, stability, acceptability to users, including prescribers and patients, and appropriate packaging, labeling, and validation. Two crucial elements that can guarantee the aforementioned characteristics in the manufacturing process are process controls and process validation. Measure controls include process controls that address raw materials. The goal is to approve and screen line production process operations. Following this, the process is approved for presentation and confirmed, guaranteeing a well-crafted methodology for the cycle controls.
The goal of process validation, which is broadly applicable to manufacturing processes, is to help producers comprehend the requirements of the quality management system (QMS) with regard to process validation. Validation is a crucial component of pharmaceutical organizations that underpins their dedication to quality assurance. One tool used in quality assurance is validation, which verifies the accuracy of software, hardware, manufacturing processes, and testing procedures (1).
NEED OF PROCESS VALIDATION:
FDA Guidelines:
Establishing recorded proof that provides a high degree of certainty that a specific process will consistently produce a product satisfying its predetermined specifications and quality features is known as process validation, according to regulations found by the FDA. for a thorough analysis and management of every single process, including quality assurance and manufacturing (3).Bottom of Form
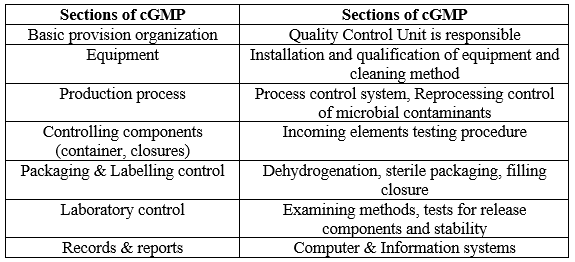
Table 1: PV Checklist (3).
Process validation:
Process validation is an essential part of the quality assurance system employed by pharmaceutical producers since it is a crucial factor in the safety and quality of drug products. In order to guarantee repeatable, high-quality goods, process validation is a systematic method of indenting, measuring, assessing, recording, and reevaluating the crucial steps in the manufacturing process. Process validation is a function of quality
assurance that contributes to the assurance of pharma product quality by offering documented proof that the manufacturing process continuously performs as intended.
A number of variables, including the careful selection of high-quality materials and components, product and process design, process control, in-process control, and end-product testing, guarantee the product's quality, safety, and efficacy. Routine end-product testing is insufficient because of the complexity of drug products for a number of reasons. Furthermore, quality must be ingrained in the production processes rather than being tested into the final medicinal product, and these procedures must be closely monitored to ensure that the result fulfills all quality requirements. One can be very confident that all produced lots or batches will satisfy their specified specifications provided systems and process controls are carefully designed and validated (1).
Objectives of process validation (2):
- Validation is required for both the manufacturing process and the individual pieces of equipment.
- The objective is to develop a strong manufacturing process that reliably yields a pharmaceutical product that satisfies purity, identity, and potency requirements with the least amount of variance.
- To comply with rules, engineers need to create and implement a validation plan for the manufacturing process. Typically, only a PQ segment is included in the validation plan.
- Similar to equipment validation, significant alterations made after the first validation will necessitate a second validation.
- Ultimately, process validation will guarantee a reliable product that is consistently highly repeatable.
Benefits of process validation:
- Reduction in rejections and reworks
- Increased throughput
- Reduction in utility costs
- Avoidance of capital expenditures
- Fewer complaints about process related failures
- Reduced testing in process and finished goods
- More prompt and precise examinations of process deviations
- More prompt and dependable startup of new machinery
- Easier scale-up from development work
- Easier maintenance of the equipment
- Improved employee awareness of processes
- More rapid automation
A program for process validation can be made more successful and efficient by using (1):
- Good project management
- Robust scientific knowledge collection, management and archiving
- Uniform collection and assessment of information methods
- Reducing the burden of redundant information gathering
- Use of an integrated team approach
- Appropriately documented Project Plans
- The support of senior management
- Statistical assessment of data
Basics Principles Of Validation:
The following could be said to be the fundamental validation principle: Installation Qualification (IQ) is the process of proving through objective evidence that all important components of the installation of ancillary systems and process equipment follow the manufacturer's certified specification and that the equipment supplier's recommendations are appropriately taken into account(2).
Installation qualifications:
Begin with evidence that the installation and its equipment meet the Accepted 2 criteria.
IQ considerations are (3):
- Equipment configuration highlights
- Installation provisions (wiring)
- Measures, precautions to be taken, cleaning plans.
- Safety features.
- Supplier documentation, manuals etc
- Spare parts list.
- Environmental prospects just like clean facilities, humidity
Operational Qualification (OQ):
It provides the strongest reassurance that the device performs as intended and meets requirements.
OQ considerations are:
- Control limits (time, line speed)
- Raw material specifications. Handling3 requirements, Training, Short-term stability & potential (studies or charts).
- Possible failure modes & worst-case.
OQ considerations include (2):
- Process control limits (time, temperature, pressure, line speed, setup conditions, etc.)
- Software parameters.
- Raw material specifications.
- Process operating procedures.
- Material handling requirements.
- Process change control.
- Training.
- the process's capacity and short-term stability, (latitude studies or control charts).
- Potential failure modes, action levels and worst-case
conditions.
Performance Qualification (PQ):
proving by objective evidence that the method regularly yields a product that satisfies all set standards even in unexpected circumstances (4).
PQ considerations include:
- Actual product and process parameters and procedures established in OQ.
- Acceptability of the product.
- Assurance of process capability according to OQ standards.
- Process repeatability, long term process stability.
Re -Qualification:
Equipment relocation or modifications must be approved by the change control procedure after a thorough evaluation and authorization process. Re-qualification of the equipment ought to be taken into consideration during this official examination.
Modest adjustments or adjustments that don't directly affect the end or in-process product quality should be managed via the preventive maintenance program's documentation system.
Phases of Validation (2,3):
There are three categories for the activities associated with validation studies.
phases:
Phase 1: This is known as the Pre-validation Qualification Phase, and it includes all of the following: master product document, equipment qualification, installation qualification, process capacity, transfer of technology to commercial scale batches, formulation pilot batch studies, scale-up studies, handling of in-process and finished dosage forms, and establishment of stability conditions and storage.
Phase 2: The process validation phase is this one. Its purpose is to confirm that even in the most adverse circumstances, acceptable goods may be produced and that all defined limitations of the important process parameter are valid.
Phase 3: This step of preservation calls for the most thorough examination of all documents related to the process, including validations and reports to ensure that there haven't been any changes, deviations, or failures with regard to Standard Operating Procedures. It is assumed that all manufacturing and related control operations are carried out in accordance with GMP.
The following are the recommended validation steps:
1. It is imperative that investigations follow a detailed, pre-established convention or set of conventions; this means that formal change control procedures are necessary.
2. The employees who oversee the exams as well as those in charge of the procedure must be qualified, reasonable, and able to play.
3. Data from the investigations must be formally examined and verified as considered in comparison to predetermined models.
4. Accessible testing facilities, equipment, supplies, and methodologies should be available.
5. Reasonably priced clean-up rooms should be available in both foundation and "neighbourhood" climates. It should be confirmed that the designated clean room environment is achieved by starting dispatching (capability) and ensuring that the necessary equipment is introduced, trained, and maintained.
6. After giving the aforementioned enough thought, procedures for "measure recreation" may be used to approve the cycle, if it is aseptic.
7. Periodic revalidations of the interaction are necessary.
8. Ample documentation must be available for approval.
Types Of Process Validation (2,4):
Prospective validation is the process of evaluating a product before it is released into the market, whether it be a new product or one that has undergone major production process alterations that could impact its features. Before the process is placed into commercial usage, an experimental strategy known as the validation protocol is carried out in prospective process validation (after the qualification trials are finished).
The validation technique is carried out under prospective validation prior to the process being used for commercial purposes. Three successive batches or runs, all within the ultimately decided parameters and producing a product of the specified quality, are generally seen as sufficient validation of the process. This is an official statement regarding the three commercial batches prior to marketing (2).
Concurrent Process Validation (2,4):
in-process monitoring, and end-product testing of ongoing production can offer verifiable proof that the manufacturing process is under control.
Examples of these may be when:
- A previously approved procedure is being moved to a different location or to a contract manufacturer.
- The product is a variant of a previously approved medicine with an identical active/inactive component ratio.
- There weren't enough lots assessed during the retrospective validation to get a high degree o assurance showing that all aspects of the process are under control.
The number of batches that can be generated is limited.
- A method based on market demand and modest manufacturing volume per batch.
- The process of producing a medicine that is in high demand because there is a shortage or no supply.
- Concurrent validation is valid in all of the aforementioned scenarios, given that the prerequisites are met.
- Pre-approved protocol utilizing reasoning for concurrent validation.
A deviation must be requested and justified, and the plant manager, head process owner, or head-QMS must approve it.
- Product history and behavior will be examined in light of test batches, scale-ups, and developmental phases.
- A comprehensive protocol needs to be designed to address the marketed product in the event that any unfavorable reactions are detected throughout the ongoing validation process.
- All primary disciplines must approve concurrent validation batches and record them in a report.
Retrospective Process Validation:
Retrospective validation is the alternative used for well-established products whose production processes are deemed robust and when prospective validation projects cannot be justified solely on the basis of financial considerations and resource constraints.
several fundamental components of Retrospective Validation include:
- Batches produced for a certain amount of time (at least 10 most recent batches in a row).
- The annual number of lots released.
- Manufacturer, year, time, batch size, strength, etc.
- Master packing and manufacturing records.
- A list including modifications to manufacturing documents, corrective actions, and process deviations.
- Details for evaluating the consistency across multiple batches.
- Analysis of trends, including concerns about quality.
Process Re-Validation:
Required in the event that any of the formulation, main packaging components, raw material fabricator, significant equipment, or premises are altered, as well as any of the critical process parameters. Process revalidation would also be necessary if batches failed to fulfill product and process specifications’-Validation becomes necessary in certain situations. The following are examples some of the planned or unplanned changes that may require re-validation:
- alterations to the raw materials (physical characteristics that could have an impact on the process or final product, such as moisture, viscosity, density, and particle size distribution).
- Modifications to the manufacturer of active raw materials' source.
- Modifications to the principal container and closure system used in packing.
- Modifications to the procedure (such as batch size, drying temperatures, and mixing times).
- Modifications to the apparatus (such as the inclusion of an automated detecting system).
- With the exception of this new equipment, equipment changes involving the replacement of equipment "like for like" typically do not call for revalidation.
Needs to be eligible.
- A change in the facility or plant. Trend analysis reveals variations, such as process drifts.
DOCUMENTATION:
Effective communication in intricate, protracted, and multidisciplinary projects depends on documentation at every level of the process validation life cycle.
Documentation is essential to ensure that people participating in every stage of the product and process life cycle can easily access and understand the knowledge that has been collected about them. Transparency and accessibility of information are cornerstones of the scientific method. Additionally, they are necessary to empower the organizational units in charge of the process to decide wisely and scientifically, which in the end supports the introduction of a product into the marketplace (4).
CONCLUSION:
Pharmaceutical Process Validation is the most significant and well-known cGMP parameter, according to the study. Manufacturing operations must be planned and managed in accordance with the cGMP standard to guarantee that input materials and final product consistently and reliably meet specified quality requirements. The product must be sufficiently robust in its design to endure fluctuations in the manufacturing process, and the manufacturing process itself must be capable and stable in order to guarantee the continuous production of safe products with satisfactory performance. A number of actions must be taken throughout the course of the process and product lifetimes in order to validate the process
REFERENCE
- Prabu, S. Lakshmana, T. N. K. Suriyaprakash, R. Thirumurugan, and A. J. P. T. Shanmugarathinam. "Process validation: A review." Pharma times 46, no. 4 (2014): 12-5.
- Kaur, Harpreet, Gurpreet Singh, and Nimrata Seth. "Pharmaceutical process validation: a review." Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics 3, no. 4 (2013): 189-194.
- Karthick, C., and K. Kathiresan. "Pharmaceutical process validation: a review." Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics 12, no. 1-S (2022): 164-170.
- Sharma, Sumeet, and Gurpreet Singh. "Process validation in pharmaceutical industry; an overview." Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics 3, no. 4 (2013): 184-188.
- Mishra, Manish Kumar, and Pooja Kumari. "A review on pharmaceutical process validation." The Pharma Innovation Journal 6 (2019): 960-958.
- Elsie Jatto , Augustine and O. Okhamafe; An Overview of Pharmaceutical Validation andProcess Controls in Drug Development, Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, December 2002; 1 (2): 115-122.
- Guide to Inspections of Oral Solid Dosage Forms Pre/Post Approval Issued for Development and Validation. Washington DC: US Food and Drug Administration, 1994. Guidance for Industry: Process Validation:General Principles and Practices. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services,
- Food and Drug Administration, Centre for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Centre for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER), Centre for Veterinary Medicine (CVM), January 2011.
- Quality Management System – Process Validation Guidance GHTF/SG3/N99-10:2004 (Edition 2).
- Health Canada / Health Products and Food Branch Inspectorate Validation Guidelines forPharmaceutical Dosage Forms (GUI – 0029) / December, 2009.
- Validation Master Plan Installation and Operational Qualification –PharmaceuticalInspection Convention; Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-Operation Scheme; PI 006 – 2; July,2004.
- Kathiresan K*, Moorthi C, Prathyusha Y, Gade B. R, Reddy B. K, Manavalan R, ; An overview of pharmaceutical validation; Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences; ISSN: 0975-8585; October – December 2010; RJPBCS 1(4); Page No. 1026.
- Guidelines for Process Validation of Pharmaceutical Dosage Form – Saudi Food & Drug Authority; Version 2; February, 1992.
- Health Canada / Health Products and Food Branch Inspectorate Validation Guidelines forPharmaceutical Dosage Forms (GUI – 0029) / December, 2009.
- Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations. Good Manufacturing Practices for Pharmaceutical Products. WHO Technical Report Series no. 82. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1992, pp 14-79
- European medicines agency. Guideline on Process Validation (Draft), Geneva, Switzerland; 2012:10-11.
- Guidelines for Process Validation of Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms, Drug Sector Saudi Food & Drug Authority, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.5?14.
- Guidelines on General Principles of Process Validation, Division of Manufacturing and Product Quality, CDER, FDA, Rockville, Maryland (May 1987).
- Current Good Manufacturing Practices in Manufacture, Processing, Packing and Holding of Human and Veterinary Drugs, Federal Register 43(190), 45085 and 45086, September 1978.
- Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations. Good Manufacturing Practices for Pharmaceutical Products. WHO Technical Report Series no. 82. Geneva: World Health Organization, 1992, pp 14-79.
- Patel VB, Rathwa MR, Patel K. Studies in prospective process validation ofcimetidine tablet dosage form. Int J Res Pharm Biomed Sci, 2011; 2(4): 1823-1836.
- FDA/ICH, (CDER and CBER), Q9 Quality Risk Management, guidance for industry, June 2006.
- FDA/ICH, (CDER and CBER), Q7 Good Manufacturing Practice for Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, guidance for industry, August 2001.
- FDA/Global Harmonization Task Force (GHTF; medical devices), Quality Management Systems – Process Validation, edition 2, guidance, January 2004.
- Nash RA and Berry IR. Pharmaceutical Process Validation., second edition, Marcel Dekker inc., 167-188,200-202,205.
- European medicines agency. Guideline on Process Validation (Draft), Geneva, Switzerland; 2012:10-11.
- Guidelines for Process Validation of Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms, Drug Sector Saudi Food & Drug Authority, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.5?14.
- Kiffer,R.G, J. Pharma. sic. tec., 1995, 44, 5, p.249.
- Kumar NL, MoorthyDG, Kumar RS, Sekaran CS. An overview of pharmaceutical validation: quality assurance viewpoint, 2011; 1(4): 1003-1014.
- Agalloco J. The validation life cycle. J ParenterSci Technol. 1993; 47(3):142-14
- Satyabratajena, Arjun G, Anil kumarravipati N V, SatishkumarD,Vinod K R, David banji . Industrial Process Validation of SolidDosage Forms–An Overview International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences reviw and rsearch. 2010, 4(2).
- Guidelines for Process Validation of Pharmaceutical Dosage Form – Saudi Food & Drug Authority; Version 2; February, 1992.
- Kathiresan K, Moorthi C, Prathyusha Y, Gade B. R, Reddy B. K, Manavalan R, ; An overview of pharmaceutical validation; Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences; ISSN: 0975-8585; October – December 2010; RJPBCS 1(4); 1026.
- Validation Master Plan Installation and Operational Qualification – Pharmaceutical Inspection Convention; Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-Operation Scheme; PI 006 – 2; July, 2004.
- Good manufacturing practices for pharmaceutical products, WHO expert. Committee on specification for pharmaceutical prepration, 32andreport, WHO technical report series no.823, WHO, Geneva, 1992,14-96.
- This concept is discussed in more detail in FDA’s guidance for industry, Quality Systems Approach to Pharmaceutical Current Good Manufacturing Practice Regulations,http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRe gulatoryInformation/Guidances/default.htm.
- \Guidance for Industry: Process Validation: General Principles and Practices. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Centre for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Centre for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER), Centre for Veterinary Medicine (CVM), January 2011.
- Oechslein C, Lazar M. S – Process Validation from view report of the FDA, Maas & Peither AG – GMP Publishing, LOGFILE No. 3/ February 2012.
- Quality Management System – Process Validation Guidance GHTF/SG3/N99-10:2004 (Edition 2).
- Nash R. And Wachter A. H, Pharmaceutical Process Validation an International Third Edition. Revised and expanded, Marcel Dekkar, Inc., New York, 2003; 17 – 40. https://doi.org/10.1201/9780203912119
- Patel R. C, Bhuva C. K, Singh R. P, Dadhich A, Sharma A., - Pharmaceutical Process Validation, Pharma tutor – ART – 1053.
- Kathiresan K*, Moorthi C, Prathyusha Y, Gade B. R, Reddy B. K, Manavalan R, An overview of pharmaceutical validation; Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences; 2010; 1(4):1026.
- Pharmaceutical Process Validation: Guide to Inspections of Oral Solid Dosage Forms pre/post Approval Issue for Development and Validation; issue (1/94); January 2010.M8.
- Green JM. A Practical Guide to Analytical Method Validation, Anal. Chem. News and Features 1996; 60:305A-9A. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac961912f
- Akers, J. Simplifying and improving process validation. J. Parent. Sci. Technol. 1993, 47, 281–284.
- Avallone, H.L.; D?Eramo, P. Scale-up and validation of ANDA/NDA products. Pharm. Eng.1992, 12 (6):36–39. Karthick et al Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics. 2022; 12(1-s):164-170 ISSN: 2250-1177 [170] CODEN (USA): JDDTAO
- Chowhan, Z.T. Development of a new drug substance into a compact tablet. Pharm. Technol.1992, 16 (9):58–67.
- Nash RA. Process Validation of a 17-Year retrospective study of solid dosage forms Drug DevInd Pharm 1966; 22 (1):25-34. https://doi.org/10.3109/03639049609043869
- Therapeutics Products Programme. Process Validation: Aseptic Processes for Pharmaceuticals. http://www.hc sc.gc.ca/hpbdgps/therapeutic; downloaded March 30, 2001.
- Lambert J. Validation Guidelines for Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms. Health Canada / Health Products and Food Branch Inspectorate; 2004. pp. 7-15.
- Gupta GD, Garg R, Aggarwal S. Guidelines on General Principles of Validation: Solid, Liquid and Sterile dosage forms. Pharm Sci Tech, 2008; 6:28-33
- Dashora K, Singh D, Saraf S. Validation – the Essential Quality Assurance Tool for Pharma Industries. Pharminfo, 2005; 3:45-47.
- FDA Guidance Update: process Validation: General Principles and Practices; version 01; 2009.
- Validation Master Plan Installation and Operational Qualification – Pharmaceutical Inspection Convention; Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-Operation Scheme; PI 006 – 2; July, 2004.
- Kiffer,R.G, J. Pharma. sic. tec., 1995, 44, 5, p.249.
- Kumar NL, MoorthyDG, Kumar RS, Sekaran CS. An overview of pharmaceutical validation: quality assurance viewpoint, 2011; 1(4):1003-1014.
- Agalloco J. The validation life cycle. J ParenterSci Technol. 1993; 47(3):142-147
- Sharp JR. The Problems of Process Validation. Pharm J 1986; 1:43- 5.


 Durga Bhagavan zade*
Durga Bhagavan zade*
 Mrs, Smita.S.Aher
Mrs, Smita.S.Aher

 10.5281/zenodo.12684461
10.5281/zenodo.12684461