Abstract
Under-eye gel patches are used as a cosmetic as well as a cosmeceutical formulation for their targeted delivery of active ingredients to the delicate under-eye area. This research focuses on the development and assessment of under-eye hydrogel patches aimed at enhancing skin hydration, reducing fine lines, dark circles, pigmentation and improving overall skin appearance as well as provide a soothing and cooling sensation by utilizing the hydration-retaining power of hydrogels. The study begins with the formulation of gel patches using various polymers and bioactive compounds known for their moisturizing, soothing and anti-aging properties. Methods include characterization of patch morphology, evaluation of hydration efficacy through water loss measurements, and assessment of overall physicochemical parameter of the formulation. Additionally, sensory evaluations and subjective feedback from a participant contribute to understanding user perception and comfort. Results indicate significant improvements in skin hydration levels and elasticity following patch application, alongside positive user experience. This study highlights the potential of revitalizing under eye gel patches as effective skincare solutions and underscores the importance of comprehensive assessment in product development. Future directions include optimizing formulations for better application and exploring broader area in cosmetic dermatology.
Keywords
Hydrogel, Skin Care, Under-Eye Patch, Hydrogel Eye Patch, Emollient Action
Introduction
The quest for effective and safe solutions to address under-eye concerns has long been a pursuit in both cosmetic and therapeutic realms. From puffiness and dark circles to fine lines and wrinkles, the delicate skin beneath the eyes often bears the brunt of stress, fatigue, and aging. Amidst this pursuit, hydrogel patches have emerged as a promising solution for delivering targeted relief and rejuvenation. In the realm of skincare innovations, hydrogel formulations have emerged as versatile vehicles for delivering active ingredients to target specific skin concerns. Defined by their water-rich, cross-linked polymer networks, hydrogels possess unique properties that make them well-suited for applications ranging from wound healing to cosmetic enhancement. Among their diverse applications, hydrogel-based under eye patches have garnered significant attention for their potential to address a myriad of under eye concerns effectively and conveniently.
Hydrogels are three-dimensional polymers that are crosslinked and contain hydrophilic groups that allow them to hold onto water without disintegrating. Polymers can be used to create hydrogels. Water fills the gaps between the macromolecules, causing the complex to swell and become a hydrogel. Due to the hydrophilic functional groups in the polymers, which hydrate in presence of aqueous conditions, the hydrogel have the capacity to absorb water. [1] The hydrogel can't dissolve in water because of the crosslinks in the polymer network chains. Depending on their origin, polymer content, biodegradability, and arrangement, hydrogels come in various forms. Hydrogels vary in type based on their source, polymer composition, biodegradability, and structure. They can be classified by their crosslinking type, physical appearance, the electrical charge of their network and the method of preparation. [1] Hydrogels exhibit great potential in the management of dark circles, wrinkles, fine lines, and puffiness—all of which are prevalent in the majority of the world's aging population.They can also be used in cosmetic under-eye procedures. Hydrating the sensitive area beneath your eyes is the primary goal of hydrogel under eye patches. Less sebaceous glands are found in the skin around the eyes, which makes the skin there more prone to dryness. Furthermore, the skin surrounding the eyes is substantially thinner, making it extremely sensitive and vulnerable to wrinkles and other aging symptoms. For this area, proper hydration is crucial, and patches are a great complement to your everyday skincare routine. In light of their high water content and hydrophilic basis, which form a matrix on the skin and permit highly effective delivery of active chemicals, hydrogels are frequently used as ingredients in eye patches. [2] Hydrogel patches regulate skin temperature and improve physiological activity in addition to providing the skin with enhanced moisturization and regeneration. Hydrogel patches are relatively simple to apply and have good elasticity.The development of hydrogels for use as an under-eye patch component is the goal of this project. Water permeability and the function of other chemicals in under-eye patches will be best examined in relation to the hydrogels that were developed. [2]
The delicate skin surrounding the eyes presents a unique set of challenges, characterized by increased vulnerability to environmental stressors, aging, and lifestyle factors, traditional skincare approaches, while effective to some extent, may fall short in delivering targeted relief to this sensitive and complex region. This research paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the utilization of hydrogel patches in relieving various under eye problems. By examining the latest scientific literature, clinical studies, and product formulations, we seek to elucidate the efficacy, safety, and potential mechanisms of action of these innovative skincare solutions. Through a systematic exploration of ingredients such as aloe vera, honey, egg yolk, glycerine and sandalwood we endeavor to shed light on their therapeutic properties and their ability to soothe, hydrate, and revitalize the delicate under eye area. In addition to their cosmetic benefits, hydrogel patches offer the potential for therapeutic applications in addressing under eye concerns associated with inflammation, oxidative stress, and vascular dysfunction. This paper seeks to contribute to the growing body of knowledge surrounding natural skincare remedies and their role in promoting under eye health and beauty.
MATERIAL AND METHOD
This research project was conducted in Department of Pharmacy, Barkatullah University, Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh, India in June 2024.
Collection of material:
Five types of different hydrogels were formulated using aloe vera, honey, glycerine, egg yolk, and sandalwood. Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis miller) extract was obtained from the plant available nearby whereas egg, sandalwood, glycerine, and honey were bought from the local market.
- Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis miller) - The aloe gel acts as an emollient, a good moisturizer, an anti-inflammatory agent and helps to treat skin irritation. [3]
- Honey – is utilized in reducing inflammation, healing the skin, decreasing pigmentation and hence gives an anti aging effect on skin. [4]
- Sandalwood - Sandalwood is mainly used as coolant, restores, rejuvenates skin aging and wrinkled skin, reduces dryness and itching. [5]
- Egg yolk - it acts as sun protectant, emollient and anti-inflammatory agent hence reduces puffiness. [6]
- Glycerine - plays a role in skin hydration, cutaneous elasticity, epidermal barrier repair and protects against irritating stimuli. [7]
Procedure
The process begins with the preparation of borax solution. Dissolve 4 grams of borax in 100 ml of distilled water to create borax solution, which should dissolve without heating and can be stored in a stoppered bottle. In five separate beakers, weigh 2 grams of xanthan gum and add 5 grams of glycerine, ensuring thorough mixing to prevent lumping. Next, different extracts such as aloe vera, sandalwood, egg yolk, and honey were incorporated in four different beakers and mixed well. Although all beakers contains glycerine as base, one beaker with previously added glycerine was mixed as it is, without adding aloe vera, honey, sandalwood or egg yolk to make the glycerine based hydrogel. Carefully add 25 ml of demineralized water to each beaker and continue mixing. Introduce 7.5 ml of the prepared 4% borax solution into each mixture, ensuring thorough incorporation. Allow the crosslinking reaction to proceed for one hour until the material achieves homogeneity. The resulting hydrogel demonstrates resistance to freeze-thaw cycles (from 20°C to -20°C and back to 20°C) and can be further adjusted to achieve a resistant and flexible film by reducing its water content.
Evaluation
- Organoleptic evaluation – Visual and sensory inspection of the prepared hydrogels for their color, appearance, uniformity, consistency, stickiness, greasiness and adhesion was done. Their odor was also determined.
- Hydrogel patch acidity - The hydrogel patch is dipped in 10 ml of distilled water for 2 hrs at room temperature. The hydrogel patch’s pH is then measured with a pH paper. Measurements are repeated three times, and the mean values are recorded.
- Stability test - The five formulations were kept in polyethylene boxes at room temperature for 2 days. After this time, the hydrogel samples were visually assessed for formulation appearance and evaluated for chemical stability (pH) and physical stability (color, spreadability, texture).
- Irritation test on skin – Hydrogel is placed on the skin and held with the help of very thin cotton wipe. After an hour, it is removed and the effect on skin irritation is recorded.
- Swelling index – The swelling index of a hydrogel eye patch is a measure of how much the hydrogel can absorb water or another fluid relative to its initial dry weight. It's an important property for evaluating the performance of hydrogel-based products, especially for applications like eye patches where hydration and retention of moisture are crucial for comfort and efficacy. Weigh the hydrogel eye patch in its dry state to obtain initial weight. Next, immerse the dry hydrogel in distilled water at room temperature for a specified duration of two hours, to ensure complete swelling. After the swelling period, carefully remove the hydrogel from the water bath and gently blot it with filter paper to eliminate excess surface water, avoiding any pressure that could alter its weight. Then, weigh the swollen hydrogel to determine the final weight.
Swelling Index= (WA-WB)/WB x100%
WA = hydrogel patch weight after hydration
WB = hydrogel patch weight before hydration
- Equilibrium water content percent measurements (EWC%) – Equilibrium water content percent (EWC%) refers to the maximum percentage of water absorbed by a hydrogel to reach full hydration. To calculate the EWC% hydrogel disc of 1 cm in diameter is cut from hydrogel films and weighed which is considered as the weight of the disc in equilibrium with water (W1). The discs were then fully dried by placing them in a vacuum oven at 70 degrees celsius until they reached constant weight (W2). [2]
EWC (%) = (W1-W2/W1) x 100
- Application on skin – a specific sensitive area of 2x2 cm on forearm was marked. Each hydrogel patch was applied on the skin and held with the help of very thin cotton wipe. The effect of hydrogels on skin such as cooling effect, soothing, depigmentation, softness were determined after three hours of patch being in contact with the skin.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION :-
The following results were obtained -
TABLE 1 Organoleptic evaluation results of hydrogel patches
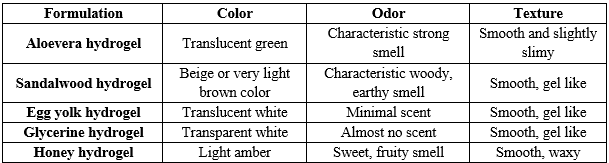
TABLE 2 Determination of pH, skin irritation, swelling index, stability and EWC% of hydrogel patches

Application on skin (User’s experience) –
The user described their experience with the newly applied hydrogel patch as positive and refreshing. They mentioned feeling a cooling sensation upon application, which provided instant relief and comfort to the skin. The hydrogel's moisturizing properties left their skin feeling noticeably softer and smoother. Additionally, the hydrogel imparted a revitalized and healthier appearance to their skin. Overall, the user expressed satisfaction with the hydrogel patch, highlighting its cooling effect, skin-conditioning benefits, and the overall improvement in skin texture and appearance.
According to the overall results and practical experience of the user, the quality of hydrogel in decreasing order is :-
Aloevera hydrogel eye patches > Sandalwood hydrogel eye patches > Glycerine hydrogel eye patches > Honey hydrogel eye patches > Egg hydrogel eye patches
Aloe vera hydrogel eye patches were of the best quality whereas the sandalwood patches provided immense cooling sensation as compared to other patches. Honey hydrogel patches provided a very slight brightning effect/decreased pigmentation on the skin.
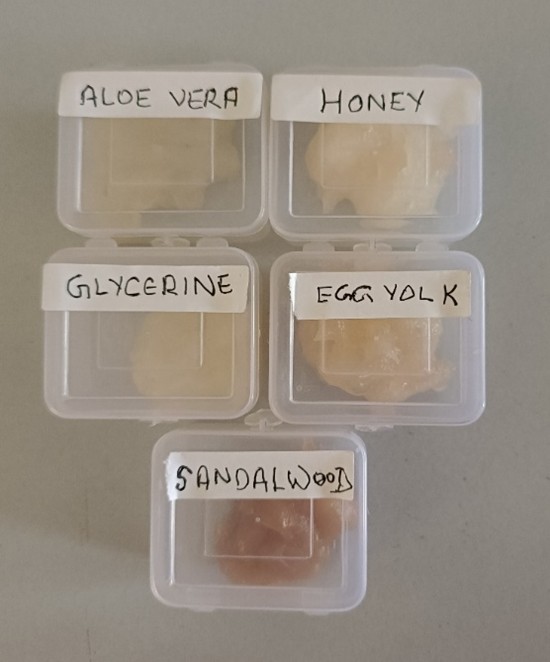

FIG 1 Five formulations of hydrogels
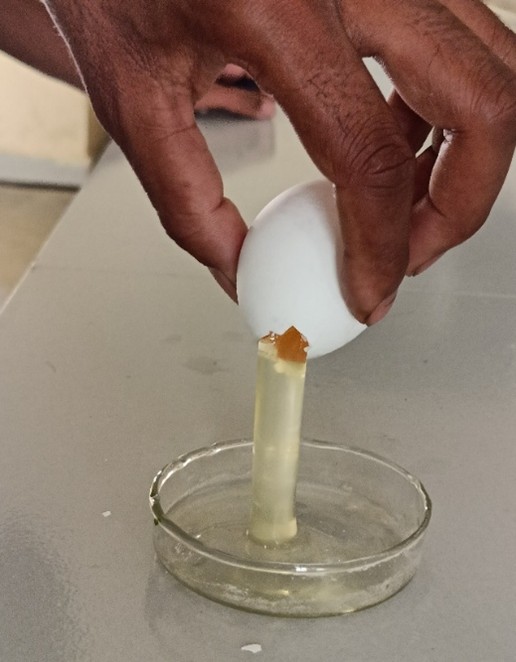

FIG 2 Egg yolk used for formulating the hydrogel
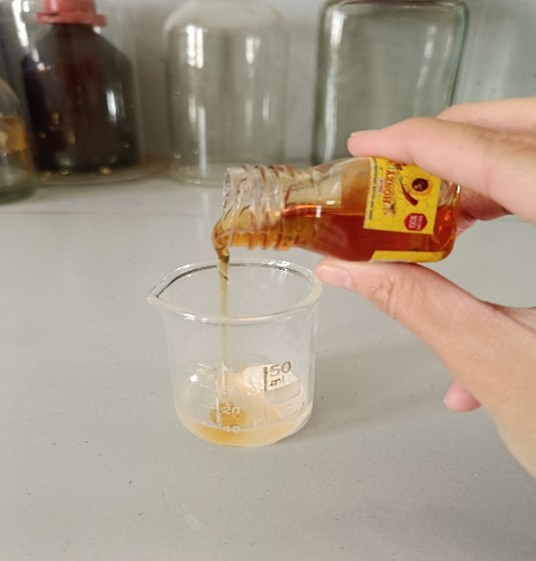

FIG 3 Honey used for formulating

FIG 4 Markings of 2x2 cm on forearm skin the hydrogel
FIG 5 Hydrogel no. 5 (honey patch)
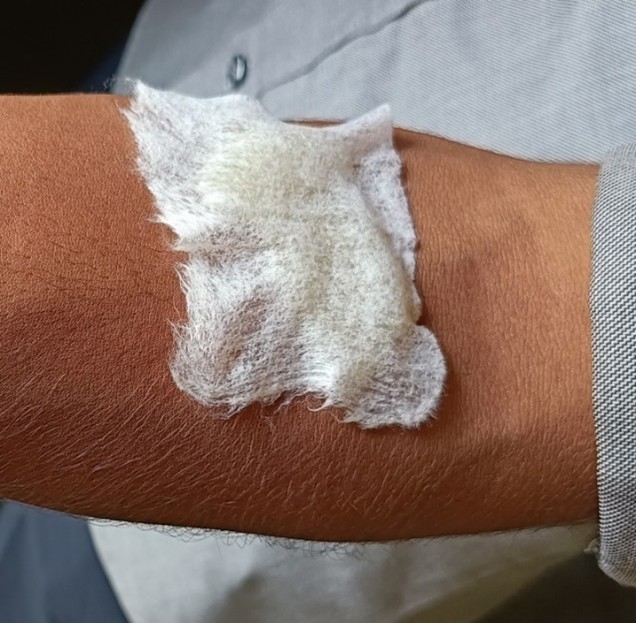
FIG 6 Hydrogel applied and secured on skin with the help of thin cottonwipe
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the development and assessment of revitalizing under-eye hydrogel patches have demonstrated promising outcomes. Clear evaluation and the positive results underscore their potential effectiveness in addressing various concerns such as fine lines, dryness, puffiness, and hydration around the delicate under-eye area. This research not only highlights the technical advancements in hydrogel patch formulation but also suggests their practical application in skincare regimens. Moving forward, further studies and rigourous trials will be essential to fully elucidate their long-term benefits and optimize their use in cosmetic and therapeutic settings. As such, revitalizing under-eye hydrogel patches represent a significant step forward in skincare innovation, promising a brighter future for holistic under-eye care. As for future prospects, the reaction to hydrogel could be initiated by pH value, temperature, ultrasound, visible light, etc. by adding sensitive agents or making specific modifications to the hydrogel-based therapy. [8] Future directions in the field of study of responsive materials, frequently referred to as stimuli-responsive hydrogels, the fabrication of so-called smart hydrogels as functional elements has revolutionized the sector. These smart hydrogels have the ability to change both structurally and volumetrically in response to external stimuli, which opens up a wide range of possibilities for varied technological applications. [9] Contact lenses, tissue engineering, hygiene products, drug administration, and wound dressing have their established roles, but their commercial applications are still restricted. Hydrogels have demonstrated remarkable properties such as biocompatibility and biodegradability, rendering them an ideal candidate in the field of biomedical devices. Hydrogels are therefore used in everyday products, even if their full potential is still being explored. [10]
REFERENCE
- Rashid F, Albayati M, Dodou K : Novel Crosslinked HA Hydrogel Films for the Immediate Release of Active Ingredients. Cosmetics. 2023; 10:2
- Khedkar S, Aher R : Cosmetic Hydrogel Under Eye Patch: Review, International Journal of Science & Engineering Development Research 2022 Vol.7, Issue 8, page no.1621 – 1636
- Pareek S, Nagaraj A, Sharma P, Naidu S, & Yousuf A: Aloe-Vera : A Herb with Medicinal Properties, International Journal of Oral Care and Research 2013
- Al-Waili N, Salom K, Al-Ghamdi AA : Honey for wound healing, ulcers, and burns; data supporting its use in clinical practice, Scientific World Journal 2011;11:766-787.
- Shahinoor, Md & Dulal, Rahman & Taher, Mohammad & Sheikh, Hasib : Sandalwood Oil Can Be A Miraculous Tackle On Skin Aging, Skin Appearance And Wrinkle Skin-A Review, World Journal Of Pharmaceutical And Medicinal Research 2019, 5(1), 51-55
- Madan K, Nanda S : Hen egg yolk oil: A potential source of bioavailable lutein and zeaxanthin for skin and sun protection, World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2016, 5(1), 71–80
- Fluhr, Joachim & Darlenski, Razvigor & Surber, Christian : Glycerol and the skin: Holistic approach to its origin and functions, The British Journal Of Dermatology 2008 159; 23-34.
- Teng Y, Li S, Tang H, Tao X, Fan Y, Huang Y : Medical Applications of Hydrogels in Skin Infections: A Review. Infect Drug Resist. 2023;16:391-401
- Sánchez-Cid P, Jiménez-Rosado M, Romero A, Pérez-Puyana V: Novel Trends in Hydrogel Development for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Polymers (Basel) 2022;14(15):3023
- Kasai, Deepak & Devi, Radhika & S Puthran, Archana & Hamzad, Shanavaz & Koutavarapu, Ravindranadh & Lee, Dong-Yeon & Shim, Jaesool: A Review On Hydrogels Classification And Recent Developments In Biomedical Applications, International Journal of Polymeric Materials and Polymeric Biomaterials 2022 72; 1-11.

 Naina Bhargava *
Naina Bhargava *
 Rachana Akhand Giri
Rachana Akhand Giri
 Harshvardhan Dangi
Harshvardhan Dangi








 10.5281/zenodo.13176042
10.5281/zenodo.13176042