Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease characterized by airway hyper-responsiveness, inflammation, and obstruction. Recent studies have increasingly utilized In-vitro and In- silico methodologies to explore potential therapeutic interventions and understand the underlying mechanisms of asthma. Bacopa Monnieri (Linn.) based empirical formulation including the components of antioxidant, cancer prevention and prevention of neurological problems it also revealed that it showed potent pharmacological activity against asthmatic condition through the results. The results indicate the ethanolic extract of Bacopa Monnieri possess anti - asthmatic effect, this activity is due to the presence of benzoyl-beta-D-glucoside and squalene
Asthma, Bacopa monnieri (Linn.), Squalene, Benzoyl-beta-D-glucoside.
Asthma is a prevalent chronic respiratory condition characterized by airway inflammation, episodic symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath and variable airflow limitation. Asthma affects approximately 235 million people globally and is marked by symptoms that can vary in intensity and frequency. The disease involves complex interactions between genetic predispositions and environmental factors, leading to airway hyper-responsiveness and inflammation. A significant aspect of asthma's pathophysiology includes T2-type inflammation, which is prevalent in both children and adults, often linked to allergen sensitization [1][2] . The perennial creeping herb Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) is a member of the Scrophulariaceae family and has tiny leaves and white or purple blooms. Native to India and Australia, it grows in warm wetlands and is also found in the United States and East Asia. Since ancient times, it has been utilised as a medicinal herb in Ayurveda. It is used to treat tumours, ulcers, asthma, and epilepsy. It was first mentioned in writings such as the Charaka Samhita, Atharva-ved, and Susurtu Samhita in the sixth century A.D [3]. Ethanolic stem extract of Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) for In-silico research employing molecular modelling and In-vitro anti-asthmatic activity was studied by the preparation of the chick trachea and ileum
MATERIALS AND METHOD
Collection of plant material
Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) plant was collected locally from Tambaram-Varadharajapuram Tamilnadu, India. The collected plant material was identified by Dr.K.N.Sunil Kumar, Research officer and HOD of pharmacognosy and approved by Dr.P.ELANKANI research officer in Siddha Central Research Institute, Arignar Anna Govt. Hospital Campus, Arumbakkam, Chennai. (Form.No.PCOG002-ACF)
Preparation of extract
A dried 500g of Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) stem powder to 90% ethanol and distilled water were mix together and kept for 72hrs. During this period the contents of the container were shaken to dissolve the extract in alcohol completely the process intended to soften and break the plant’s cell wall to release the soluble Phyto chemical. After 7 days the mixture is pressed or strained by filtration (MACERATION TECHNIQUE). The extract was centrifuged at 4500rpm for 8 mins. The fluid in the open container was place in the chamber until the alcohol is evaporated. The concentrated green extract was placed in oven (50oC) until the extract was dried and a dry matter remined. Amount of dried extract was dissolved in distilled water and a different dose of the Bacopa monnieri (linn.) stem extract (BMSE) has been utilized for further study [4].
In-vitro study of anti-asthmatic activity
Chicken Tracheal Strip and ileum Preparation:
The anti-asthmatic assay of ethanolic extract on chicken tracheal strip and ileum preparation was carried out according to method described by Kulkarni . In this method, fresh chicken trachea and ileum brought from local slaughter house was cut into zigzag fashion. It was suspended in an Organ bath of 20 ml Tyrode solution maintained at 37±100c with continue aeration. One end was tied to aerator tube and other attached to isotonic frontal writing lever to Kymograph paper on Sherrington rotating drum. Tissue was allowed to equilibrate for 45 min during which, the bathing solution was changed frequently after every 5 minutes [5].
Procedure for Assay of Chick Ileum:
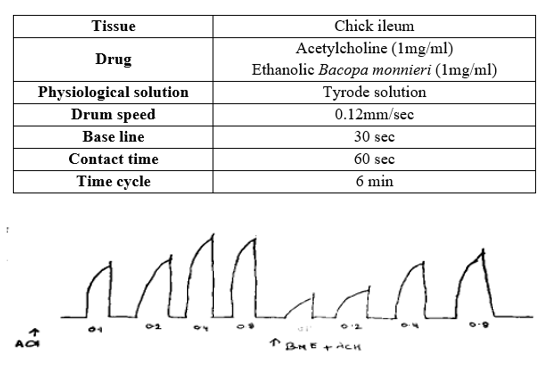
The anti-asthmatic assay of ethanolic (BMSE) was performed according to procedure. The fresh chicken ileum was collected from local slaughter house in Tyrode solution and cleaned off the mesentery. The segment of 2cm long was mounted in a 20ml tissue organ bath and maintained at 37?. The tissue was allowed to equilibrate for 30 min, during which, the bathing solution was changed at every 10 min. Contact time of 60 sec, and base line of 30 sec time cycle were opted for proper recording. Cumulative concentration-effect curves were recorded on kymograph for Acetyl choline (I0ug/ml) in absence and presence of an ethanolic extract of Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) stem (100ug/ml) on Kymograph by using Sherrington's Recording Drum. The percentage inhibition of extract and standard drug was calculated and graph was plotted by taking log dose verses height of response curve.bThe contractile responses of ileum to acetylcholine (10ug/ml) With doses of0.1ml, 0.2ml, 0.4ml, and 0.8ml were recorded in absence and presence of ethanolic extract of Bacopa monneri(Linn.) (100 ug/ml) by using Sherrington's Recording Drum with a frontal writing lever. The height of response curve was measured to express percentage inhibition. The graph was plotted by taking log dose verses height of response curve [5]
Procedure for Assay of Chick trachea:
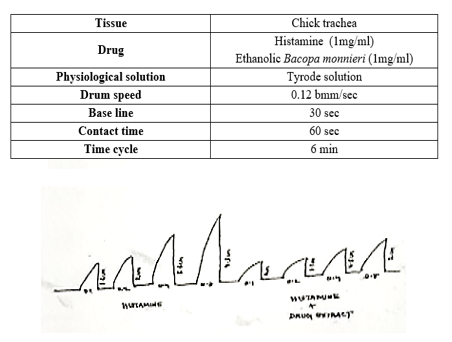
The anti-asthmatic assay of ethanolic BMSE was performed according to procedure. The fresh chicken trachea was collected from local slaughter house in Tyrode solution and cleaned off the mesentery. The segment of 2cm long was mounted in a 20ml tissue organ bath and maintained at 37oC. The tissue was allowed to equilibrate for 30 min, during which, the bathing solution was changed at every 10 min. Contact time of 60 sec, and base line of time cycle were obtained for proper recording. Cumulative concentration-effect curves were recorded on kymograph for histamine, absence and presence of ethanolic extract of Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) stem (100ug/ml) on Kymograph by using Sherrington’s Recording drum with a frontal writing lever. The Main procedure was carried for concentration-effect curve of histamine as a standard drug. The percentage inhibition of extract and standard drug was calculated and graph was plotted by taking log dose verses height of response curve. The contractile responses of trachea to histamine (10 ug/ml) With doses of 0.1ml, 0.2ml, 0.4ml, and 0.8ml were recorded in absence and presence of ethanolic extract of Bacopa monneri (Linn.) stem (100 ug/ml) by using Sherrington's Recording Drum with a frontal writing lever. The height of response curve was measured to express percentage inhibition . The graph was plotted by taking log dose verses height of response curve [5].
In-silico study of anti-asthmatic activity
Methodology Adopted:
Gas Chromatograph:
A Shimdzu GC-2010 Plus gas chromatograph was equipped with a straight deactivated 2 mm direct injector liner and a 15m Alltech EC-5 column (250? I.D., 0.25? film thickness). A split injection was used for sample introduction and the split ratio
was set to 10:1. The oven temperature program was programmed to start at 35°C, hold for 2 minutes, then ramp at 20°C per minute to 450°C and hold for 5 minutes. The helium carriergas was set to 2 ml/minute flow rate (constant flow mode).
Mass Spectrum:
A Direct connection with capillary column metal quadupole mass filter prerod bmass spectrometer operating in electron ionization (EI) mode with software GCMS solution ver. 2.6 was used for all analyses. Low-resolution mass spectra were acquired at a resolving power of 1000 (20% height definition) and scanning from m/z 25 to m/z 1000 at 0.3 seconds per scan with a 0.2 second inter-scan delay. High resolution mass spectra were acquired at a resolving power of 5000 (20% height definition) and scanning the magnet from m/z 65 to m/z 1000 at 1 second per scan.
Mass spectrometry library search :
Identification of the components of the compound was matching their recorded spectra with the data bank mass spectra of NIST library V 11 provided by the instruments software. GC/MS metabolomics Database was used for the similarity search with retention index.
Target Prediction :
Drug Target is a biomolecule which is involved in signaling or metabolic pathways that are specific to a disease process. Biomolecules play critical roles in disease progression by communicating through either protein - protein interactions or protein - nucleic acid interactions leading to the amplification of signaling events and/or alteration of metabolic processes. In structure based drug design, a known 3D structure of the target is the initial step in target identification. This is usually determined either by X-ray crystallography or by NMR to identify its binding site, the so-called active site [6] In this study the target is predicted using Swiss Target Prediction.
Ligand and Receptor preparation :
Docking can be done only with PDB [Protein data bank] format of a ligand. It is prepared by obtaining the canonical SMILES [Simplified Molecular Input line Entry System] from NCBI [National Centre for Biotechnology Information]. The obtained canonical smiles of the ligands are translated into PDB file using Online Smiles Translator. The predicted target is obtained from Protein Data Bank [PDB] in 3-D structure.
AutoDock :
Auto Dock is a molecular modeling simulation. It is especially effective for the protein-ligand complex. The compounds obtained were studied through docking to evaluate their Anti Asthmatic activity.
RESULTS
In-vitro anti asthmatic activity
Effect on chick ileum :
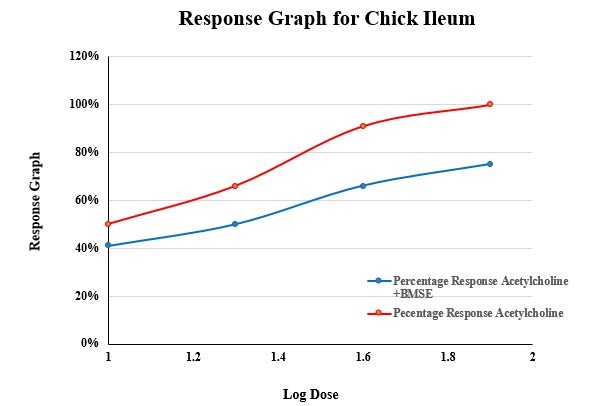
Effect of acetylcholine on excised chick ileum reflected an increase in asthmatic activity (response) with an increase in dose as shown in Figure 3. It shows anti- asthmatic effect on ethanolic extract of Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) It was evaluated by observing ts decrease in acetylcholine induced ileum contractions. These indicate that BMSE has anti-asthmatic activity.
Response curve of Acetylcholine and Acetylcholine + extract in chick ileum :
Concentration response curve of acetylcholine and its modification by ethanolic extract of Bacopa monnieri(Linn.) stem using chick ileum preparation is given in figure 3 and 4
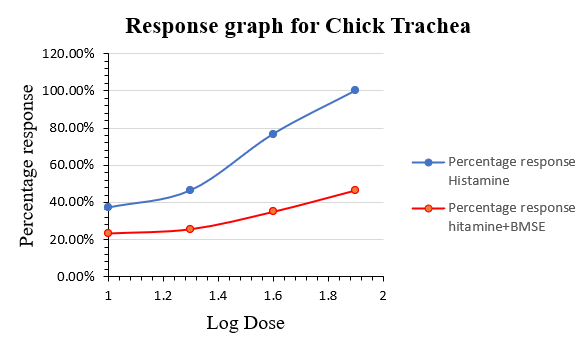
Effect on chick trachea :
Effect of histamine on excised chick trachea reflected an increase in asthmatic activity (response) with an increase in dose as shown in figure 7. it shows anti-asthmatic effect on ethanolic extract of Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) stem It was evaluated by observing its decrease in acetylcholine induced trachea contractions. These indicate that the extract fraction from Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) stem has anti-asthmatic activity.
Response curve of Histamine and Histamine + extract in chick ileum :
Concentration response curve of histamine and its modification by ethanolic extract of Bacopa monnieri(Linn.) stem using chick trachea preparation is given in the fugure 5 and 6
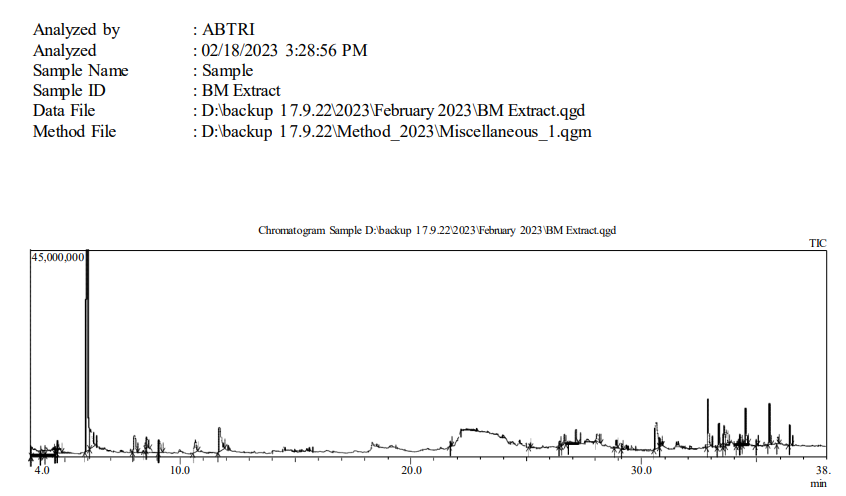
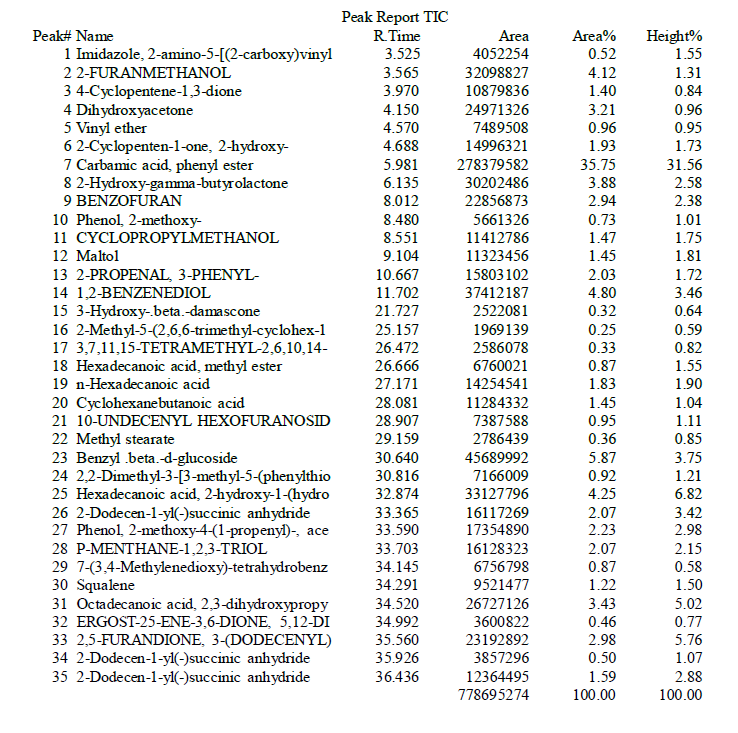
GC-MS Analysis :
The GC-MS analysis of the extract showed 35 different components present in the BM extract. The total ion chromatogram with different levels of presence showed in Figure 7 and Figure 16.
Target prediction :
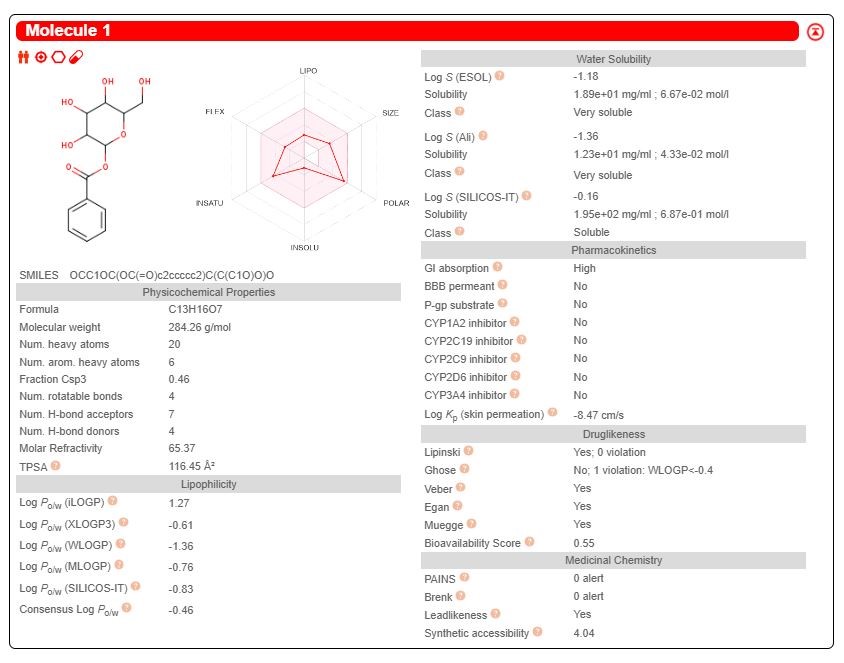
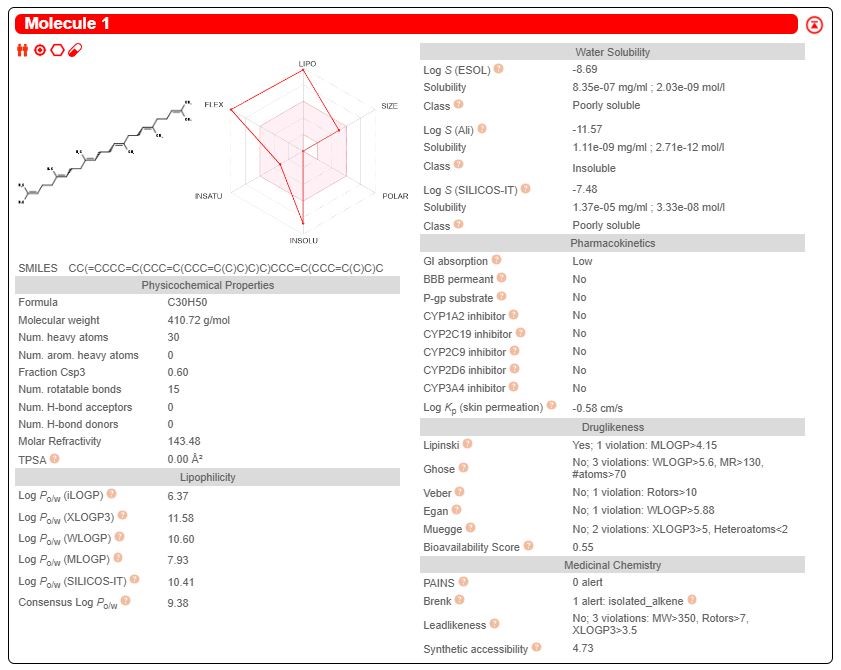
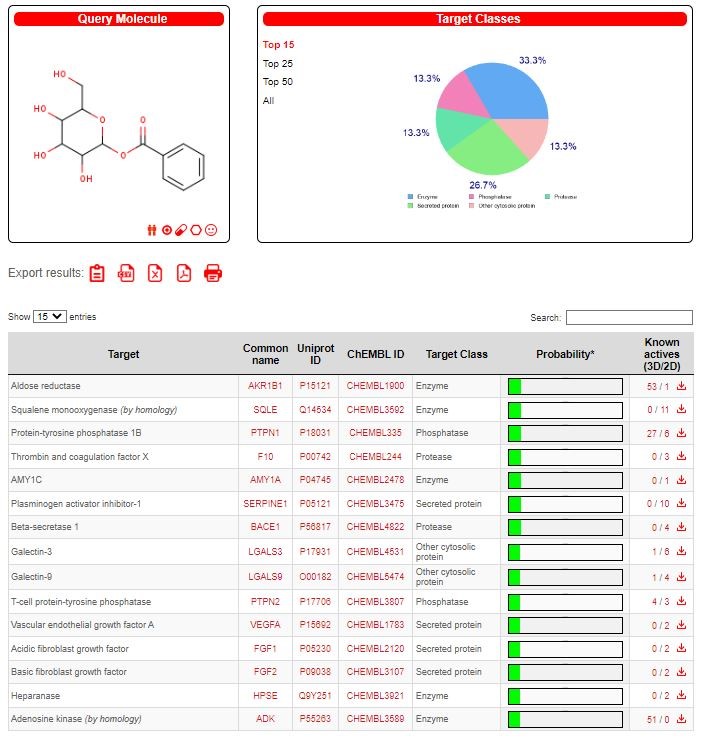
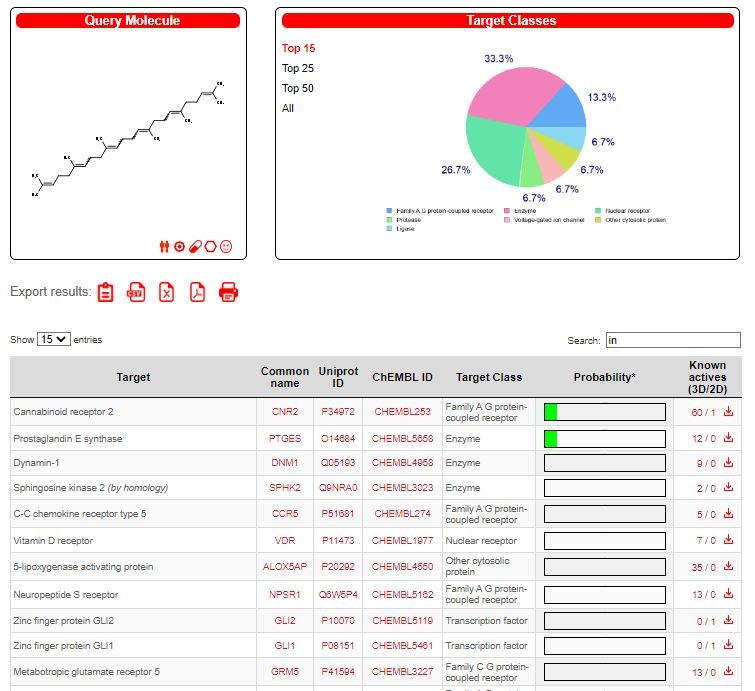
The drug target was predicted using the online program available in the SWISS database and two promising drug candidate was chosen based on their ADME properties (Figures 2-3). Among them, the target prediction of the compound Benzoyl-beta-D-glucoside showed better inhibitory against Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B (Figure 4), and the compound Squalene showed better inhibitory activity against 5-lipoxygenase activating protein (Figure 5).
Docking Studies :
Ligand preparation :
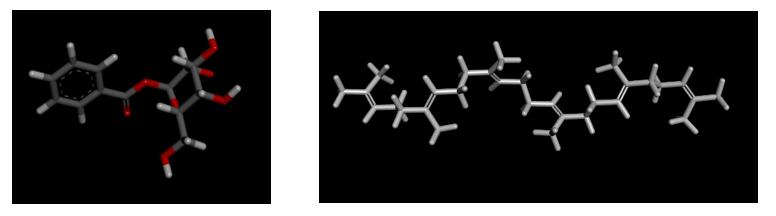
The canonical smiles of ligands were obtained from NCBI Pubmed/Pubchem database as follows in table 6 and the 3D structure of the ligands is given in Figure 12.
Receptor preparation :
The target receptors .pdb files were obtained from protein databank with their id’s is as follows:
PDB Id for Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B : PDBPTPN1
UniProt Id for Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B : P18031
PDB Id for 5-lipoxygenase activating protein 1B : PDBALOX5AP
UniProt Id for 5-lipoxygenase activating protein 1B : P20292
The 3D structure of the receptors is given in Figure 13
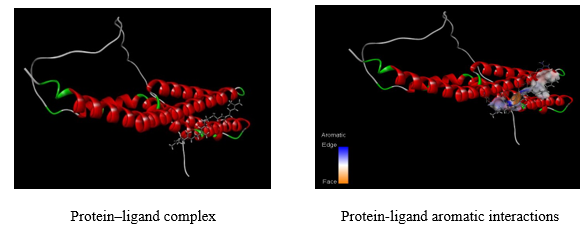
Docking Score and Protein-ligand interactions:
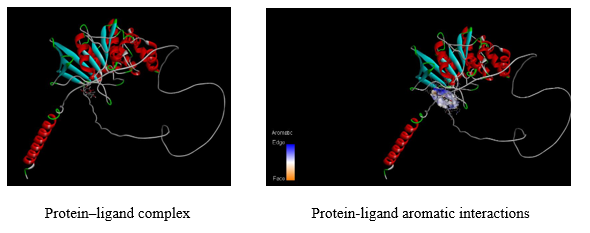
Docking results of Benzoyl-beta-D-glucoside against Protein-tyrosine phosphatase proteins was docked with Autodock software and interactions were visualized using Discovery studio software. The docking score, binding sites RMSD angle was given in table 7. The aromatic interactions with ligand-protein was showed in figure 14.
RMSD angle was given in Table 8. The aromatic interactions with ligand-protein was showed in figure 15.
DISCUSSION
From the in-vitro study it was observed that acetylcholine causes contraction of excised chick ileum and histamine cause contraction of chick trachea but when acetylcholine and histamine was given in presence of ethanolic extract of Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) stem there was a marked decrease in contraction in ileum was observed. This revealed that ethanolic extract of Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) stem possess a high anti asthmatic activity.
From the In-silico study it was observed that the anti-asthmatic effect of Bacopa monnieri(Linn.) stem extract is produced by substance Benzoyl-beta- D-glucoside and squalene present in Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) stem extract. Benzoyl- beta-D-glucoside showed better inhibitory against Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B and the compound Squalene showed better inhibitory activity against 5- lipoxygenase activating protein and produce antiasthmatic activity. But squalene is more potent than Benzoyl-beta-D-glucoside because it has more binding affinity with the receptor and needs less energy compared to Benzoyl- beta-D-glucoside. From the above shown interaction bonding energy and dock score it is predicted that Squalene has higher dock score and high interaction with receptor than Benzoyl- beta-Dglucoside. So, it is predicted that squalene has more anti asthmatic activity than Benzoylbeta-D-glucoside. It also obeys Lipinski Rule for ADME Property and have low toxicity. As many anti asthmatic drugs available in market shows side effect; so, Squalene, a natural origin drug with some degree of safety and efficacy could be a suitable alternative to existing drugs, as could be a new member of anti-asthmatic family.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We express our sincere thanks to the Department of Pharmacology , Annai Veilankanni’s Pharmacy College, Chennai for providing necessary facilities for the research work.
Authors Contribution
All authors have contributed equally
Financial Support
There is no funding to report
Conflicts Of Interest
The author declares there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approvals
This study does not involve experiments on animals or human subjects.
Data Availability
All data generated and analysed are included in this research article
REFERENCES
- Papi, A., Blasi, F., Canonica, G.W. et al. Treatment strategies for asthma: reshaping the concept of asthma management. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol 16, 75 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13223-020-00472-8
- Holgate, S., Wenzel, S., Postma, D. et al. Asthma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 1, 15025 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.25
- Rai, Kriti & Gupta, Nirmala & Dharamdasani, Lakshya & Nair, Pallavi & Bodhankar, Prerna. (2017). Bacopa Monnieri: A Wonder Drug Changing Fortune of People. International Journal of Applied Sciences and Biotechnology. 5. 127. 10.3126/ijasbt.v5i2.16952.
- ElhamDanesh, SaeidKhatamsa, ManzarbanoShojaeifard, ZahraKhabbaz: A review: Effects of hydro-alcoholic extract of bacopa monnieri on sensory threshold of pain using the formalin test in adult male rats. Doi: 10.15412/J.JBTW.01030702.
- Ashok Muchandi, Asha Jadhav, SameekshaJadhav, BhagyashriGaikwad, Nishiganda Yadav: A review: In-vitro Antihistaminic and Antispasmodic Study of Aqueous Extract of Leaves of BryophyllumpinnatumL. Imperial Journal of Interdisciplinary Research (MIR) vol-3, Issue-5, 2017 ISSN: 2454-1362.
- Le Anh Vu, Phan Thi Cam Quyen, Nguyen Thuy Huong, In silico Drug Design: Prospective for Drug Lead Discovery, www.ijesi.org, Volume 4 Issue 10, October 20
Tables:

 Guhan G.*
Guhan G.*
 Yamuna V.
Yamuna V.


 10.5281/zenodo.14234629
10.5281/zenodo.14234629